Khilji dynasty facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Khalji Sultanate
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1290–1320 | |||||||||||
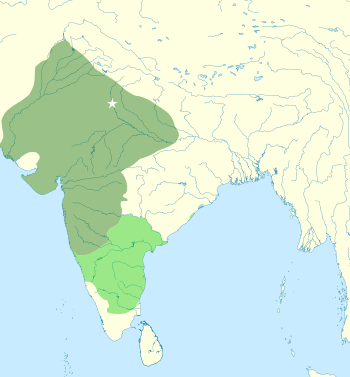
Territory controlled by the Khaljis (dark green) and their tributaries (light green)
|
|||||||||||
| Capital | Delhi | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Persian (official) | ||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||||
| Government | Sultanate | ||||||||||
| Sultan | |||||||||||
|
• 1290–1296
|
Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji | ||||||||||
|
• 1296–1316
|
Alauddin Khalji | ||||||||||
|
• 1316
|
Shihab ad-Din Umar | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1290 | ||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1320 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
The Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Muslim ruling family. They controlled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from 1290 to 1320. Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji started this dynasty. It was the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate in India.
The Khaljis were known for being strong and sometimes harsh rulers. They expanded their empire into the southern parts of India. They were also successful in defending their lands from repeated attacks by the Mongols.
Contents
Important Rulers
The Khalji dynasty had several important rulers during its time. They each played a role in shaping the empire.
Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji
Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji founded the Khalji dynasty in 1290. He was the first Sultan of this new ruling family. He ruled for six years, from 1290 to 1296.
Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji was one of the most powerful Khalji rulers. He ruled from 1296 to 1316. He made many changes to how the empire was run.
He changed the tax rules to get more money for his government. This money helped him pay for his growing army and his wars. He increased taxes on farming from 20% to 50%. This new tax system had a lasting effect on how taxes were collected in India.
During his rule, a large number of people worked as servants and guards. They worked for the Muslim nobles and government officials.
Other Rulers
After Alauddin Khalji, his son Shihab ad-Din Umar ruled briefly in 1316. Then, Qutb ad-Din Mubarak took over. He ruled from 1316 to 1320. The Khalji dynasty ended in 1320.
Khalji Society
The Khalji rulers were seen as different from the Turks who had ruled before them. Over many years, the Khaljis had married people from the local Afghan communities. They also adopted many Afghan customs and ways of life.
Images for kids
-
Gold coinage of ‘Ala al-Din Muhammad (AH 695-715 / AD 1296-1316). Dar al-Islam mint. Dated AH 709 (AD 1309-10).
-
The Koh-i-Noor diamond was seized by Alauddin Khalji's army in 1310, from the Kakatiya dynasty in Warangal.
-
Alauddin Khalji's Madrasa, Qutb complex, Mehrauli, which also has his tomb to the south.
-
Courts to the east of Quwwat ul-Islam mosque, in Qutb complex added by Khalji in 1300 CE.
-
The unfinished Alai Minar
See also
 In Spanish: Dinastía Khilji para niños
In Spanish: Dinastía Khilji para niños









