Lake Agassiz facts for kids
Lake Agassiz was a huge glacial lake that existed in the middle of North America. It formed at the end of the last ice age when large glaciers melted. This ancient lake was so big that its area was larger than all of today's Great Lakes combined!
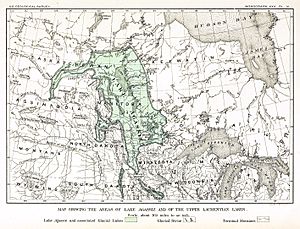
The area once covered by Lake Agassiz is now the geographic center of North America. It stretched across parts of what are now Canada and the United States.
Scientists first thought about the idea of this lake in 1823. It was officially named Lake Agassiz in 1879. The name honors Louis Agassiz, a famous scientist who studied glaciers.
Contents
What was Lake Agassiz?
Lake Agassiz was a "proglacial lake." This means it formed right in front of a melting ice sheet. As the huge Laurentide Ice Sheet melted, its water got trapped. The land around it was tilted, creating a giant basin. This basin filled up with the meltwater, forming Lake Agassiz.
Where was Lake Agassiz located?
Lake Agassiz covered a vast area. It stretched across parts of modern-day Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Ontario in Canada. In the United States, it covered parts of Minnesota and North Dakota. Imagine a lake so big it covered several states and provinces!
How big was it?
At its largest, Lake Agassiz was about 700 miles (1,100 km) long. It was also about 250 miles (400 km) wide. This made it one of the largest freshwater lakes in Earth's history. Its depth could reach up to 600 feet (180 meters) in some places.
The End of Lake Agassiz
Lake Agassiz did not last forever. As the ice sheet continued to melt, new paths opened up for the water to flow away. The lake drained in several huge floods over thousands of years. These floods were so powerful they changed the landscape.
The Great Floods
One of the biggest floods happened about 8,200 years ago. This event is sometimes called the "8.2-kiloyear event." A large amount of water from Lake Agassiz suddenly drained into the Atlantic Ocean. This massive influx of freshwater affected ocean currents and even changed the global climate for a short time.
What's left today?
Today, Lake Agassiz is gone. But it left behind many clues. The flat, fertile lands of the Red River Valley in North Dakota and Manitoba were once the bottom of the lake. These lands are now excellent for farming. Many smaller lakes, like Lake Winnipeg in Manitoba, are also remnants of Lake Agassiz. They are like small puddles left behind from a giant spilled drink.
Scientists continue to study Lake Agassiz. It helps them understand past climates and how large ice sheets melt. It also shows how much the Earth's surface can change over time.
See also
 In Spanish: Lago Agassiz para niños
In Spanish: Lago Agassiz para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |