Energy industry facts for kids
The energy industry is a huge group of businesses that find, make, and sell energy. This includes getting fuels like oil and coal, making them ready to use, and delivering them to homes and businesses. Modern life needs a lot of energy, so this industry is super important for how almost every country works.
The energy industry includes:
- Fossil fuels: These are old fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas. This part of the industry includes oil companies, refineries (where oil is cleaned), fuel transport, and gas stations. It also covers digging up coal and getting natural gas.
- Electric power: This involves making electricity, sending it through power lines, and selling it.
- Nuclear power: This uses nuclear reactions to create electricity.
- Renewable energy: This is about clean energy sources like hydroelectric power (from water), wind power, and solar power. It also includes making and selling cleaner fuels.
- Traditional energy: This is about collecting and using firewood, which is still common for cooking and heating in many poorer countries.
For a long time, we've used a lot of fossil fuels and other sources like biomass that release carbon. This means the energy industry has often caused a lot of pollution and harmed the environment. Fossil fuels were the main energy source for most of the world and are a big reason for global warming and pollution. To help with global warming, many countries are now investing in renewable and sustainable energy.
Contents
History of Energy Use
Using energy has been key to how human society has grown. It helps us control and live with our surroundings. Managing energy is a must for any working society. In modern countries, having enough energy is vital for agriculture (farming), transportation, cleaning up waste, information technology, and communication. These things are now basic needs for a developed society. But using more and more energy since the Industrial Revolution has also caused serious problems, like global warming, which could be very risky for the world.
In some industries, "energy" also means "energy resources." These are things like fuels, oil products, and electricity. A lot of the energy in these resources can be easily used for something helpful. After a process, the total energy is still there, but the resource itself isn't, because the energy often changes into forms we can't use, like wasted heat.
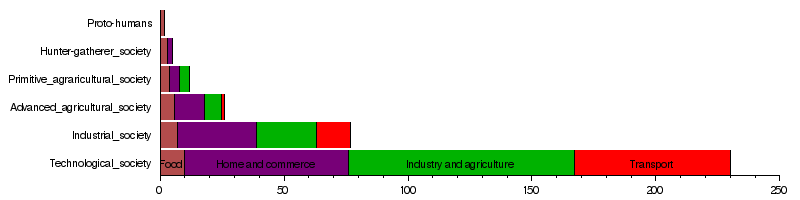
Since humans found different energy resources in nature, we've invented machines to make life easier by using these resources. For example, early humans used fire to cook. But inventions like gas burners and microwave ovens have made us use much more energy just for cooking. This trend is true for almost every part of society, whether it's building things, making clothes, printing, decorating, or moving people and goods (like with automobiles).
Energy and the Economy
Making and using energy is super important for the world's economy. Every economic activity needs energy. This could be to make goods, provide transportation, or run computers and other machines.
When there's a lot of demand for energy, it can lead to different energy companies competing. This also creates retail energy markets where energy is sold to customers.
Managing Energy Use
The cost of energy has become a big deal for how well societies' economies work. So, managing energy resources is now very important. Energy management means using the energy we have more effectively. This often means saving money on energy without needing new technology, just by using smart management ideas. It's about using energy more efficiently by stopping waste or making sure we have enough energy for what we need. This process connects being aware of energy with saving energy.
How Energy Industries are Grouped
Different groups classify energy industries in various ways.
Government Classifications
The United Nations has a list of economic and social groups called the International Standard Industrial Classification. It doesn't have a separate group just for the "energy industry." This is because the system groups things by activities, products, and what money is spent on.
In North America, countries use the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Sections #21 (mining) and #22 (utilities) in NAICS roughly cover the energy industry there. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission uses this system.
Financial Market Classifications
The Global Industry Classification Standard, used by Morgan Stanley, says the energy industry includes companies mainly dealing with oil, gas, coal, and other fuels we use up. It doesn't include companies that work with certain industrial gases.
Environmental Impact of Energy
Governments often give money or tax breaks to encourage people to save energy. This has made energy saving a big part of the energy industry. Saving energy can bring almost the same economic benefits as making that same amount of energy. One goal of a smart grid is to balance how much energy is used with how much can be supplied.
Some parts of the energy industry cause a lot of pollution. This includes harmful gases and greenhouse gases from burning fuels. There's also nuclear waste from nuclear power and oil spillages from getting oil. Governments are making more rules to deal with these problems. Also, buying and selling carbon credits and pollution credits can make energy companies focus more on saving energy and controlling pollution.
Using energy resources, like turning on a light, uses up resources and affects the environment. Many power plants burn coal, oil, or natural gas to make electricity. While burning these fossil fuels gives us quick electricity, it also releases air pollutants. These include carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SOx), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas that is thought to be a big reason for the fast increase in climate change seen in the 20th century. Burning fossil fuels also releases tiny amounts of metals like mercury into the environment, which are also pollutants.
Using renewable energy technologies on a large scale would greatly reduce or stop many environmental and health problems from energy use. Renewable energy includes biofuels, solar heating and cooling, hydroelectric power, solar power, and wind power. Saving energy and using it efficiently would also help a lot.
It's also believed that we can make the energy sector more efficient. This can be done by:
- Switching from coal to natural gas in power plants.
- Improving existing power plants to make them work better.
- Using Combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which make both electricity and heat.
- Recovering wasted heat.
The best available technologies offer much higher efficiency levels than what's common globally. For example, coal-fired plants built today can be 46-49% efficient, compared to 32-40% for older plants. Gas plants can reach 58-59% efficiency with the best technology. Meanwhile, combined heat and power systems can be 80-90% efficient.
Energy and Politics
Since energy is so important in modern societies, who owns and controls energy resources plays a bigger role in politics. Within a country, governments try to control how energy resources are shared among different parts of society. They do this through pricing or even by deciding who owns resources inside their borders. They might also try to influence how people and businesses use energy to help with environmental issues.
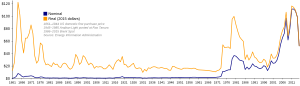
A recent international political issue about energy resources is linked to the Iraq Wars. Some experts believe that a hidden reason for both the 1991 and 2003 wars was to control international energy resources. Others disagree, looking at the economic numbers. They say the U.S. spent about $336 billion in Iraq, which is much more than the $25 billion per year budget for all U.S. oil imports.
Energy Policy
Energy policy is how a government decides to handle energy. This includes how energy is made, sent out, and used. Energy policy can involve laws, international agreements, ways to encourage investment, rules for saving energy, and taxes.
Energy Security
Energy security is about how a country's national security is connected to having enough natural resources for energy. Having access to cheap energy is now vital for modern economies. But energy supplies are not spread evenly among countries, which can cause problems. Threats to energy security include unstable energy-producing countries, controlling energy supplies, competition over energy sources, attacks on energy systems, and natural disasters.
Because fossil fuels like oil and gas have limited supplies, are unevenly distributed, and are getting more expensive, we need to switch to more sustainable energy sources. As oil production might reach its peak, economies and societies could start to feel the decline in this resource we depend on. Energy security is a top issue today because oil and other resources are so important. With new advances in renewable resources like geothermal, solar, wind, and hydro-electric power, there's less pressure on oil companies. These new resources will become more useful as the price of importing oil goes up due to higher demand.
Developing New Energy Sources
Making energy to meet human needs is a key activity, and a lot of effort goes into it. While much of this effort focuses on making more electricity and finding more oil, new ways to get usable energy from existing resources are being explored. One example is trying to make hydrogen fuel from water. Even though using hydrogen is good for the environment, making it needs energy, and current ways to do it aren't very efficient. Scientists are also researching how to break down biomass using special enzymes.
Other traditional energy resources are also being used in new ways. Coal gasification and liquefaction are newer technologies that are becoming popular. This is because people realize that oil reserves, at current usage rates, might not last very long. You can learn more about these in alternative fuels.
Energy is a big topic for research around the world. For example, the UK Energy Research Centre is a main hub for energy research in the UK. The European Union also has many technology programs and ways to involve social science and humanities in energy research.
Transporting Energy
All societies need materials and food to be moved over distances, often against friction. Since moving things needs a source of usable energy, these energy sources are very valuable to society.
While energy resources are vital for all types of transportation, moving energy resources themselves is becoming just as important. Energy resources are often found far from where they are used. So, how to transport them is always a question. Some energy resources, like liquid or gas fuels, are moved using tankers or pipelines. Electricity transport always needs a network of grid cables. Transporting energy, whether by tanker, pipeline, or power line, creates challenges for scientists, engineers, and economists to make it safer and more efficient.
Energy Crises
Economic and political problems can lead to an energy crisis. Famous oil crises include the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 oil crisis. The arrival of peak oil, which is when the world produces the most oil it ever will, will likely cause another energy crisis.
See also
 In Spanish: Industria de la energía para niños
In Spanish: Industria de la energía para niños
- Alternative energy
- Climate lawsuit
- Energy accounting
- Energy quality
- Energy system – how the energy sector works as a system
- Energy transformation
- Economics of climate change
- Hydrogen economy
- List of books about the energy industry
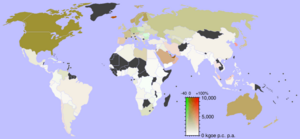
- List of countries by energy consumption per capita
- List of energy resources
- List of largest energy companies
- Stranded asset
- World energy consumption
- Worldwide energy supply