Energy transformation facts for kids
Energy is all around us, and it's always changing! Energy can't be created or destroyed. It just changes from one form to another. Think of it like play-doh: you can squish it, roll it, or shape it, but it's still the same amount of play-doh. Energy works in a similar way.
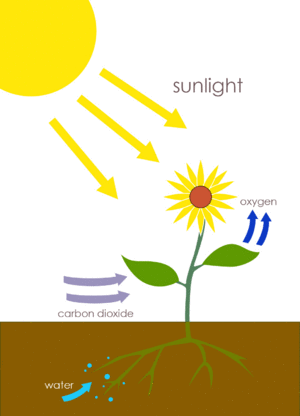
Both nature and machines are great at changing energy. For example, plants use photosynthesis to turn sunlight into chemical energy, which is their food. This chemical energy helps them grow. Machines like wind farm turbines change the energy of moving wind into electrical energy that we can use in our homes.
Contents
How Energy Changes in Machines
Energy transformations happen in many machines we use every day. Here are some examples of how energy changes form step-by-step.
Power Plants: Making Electricity
A coal-fired power plant is a big factory that makes electricity. Here's how energy changes inside it:
- The chemical energy stored in coal changes into heat energy when the coal burns.
- This heat energy from the burning coal heats up water, turning it into hot steam.
- The hot steam pushes against a giant spinning machine called a turbine, turning the heat energy into mechanical energy.
- Finally, the spinning turbine powers a generator, which changes the mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is the electricity that comes to our homes!
These power plants try to be as efficient as possible, meaning they try to waste as little energy as possible. Modern gas-fired power stations can turn about half of the original energy into electricity.
Cars: Making Them Move
Cars are amazing machines that use many energy changes to move.
- The chemical energy in the car's fuel (like gasoline) changes into kinetic energy (energy of motion) when it burns inside the engine. This makes gases expand quickly.
- The expanding gases push parts called pistons, making them move back and forth. This is a change to linear motion.
- The back-and-forth motion of the pistons is changed into a spinning motion by a part called the crankshaft.
- This spinning motion then goes through the car's transmission system.
- The motion continues through other parts, like the differential.
- Finally, this spinning motion reaches the car's wheels, making them spin.
- The spinning wheels push against the road, turning their spinning motion into the forward movement of the car.
Other Ways Energy Transforms
There are many different devices and machines that change one form of energy into another. Here are some cool examples:
- Thermoelectric devices: These turn heat directly into electrical energy.
- Geothermal power: This uses heat from inside the Earth to make electricity.
- Heat engines: Like the engine in a car or an old steam engine, these turn heat into movement.
- Hydroelectric dams: These use the energy of falling water to create electricity.
- Electric generators: These turn motion or mechanical work into electrical energy.
- Fuel cells: These change chemical energy into electrical energy.
- Batteries: These store chemical energy and turn it into electrical energy when you use them.
- Fire: When something burns, its chemical energy changes into heat and light.
- Electric lamps: These turn electrical energy into heat and light.
- Microphones: These change sound energy into electrical energy.
- Wave power: This uses the motion of ocean waves to make electricity.
- Windmills: These use wind energy to make electricity or to do mechanical work (like grinding grain).
- Piezoelectrics: These materials create electrical energy when they are squeezed or bent.
- Friction: When two things rub together, their motion energy changes into heat.
- Electric heaters: These turn electrical energy into heat.
- ATP hydrolysis: This is a process in living things where chemical energy in a molecule called ATP is changed into mechanical energy for things like muscle movement.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Transformación energética para niños
In Spanish: Transformación energética para niños




