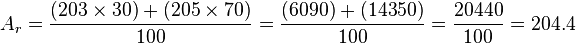Relative atomic mass facts for kids
A relative atomic mass (symbol: Ar) helps us understand how heavy atoms are. It compares the average weight of an atom of an element to a tiny part of a carbon-12 atom. Think of it like this: it tells you how many times an average atom of an element is heavier than one-twelfth (1/12) of a carbon-12 atom.
The word relative means we are comparing it to something else – in this case, carbon-12. Relative atomic mass values are like ratios, so they don't have any units. This term is also known as atomic weight, which is an older name.
Contents
What are Atoms and Isotopes?
Every atom has a certain number of protons. This number decides what element the atom is. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons.
However, most elements in nature have atoms with different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
Thallium: An Example of Isotopes
Let's look at thallium. It has two common isotopes: thallium-203 and thallium-205.
- Both isotopes have 81 protons (that's what makes them thallium!).
- Thallium-203 has 122 neutrons.
- Thallium-205 has 124 neutrons (two more than thallium-203).
Each isotope has its own weight, called its isotopic mass. A relative isotopic mass is the weight of one specific isotope compared to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom. This number is usually very close to the isotope's mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons). Like relative atomic mass, relative isotopic mass has no units.
How Do We Calculate Relative Atomic Mass?
To find the relative atomic mass of an element sample, we average the relative isotopic masses. But we don't just do a simple average! We have to consider how much of each isotope is present. This is called an "abundance-weighted average."
Thallium Calculation Example
Imagine a sample of thallium that is 30% thallium-203 and 70% thallium-205. Here's how we calculate its relative atomic mass:
So, the relative atomic mass for this thallium sample would be 204.4.
Why Do Relative Atomic Masses Change?
If you take samples of the same element from different places on Earth, their relative atomic masses might be slightly different. This happens because the amounts (proportions) of each isotope can vary a little depending on where the sample came from.
What is Standard Atomic Weight?
A standard atomic weight is a special average. It's the average of the relative atomic masses from many normal samples of an element. These values are published regularly by a group called the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). You can find the standard atomic weight for each element on the periodic table.
Sometimes, people use "relative atomic mass" when they really mean "standard atomic weight." But they are not exactly the same! Relative atomic mass refers to a specific sample, which might have a slightly different value than the official standard atomic weight. For example, a sample of an element from another planet could have a very different relative atomic mass compared to the standard value we use on Earth.
Relative Atomic Mass vs. Other Terms
It's easy to confuse relative atomic mass with other terms. Here's how they are different:
- atomic mass (symbol: ma): This is the actual mass of a single atom. It's usually measured in unified atomic mass units.
- mass number (symbol: A): This is the total count of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. It's always a whole number.
- atomic number (symbol: Z): This is just the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This number defines the element!
See also
 In Spanish: Peso atómico para niños
In Spanish: Peso atómico para niños