Julius Lothar Meyer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Julius Lothar von Meyer
|
|
|---|---|

Julius Lothar Meyer
|
|
| Born | August 19, 1830 Varel, Lower Saxony, Germany
|
| Died | April 11, 1895 (aged 65) Tübingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
|
| Known for | Periodic table of chemical elements |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Chemistry |
| Institutions | University of Tübingen |
| Influences | Robert Bunsen |
Julius Lothar von Meyer (born August 19, 1830 – died April 11, 1895) was an important German chemist. He is famous for his work on the periodic table of chemical elements. He worked alongside another famous chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev, to help create the first versions of this table. He also worked with Robert Bunsen, who invented the Bunsen burner.
Contents
Who Was Lothar Meyer?
Julius Lothar von Meyer was born in Varel, Germany. He grew up to become a brilliant scientist. He studied many subjects, including medicine, mathematics, and physics, before focusing on chemistry. His deep understanding of these different fields helped him make big discoveries in chemistry.
Meyer's Early Life and Studies
Lothar Meyer began his studies in medicine. But he soon became very interested in chemistry. He studied at several universities in Germany. These included the University of Würzburg and the University of Heidelberg. At Heidelberg, he worked with Robert Bunsen. Bunsen was a well-known chemist who taught Meyer a lot.
Discovering the Periodic Table
Meyer is best known for his work on the periodic table. This table organizes all the known chemical elements. It arranges them based on their properties. Elements with similar properties are grouped together. This makes it easier to understand how they behave.
How Meyer Helped Create the Periodic Table
In the 1860s, scientists were trying to find a way to organize the elements. Meyer noticed a pattern when he looked at the atomic weights of elements. He saw that certain properties, like how elements react, repeated in a regular way. This repeating pattern is called "periodicity."
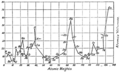
In 1864, Meyer published a table of 28 elements. He grouped them by their valency. Valency is how many chemical bonds an element can form. Later, in 1868, he created a more complete table. This table included almost all the known elements at the time. It also showed how the atomic volume of elements changed in a periodic way. Atomic volume is the space an atom takes up.
Meyer and Mendeleev: Two Great Minds
At almost the same time, another chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev, also developed a periodic table. Both Meyer and Mendeleev came up with very similar ideas. They both saw the importance of atomic weights. They also understood that elements had repeating properties.
Even though they worked separately, their discoveries supported each other. This showed that the periodic law was a real scientific principle. Meyer's work focused more on the physical properties of elements. Mendeleev's work was more about predicting new elements. Today, the periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry. It helps scientists understand and predict how elements will behave.
Meyer's Legacy in Chemistry
Lothar Meyer's contributions helped shape modern chemistry. His periodic table was a big step forward. It provided a clear way to organize elements. It also helped future scientists discover new elements. His ideas are still taught in schools and universities today.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Julius Lothar Meyer para niños
In Spanish: Julius Lothar Meyer para niños