North Dakota facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
North Dakota
Dakȟóta waziyata (Lakota)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Peace Garden State
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Liberty and union, now and forever, one and inseparable
|
|||
Location of North Dakota within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Dakota Territory | ||
| Admitted to the Union | November 2, 1889 (39th) | ||
| Capital | Bismarck | ||
| Largest city | Fargo | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Cass | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Fargo | ||
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | North Dakota Supreme Court | ||
| U.S. senators | John Hoeven (R) Kevin Cramer (R) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | Julie Fedorchak (R) (list) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 70,706 sq mi (183,125 km2) | ||
| • Land | 68,995 sq mi (178,694 km2) | ||
| • Water | 1,719 sq mi (4,428 km2) 2.3% | ||
| Area rank | 19th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 300 mi (482 km) | ||
| • Width | 200 mi (321 km) | ||
| Elevation | 1,901 ft (580 m) | ||
| Highest elevation
(White Butte)
|
3,609 ft (1,069 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Red River of the North at Manitoba border)
|
864 ft (216 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 47th | ||
| • Density | 10.73/sq mi (4.13/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 47th | ||
| • Median household income | $76,500 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 20th | ||
| Demonym(s) | North Dakotan | ||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English | ||
| Time zones | |||
| most of state | UTC−06:00 (Central) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−05:00 (CDT) | ||
| southwest | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
ND
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-ND | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | N.D., N.Dak., Nodak | ||
| Latitude | 45° 56′ N to 49° 00′ N | ||
| Longitude | 96° 33′ W to 104° 03′ W | ||
| Dance | Square dance Line dance |
|---|---|
| Bird | Western meadowlark |
| Fish | Northern pike |
| Flower | Wild prairie rose |
| Fruit | Chokecherry |
| Tree | American Elm |
| Insect | Western honeybee |
North Dakota (də-KOH-tə) is a state in the Upper Midwest of the United States. It is named after the Dakota Sioux, who are Native American people. North Dakota is surrounded by land, meaning it has no coastlines. To the north, it shares a border with the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba. To the east, it borders Minnesota, to the south, South Dakota, and to the west, Montana.
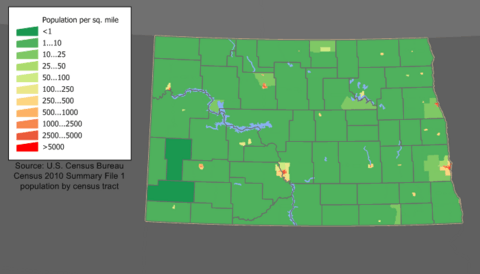
This state is part of the Great Plains region. This area is known for its wide prairies, dry grasslands, and badlands. North Dakota is the 19th largest state by size. However, it has a small population of less than 800,000 people. This makes it the fourth least populated state and one of the most spread out. The state capital is Bismarck. The biggest city is Fargo, where almost one-fifth of the state's people live. Both Bismarck and Fargo are growing fast. Still, about half of North Dakota's residents live in rural areas.
For thousands of years, different Native American tribes lived in what is now North Dakota. These included the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara tribes along the Missouri River. The Ojibwe and Cree lived in the northeast. Several Sioux groups, like the Nakota, Dakota, and Lakota, lived across the rest of the state. European explorers and traders first arrived in the early 1700s. They mostly came looking for valuable furs.
The United States took control of this region in the early 1800s. More settlers moved in, which led to conflicts with Native Americans. The Dakota Territory was created in 1861. The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged many pioneers to move there. This caused the population to grow a lot. Farming, especially wheat, became more important than the fur trade. From 1878 to 1886, during the Dakota Boom, huge farms appeared on the prairies. The territory became a strong economic area.
Railroad companies like the Northern Pacific and Great Northern competed to reach places where grain was grown. Farmers joined together in groups that were part of the larger Populist Movement. North and South Dakota became states on November 2, 1889. President Benjamin Harrison signed the papers without looking to see which one was first. So, the two states are officially listed in alphabetical order. By 1920, the state was fully settled. Later, North Dakota saw a rise in farmer-led movements and economic groups. One result is the Bank of North Dakota, which is the only state-run bank in the U.S.
Starting in the mid-1900s, North Dakota's rich natural resources became very important. In the 2000s, oil extraction from the Bakken formation in the northwest has greatly helped the state's economy. This has led to more people moving to the state and fewer people being unemployed. North Dakota is known for its good infrastructure, quality of life, and public safety. The town of Rugby is believed to be the geographic center of North America. The state was also home to the KVLY-TV mast, which was once the tallest human-made structure in the Western Hemisphere.
Contents
North Dakota's Past: A Journey Through Time
Early Native American Life
Native American people lived in what is now North Dakota for thousands of years. The Mandan people arrived around the 11th century. The Hidatsa group came a few hundred years later. Both tribes built villages along the Missouri River. Crow Indians traveled from the west to trade with the Hidatsas.
Later, different groups of the Sioux arrived. These included the Lakota, Santee, and Yanktonai. The Assiniboine and Plains Cree traveled south to trade or fight with the village tribes. Some Cheyennes lived in earth lodges by the Sheyenne River in the 1700s. They later moved west of the Missouri River.
Before the mid-1800s, the Arikara tribe came from the south. They joined the Mandan and Hidatsa. Over time, many tribes signed agreements with the United States. These agreements often set the boundaries for each tribe's land.
European Explorers and Settlers
The first European to explore this area was French-Canadian trader Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye. He led a group to the Mandan villages in 1738. He was guided by Assiniboine Indians.
From 1762 to 1802, this region was part of Spanish Louisiana.

European Americans did not settle much in Dakota Territory until the late 1800s. This changed when railroads were built, opening up the region. Railroad companies offered land grants and advertised the area as perfect for farming.
Becoming a State
There were disagreements between the northern and southern parts of the territory. The southern part thought the northern part was wilder, with more cattle ranchers and fur traders. It also had more conflicts with Native Americans. The northern part was happy to remain a territory. But after the capital moved from Yankton (in the south) to Bismarck (in the north), the southern part wanted to split. In 1887, voters agreed to divide the territory into two.
Congress passed a bill on February 22, 1889, to make North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington states. President Benjamin Harrison signed the papers on November 2, 1889. He shuffled the papers so no one would know which Dakota became a state first. Because North Dakota comes first alphabetically, its statehood was announced first.
North Dakota in the 1900s and 2000s
Farmers, especially Norwegian immigrants, started a political movement called the Non Partisan League (NPL) around World War I. The NPL wanted to protect North Dakota from big banks and companies outside the state.
They created the state-owned Bank of North Dakota and the North Dakota Mill and Elevator. Both still exist today. The NPL also made laws that made it hard for corporations to own farmland. These laws still help protect farmers today. The Bank of North Dakota also helped prevent a housing market crash in 2008.

The original North Dakota State Capitol building burned down in 1930. A new Art Deco skyscraper was built in its place. In the 1950s, the government invested in projects like the Garrison Dam and Minot and Grand Forks Air Force bases.
Western North Dakota saw a big increase in oil exploration in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This happened when oil prices were high. The boom ended when prices dropped.
In recent years, North Dakota has had low unemployment rates. It has also seen more jobs and people. Much of this growth comes from developing the Bakken oil fields in the western part of the state. Some estimates suggest there could be over 100 years' worth of oil left there.
North Dakota's Landscape and Climate
Exploring North Dakota's Geography
North Dakota is in the Upper Midwest of the United States. It is near the center of the North American continent. The state borders Canada to the north. A stone marker in Rugby marks the "Geographic Center of the North American Continent." Bismarck is the capital, and Fargo is the largest city.
North Dakota is part of the Great Plains region. The Red River of the North forms its eastern border with Minnesota. South Dakota is to the south, Montana to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north. North Dakota is the 19th largest state, with about 69,001 square miles (178,694 km2) of land.
The western half of the state has rolling hills of the Great Plains. It also has the northern part of the Badlands, which are west of the Missouri River. The state's highest point, White Butte, is in the Badlands. This area has many fossil fuels like natural gas, crude oil, and lignite coal. The Missouri River creates Lake Sakakawea, which is the third largest artificial lake in the U.S.
The middle of the state is called the Drift Prairie and the Missouri Plateau. The eastern part is the flat Red River Valley. This area was once the bottom of a large glacial lake called Lake Agassiz. Its rich soil is perfect for farming. The Red River flows north into Lake Winnipeg. Devils Lake, the state's largest natural lake, is also in the east.
Most of North Dakota is covered in grassland. Crops cover much of eastern North Dakota, but less so in the center and west. Natural trees grow where there is good drainage, like in ravines and valleys. This includes areas near the Pembina Gorge and Killdeer Mountains. The state's varied landscape supports almost 2,000 types of plants.
Soil is North Dakota's most valuable resource, supporting its agriculture. The state also has huge mineral resources, including billions of tons of lignite coal. Large oil reserves were found in 1951. In the early 2000s, new drilling methods helped extract a lot of oil from the Bakken shale rock.
North Dakota's Wildlife
North Dakota is home to many different animals. There are 36 Level I species, 44 Level II species, and 35 Level III species.
The state has 420 confirmed bird species. This includes two species that are now extinct. There are 87 known mammal species, including some that no longer live in North Dakota. These include the gray wolf and grizzly bear.
North Dakota also has 1,126 known insect species and 98 fish species. For reptiles and amphibians, there are 16 reptile species and 12 amphibian species. The state has three types of crawfish: Devil, Calico, and Virile. There are also three freshwater shrimp species.
North Dakota's Climate
North Dakota has a continental climate. This means it has warm summers and cold winters. The temperatures change a lot because the state is far from the ocean. It is also about halfway between the North Pole and the Equator.
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | January (°F) | January (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fargo | 82/59 | 28/15 | 18/0 | −7/−17 |
| Bismarck | 84/57 | 29/14 | 23/2 | −5/−16 |
| Grand Forks | 81/56 | 27/13 | 16/−3 | −8/−19 |
| Minot | 81/58 | 27/14 | 21/3 | −6/−16 |
| West Fargo | 82/59 | 28/15 | 16/-2 | −9/−19 |
| Williston | 84/56 | 29/13 | 22/0 | −5/−17 |
| Dickinson | 83/55 | 28/12 | 26/6 | −3/−14 |
| Mandan | 84/57 | 29/14 | 20/−1 | −6/−18 |
| Month | Maximum
°F (°C) |
Year | Place | Minimum
°F (°C) |
Year | Place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 70/21 | 1908 | Chilcot | -56/-49 | 1916 | Goodall |
| Feb | 72/22 | 1992 | Fort Yates | -60/-51 | 1936 | Parshall |
| Mar | 90/32 | 1910 | Edmore | -48/-44 | 1897 | McKinney |
| Apr | 101/38 | 1980 | Oakes | -24/-31 | 1975 | Powers Lake |
| May | 111/44 | 1934 | Langdon | -3/-19 | 1967 | Larimore |
| Jun | 112/44 | 2002 | Brien/Flasher | 18/-8 | 1969 | Belcourt Indian Reservation |
| Jul | 121/49 | 1936 | Steele | 23/-5 | 1911 | Manfred |
| Aug | 115/46 | 1922 | Cando | 19/-7 | 1915 | New Rockford |
| Sep | 109/43 | 1906 | Larimore | 4/-16 | 1942 | Parshall |
| Oct | 98/37 | 1963 | Watford City | -18/-28 | 1919 | Zap |
| Nov | 88/31 | 1909 | Haley | -39/-39 | 1985 | Pembina |
| Dec | 70/21 | 1939 | New England | -50/-46 | 1983 | Tioga/Williston |
On February 21, 1918, Granville, North Dakota had a huge temperature change. It went up 83 °F (46 °C) in just 12 hours. The temperature went from -33 °F (-36 °C) to 50 °F (10 °C). Another record was set in Langdon in the winter of 1935–36. The temperature stayed below 0 °F (−17.8 °C) for 41 days in a row. This is a record for any place in the connected U.S.
How North Dakota is Governed
As in the U.S. federal government, North Dakota's state government has three parts. These are the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The Constitution of North Dakota and the North Dakota Century Code are the main laws. The North Dakota Administrative Code adds more rules from state agencies.
Executive Branch: The Governor's Role
The elected governor leads the executive branch. The governor and lieutenant governor serve four-year terms. The governor has a team of leaders called commissioners. These leaders are in charge of different state agencies. Other elected officials include the secretary of state and attorney general.
Legislative Branch: Making Laws
The North Dakota Legislative Assembly has two parts. These are the Senate and the House of Representatives. The state has 47 districts. Each district has one senator and two representatives. Both senators and representatives are elected for four-year terms. The state's laws are collected in the North Dakota Century Code.
Judicial Branch: Courts and Justice
North Dakota's court system has four levels, though one is not often used. City courts, called municipal courts, handle local cases. Decisions from these courts can be appealed to district court. Most cases begin in the district courts. There are 42 district court judges in seven areas. Appeals from district court decisions go to the North Dakota Supreme Court. There is also a court of appeals, but it rarely meets.
Native American Tribes and Reservations
Historically, North Dakota was home to the Mandan, Hidatsa, Lakota, Ojibwe, Sanish, and Métis tribes. Today, five federally recognized tribes have their own governments and reservations in North Dakota:
- Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation, Fort Berthold Reservation
- Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate, Lake Traverse Indian Reservation
- Standing Rock Sioux, Standing Rock Indian Reservation
- Spirit Lake Tribe, Spirit Lake Reservation
- Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians, Turtle Mountain Reservation
People and Culture of North Dakota
North Dakota's Population
In 2022, North Dakota's population was about 779,261. This was a small increase since the 2020 United States census. North Dakota is the fourth least-populated state. Only Alaska, Vermont, and Wyoming have fewer people.
From fewer than 2,000 people in 1870, North Dakota's population grew to almost 680,000 by 1930. Growth then slowed down. The population reached a low of 617,761 in 1970. In the 2000s, North Dakota has grown a lot. It reached a record population of 783,926 in 2023.
Except for Native Americans, North Dakota has fewer minority groups than the rest of the country. In 2011, about 20.7% of babies born in North Dakota were from minority groups. The middle point of North Dakota's population is in Wells County, near Sykeston.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 2,405 | — | |
| 1880 | 36,909 | 1,434.7% | |
| 1890 | 190,983 | 417.4% | |
| 1900 | 319,146 | 67.1% | |
| 1910 | 577,056 | 80.8% | |
| 1920 | 646,872 | 12.1% | |
| 1930 | 680,845 | 5.3% | |
| 1940 | 641,935 | −5.7% | |
| 1950 | 619,636 | −3.5% | |
| 1960 | 632,446 | 2.1% | |
| 1970 | 617,761 | −2.3% | |
| 1980 | 652,717 | 5.7% | |
| 1990 | 638,800 | −2.1% | |
| 2000 | 642,200 | 0.5% | |
| 2010 | 672,591 | 4.7% | |
| 2020 | 779,094 | 15.8% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 783,926 | 16.6% | |
| Source: 1910–2020 | |||
Diversity in North Dakota
| Racial composition | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 94.6% | 92.4% | 90.0% | 82.9% |
| Native American | 4.1% | 4.9% | 5.4% | 5.0% |
| Black | 0.6% | 0.6% | 1.2% | 3.4% |
| Asian | 0.5% | 0.6% | 1.0% | 1.7% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander |
– | – | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Other race | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 1.5% |
| Two or more races | – | 1.2% | 1.8% | 5.4% |
| Hispanic Origin | 0.7% | 1.2% | 2.0% | 4.3% |
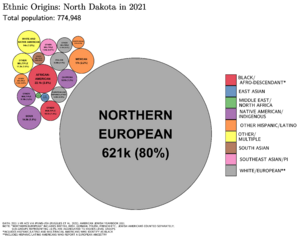
In the mid-1800s, Native Americans were the main people in Dakota Territory. Their population decreased due to conflicts and illness. At the same time, more Europeans and Americans moved in. From the late 1800s to early 1900s, many newcomers arrived. These included immigrants from Norway, Iceland, Sweden, Germany, and the United Kingdom. They often settled in the fertile Red River Valley.
From the 1930s to the late 1900s, North Dakota's population slowly went down. Many young adults, especially college graduates, left the state. Farming became more mechanized, and smaller farms struggled. Many people moved to cities for jobs.
Since the late 1900s, the population has grown. This is largely due to jobs in the oil industry. Also, Native American populations have grown as some people return to reservations.
In 2010, about 88.7% of North Dakota's population was non-Hispanic white. About 5.4% were Native American. In 2019, 4.1% of residents were born outside the U.S. The top countries of origin for immigrants are the Philippines, Bhutan, Nepal, Canada, and Liberia.
Languages Spoken in North Dakota
In 2010, most North Dakotans (94.86%) over five years old spoke English at home. About 5.14% spoke another language. German was spoken by 1.39% of people, and Spanish by 1.37%. Norwegian was spoken by 0.30%. Other languages included Serbo-Croatian, Chinese, Japanese, Native American languages, and French.
In 1940, about 355,400 North Dakotans spoke English. About 128,700 spoke German, and 81,300 spoke Norwegian.
Religion in North Dakota
Religious self-identification, per Public Religion Research Institute's 2022 American Values Survey Christianity (80%) Unaffiliated (12%) Other (8%)

In 2014, the Pew Research Center found that 77% of adults in North Dakota were Christian. Mainline Protestantism was the largest type of Protestantism. The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America was the largest mainline Protestant group. The Roman Catholic Church was the single largest Christian group. In 2022, the Public Religion Research Institute found that 80% of the population was Christian.
Non-Christian religions made up 3% of the adult population in 2014. Islam was the largest non-Christian religion. About 20% of people were not connected to any religion. In 2006, North Dakota had the most churches per person of any state. It also had the highest percentage of people who attended church.
Native American Culture: Powwows
In the 2000s, North Dakota has a growing Native American population. In 2010, they made up 5.44% of the people. The word "Dakota" means "allies" or "friends" in the Sioux language.
The main historic tribes in North Dakota are the Lakota and Dakota (known as "The Great Sioux Nation"), the Blackfoot, the Cheyenne, the Chippewa (Ojibwe), and the Mandan. There are six Indian reservations in North Dakota.
Powwows (or wacipis in Lakota/Dakota) are important social gatherings. They are held regularly across the state. Historically, powwows were held in the spring to celebrate new life. They brought tribes together for singing, dancing, and meeting friends. Many powwows also had religious meaning. Today, powwows are still a part of Native American culture. Both Native and non-Native people attend them. The United Tribes International Powwow in Bismarck is one of the largest in the U.S.
A powwow includes parades and Native American dancers in special clothing called regalia. Male dancers wear regalia with beads, quills, and eagle feathers. Male grass dancers wear colorful fringe. Male fancy dancers wear bright feathers. Female dancers move more gently. Fancy female dancers wear cloth, beaded moccasins, and jewelry. Jingle dress dancers wear dresses with metal cones. During inter-tribal dances, everyone can join in the dancing.
Norwegian and Icelandic Heritage
Around 1870, many European immigrants from Norway settled in northeastern North Dakota. Icelanders also arrived from Canada. Pembina was a town with many Norwegians. They worked on family farms and started Lutheran churches and schools.
These groups have unique foods like lefse and lutefisk. The largest Scandinavian event in North America is Norsk Høstfest. It is held every September in Minot. This festival features art, architecture, and culture from all five Nordic countries. The Icelandic State Park and an annual Icelandic festival celebrate immigrants from Iceland.
Old traditions like weaving, silver crafting, and wood carving are still practiced. Traditional turf-roof houses, like those from Iceland, are displayed in parks. A stave church is a landmark in Minot. About 30.8% of North Dakota's population has Norwegian heritage.
Germans from Russia: A Unique Community
Ethnic Germans who had lived in Russia for many generations moved to America. They were unhappy due to economic problems and loss of religious freedoms. Many Mennonites and Hutterites, who were exempt from military service, lost this right in 1871. Most Mennonites and Hutterites moved to America in the late 1870s.
By 1900, about 100,000 had come to the U.S. They settled mainly in North Dakota, South Dakota, Kansas, and Nebraska. The south-central part of North Dakota became known as "the German-Russian triangle." By 1910, about 60,000 ethnic Germans from Russia lived in Central North Dakota. These people were Lutherans, Mennonites, Hutterites, and Roman Catholics. They kept most of their German customs and were dedicated to farming. Traditional iron cemetery grave markers are a famous art form by ethnic Germans.
Arts and Entertainment
North Dakota has several major fine art museums and venues. These include the Chester Fritz Auditorium and the Plains Art Museum. The Bismarck-Mandan Symphony Orchestra and Fargo-Moorhead Symphony Orchestra are professional music groups. They perform concerts and offer educational programs.
Many famous musicians are from North Dakota. These include blues guitarist Jonny Lang, country music singer Lynn Anderson, and jazz singer Peggy Lee. Big band leader Lawrence Welk and pop singer Bobby Vee are also from the state.
Hollywood and TV star Angie Dickinson was born in Kulm. Josh Duhamel is an Emmy Award-winning actor. Nicole Linkletter and CariDee English won America's Next Top Model. Actor Kellan Lutz has appeared in movies like Twilight.
Sports and Outdoor Fun
Bismarck was home to the Dakota Wizards basketball team. It now hosts the Bismarck Bucks football team.
North Dakota has two NCAA Division I college teams: the North Dakota Fighting Hawks and North Dakota State Bison. There are also two Division II teams: the Mary Marauders and Minot State Beavers.
Fargo has the USHL ice hockey team, the Fargo Force. It is also home to the Fargo-Moorhead RedHawks baseball team.
The North Dakota High School Activities Association has over 25,000 students participating in sports.
Many North Dakotans enjoy outdoor activities like hunting and fishing. Ice fishing, skiing, and snowmobiling are popular in winter. People often own or visit cabins by lakes. Popular fish to catch include walleye, perch, and northern pike.
The North Country National Scenic Trail starts at Lake Sakakawea. It connects with the Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail.
North Dakota's Economy
Agriculture is North Dakota's biggest industry. However, oil, food processing, and technology are also very important. The state's economy is growing at about 4.1% per year. In 2018, North Dakota's total economic output was $55.180 billion. The average income per person was $34,256 from 2013 to 2017.
According to Gallup, North Dakota led the U.S. in creating jobs in 2013. It has done so since 2009. The state has added 56,600 private-sector jobs since 2011. This is a growth rate of 7.32% per year. North Dakota also had the highest growth in spending on housing and utilities. This shows the high demand for homes in the 2010s.
More than 21% of North Dakota's total economic output in 2013 came from natural resources and mining.
North Dakota is the only state with a state-owned bank. This is the Bank of North Dakota in Bismarck. It also has a state-owned flour mill, the North Dakota Mill and Elevator in Grand Forks. These were started before World War II.
As of 2012, Fargo is home to the second-largest Microsoft campus, with 1,700 employees. Amazon.com employs hundreds of people in Grand Forks.
As of December 2019, the state's unemployment rate was 2.4%. This is one of the lowest in the nation. The unemployment rate has been below five percent every month since 1987, except for a short time in 2020. The increase in income and lower unemployment are due to the oil boom. North Dakota has had a budget surplus every year since 2008. This is thanks to oil development and investments in technology.
Farming in North Dakota
North Dakota's first industries were fur trading and agriculture. Even though less than 10% of people work in farming, it is still a huge part of the state's economy. North Dakota ranks 9th in the U.S. for the value of its crops. Large farms produce the most crops. About 90% of North Dakota's land is used for farms. This includes 27.5 million acres (111,000 km2) of cropland.
The state is the largest producer in the U.S. of many grains. These include barley, durum wheat, hard red spring wheat, and oats. It is also the second largest producer of buckwheat. As of 2007, corn became the state's largest crop. Most of these grains are grown to feed livestock.
North Dakota is a top producer of many oilseeds. It grows 92% of the U.S. canola crop and 94% of flax seed. Canola grows well in cold winters. After processing canola for oil, the leftover part is used as high-protein animal feed.
Soybeans are also becoming more important. They are a major crop in eastern North Dakota. Soybeans were not grown in the state in the 1940s. But they have become very common since 1998. Soybeans grown in North Dakota must grow quickly because of the short growing season. They are also used for livestock feed.
North Dakota is the second largest producer of sugarbeets. These are mostly grown in the Red River Valley. The state is also the largest producer of honey, dry edible peas and beans, and lentils. It is the third largest producer of potatoes.
North Dakota's Top Agricultural Products (according to the USDA in 2011)
| 2011 rank in the U.S. | Commodity | Percent of nation's production |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beans, dry edible, all | 25% |
| 1 | Beans, navy | 35% |
| 1 | Beans, pinto | 46% |
| 1 | Canola | 83% |
| 1 | Flaxseed | 87% |
| 1 | Honey | 22% |
| 1 | Sunflower, oil | 40% |
| 1 | Wheat, durum | 36% |
| 1 | Wheat, spring | 37% |
| 2 | Sunflower, all | 38% |
| 2 | Sunflower, non-oil | 24% |
| 2 | Wheat, all | 10% |
| 3 | Barley | 11% |
| 3 | Lentils | 17% |
| 3 | Oats | 8% |
| 3 | Peas, dry edible | 21% |
| 3 | Sugarbeets | 16% |
| 4 | Safflower | 1% |
| 6 | Hay, alfalfa | 6% |
| 6 | Potatoes | 4% |
| 8 | Hay, all | 4% |
| 10 | Soybeans | 4% |
| 12 | Corn for grain | 2% |
| 17 | Hay, other | 2% |
| 26 | Wheat, winter | 1% |
| 21 | Sheep and lambs | 1% |
| 17 | Cattle and calves | 2% |
| 15 | Wool production | 2% |
Energy Production

The energy industry is a big part of North Dakota's economy. The state has both coal and oil. From 2009 to 2018, oil production grew by about 48.4% each year. Shale gas is also produced. Lignite coal from western North Dakota generates about 90% of the state's electricity. This electricity is also sent to nearby states. North Dakota is the second largest producer of lignite coal in the U.S.
Oil was found near Tioga in 1951. The Bakken Formation may hold a lot of oil. As of November 2022, North Dakota is the 2nd largest oil producer in the U.S.
The Great Plains region, including North Dakota, is known for its "wind energy." Developing wind energy is affordable here. This is because the state has large rural areas and strong winds.
Tourism in North Dakota
North Dakota is considered the least visited state. This is partly because it does not have one very famous tourist spot. However, tourism is North Dakota's third largest industry. It brings in over $3 billion to the state's economy each year. Outdoor places like the 144-mile (232 km) Maah Daah Hey Trail attract visitors. Activities like fishing and hunting are also popular. The state is known for the Lewis & Clark Trail. This was where the Corps of Discovery camped for a winter. Theodore Roosevelt National Park in western North Dakota is very popular. It gets over 475,000 visitors each year.
Regular events that attract tourists include Norsk Høstfest in Minot. This is North America's largest Scandinavian festival. There is also the Medora Musical and the North Dakota State Fair. Many visitors come from the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan. They especially visit when the exchange rate is good.
International tourists also visit the Oscar-Zero Missile Alert Facility.
Education in North Dakota
Colleges and Universities
North Dakota has 11 public colleges and universities. It also has five tribal community colleges and four private schools. The biggest schools are North Dakota State University and the University of North Dakota.
Here are some of the higher education institutions:
North Dakota University System (Public Schools):
- Bismarck State College in Bismarck
- Dickinson State University in Dickinson
- Lake Region State College in Devils Lake
- Mayville State University in Mayville
- Minot State University in Minot
- Dakota College at Bottineau in Bottineau
- North Dakota State University in Fargo
- North Dakota State College of Science in Wahpeton and Fargo
- University of North Dakota in Grand Forks
- Valley City State University in Valley City
- Williston State College in Williston
Tribal Colleges:
Private Schools:
K-12 Education
In 1917, North Dakota had 142 schools in cities and 4,722 one room schools in rural areas. City schools had 36,008 students, while one-room schools had 83,167 students. Between 1929 and 1954, 1,889 one-room schools closed. In 1954, cities had 513 schools with 94,019 students. One-room schools had 2,447 locations with 25,212 students. The Nation's Report Card ranks North Dakota fifteenth in the country for K-12 education. This ranking is based on standardized test scores.
Emergency Services
The North Dakota Department of Emergency Services helps coordinate over 50 agencies. It provides 24/7 communication and support. It also manages federal disaster recovery programs. In 2011, the Department started a project to create a statewide map. This map helps identify locations for 9-1-1 callers. In 1993, the state adopted a system to number rural roads and buildings. This helps emergency services find locations faster.
Transportation in North Dakota
The North Dakota Department of Transportation manages transportation in the state. The main Interstate highways are Interstate 29 and Interstate 94. I-29 runs north to south along the eastern side of the state. I-94 goes east to west across the state. Most of North Dakota's Interstate highways are paved with concrete. This is because of the extreme weather conditions.
BNSF and the Canadian Pacific Railway operate the state's largest rail systems. Many smaller rail lines are now run by other companies.
North Dakota's main airports include Hector International Airport in Fargo and Grand Forks International Airport. Other important airports are Bismarck Municipal Airport, Minot International Airport, and Williston Basin International Airport.
Amtrak's Empire Builder train travels through North Dakota. It stops in Fargo, Grand Forks, Minot, and four other towns. This train line is a descendant of the famous Great Northern Railway.
Bus service between cities is provided by Greyhound and Jefferson Lines. Public bus services are available in Fargo, Bismarck-Mandan, Grand Forks, and Minot. There are also rural transit systems in many counties.
Famous People from North Dakota
- Lynn Anderson, country music singer
- Angie Dickinson, Golden Globe-winning actress
- Josh Duhamel, Emmy Award-winning actor
- Louise Erdrich, Native American author
- Darin Erstad, MLB all-star baseball player
- Travis Hafner, former MLB baseball player
- Virgil Hill, former boxing champion
- Phil Jackson, famous basketball coach
- Jonny Lang, Grammy-winning blues guitarist
- Peggy Lee, jazz singer and songwriter
- Nicole Linkletter, winner of America's Next Top Model
- Kellan Lutz, actor from Twilight
- Roger Maris, former baseball home run record holder
- Cara Mund, Miss America 2018
- Sakakawea, who joined Lewis and Clark on their expedition
- Ed Schultz, talk show host
- Eric Sevareid, CBS news journalist
- Shadoe Stevens, host of American Top 40
- Bobby Vee, pop music singer
- Lawrence Welk, musician and bandleader
- Carson Wentz, professional football player
See also
 In Spanish: Dakota del Norte para niños
In Spanish: Dakota del Norte para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |