Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville
|
|
|---|---|

Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville
|
|
| Born | October 26, 1668 Trois-Rivières, New France |
| Died | June 30, 1722 (aged 53) Fort Dauphin, Île-Royale (New France) |
| Allegiance | |
| Years of service | 1676–1722 |
| Battles/wars | King William's War |
| Awards | Order of Saint Louis |
Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville (born October 26, 1668 – died June 30, 1722) was a military officer in New France. He served in the French Marines during a time when France and England often fought over land in North America.
He is most famous for leading a military operation known as the raid on Deerfield. This event happened on February 29, 1704, in what is now Massachusetts, during a conflict called Queen Anne's War. Hertel de Rouville was known for his strategy of attacking small, less protected settlements on the frontier. He also took part in other military actions against the English in Newfoundland. After the war, he helped establish new French settlements on Île-Royale (today known as Cape Breton Island).
Contents
Early Life and Military Beginnings
Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville was born in 1668 in Trois-Rivières, a town in the French colony of New France. His father was also a military man, so Jean-Baptiste grew up in a family dedicated to service.
From a young age, he joined the French Marines. In 1687, he fought alongside his father in a French military operation. This action was against the Seneca tribe, who lived in what is now western New York. The Governor of New France, Jacques-René de Brisay de Denonville, Marquis de Denonville, led this attack.
Defending Quebec in King William's War
During a conflict called King William's War, Hertel de Rouville helped defend the city of Quebec in 1690. English colonists and their Native American allies attacked Quebec, but the French forces, including Hertel, successfully defended it. In 1694, he was given the land area of Rouville at Mont Saint-Hilaire.
Leading Expeditions in Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War was another major conflict between the French and English. During this war, Hertel de Rouville led his first important independent mission, the Raid on Deerfield in 1704.
The Deerfield Expedition
Hertel gathered a force made up mostly of Abenaki, Huron, and Mohawk warriors, along with some Canadian militia. In late February, they traveled south into the English territory of Province of Massachusetts Bay. They surprised the town of Deerfield, which was not heavily guarded. The attackers engaged the town, leading to many deaths and the capture of over 100 people. The captives, including women and children, were taken on a long journey back to Quebec. Many of them were later adopted by Catholic Mohawk families in a village near Montreal called Kahnawake.
Further Actions and Reputation
Later in 1704, Hertel de Rouville was sent to Newfoundland. There, he took part in military operations against the English, including the Siege of St. John's. In 1708, he planned a larger expedition, but he could not get enough Native American allies. Because of this, he only completed one attack, a raid on Haverhill, Massachusetts.
He continued to lead similar raiding operations for the rest of Queen Anne's War. One of his English opponents described him as a very brave officer.
Building New Settlements in Île-Royale
After Queen Anne's War ended in 1713, Hertel de Rouville was given a new task. He was sent to Île-Royale (which is now Cape Breton Island) to find good locations for new French settlements.
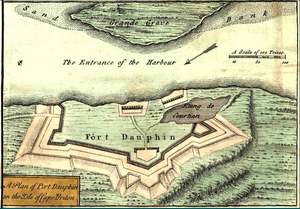
Based on his advice, Fort Dauphin (now called Englishtown, Nova Scotia) was chosen as the first settlement site. Hertel de Rouville then oversaw its construction. In 1721, he received a special award, the Order of Saint Louis, for his service. He passed away the next year on Île-Royale, while he was still in charge of Fort Dauphin.
Hertel de Rouville was married twice. He had two sons who also became important military figures in New France.
See also
 In Spanish: Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville para niños
In Spanish: Jean-Baptiste Hertel de Rouville para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |