Lamp (electrical component) facts for kids
A lamp is a part of a lighting system that makes light from electricity. You can usually replace it, like a light bulb. Lamps are often made from materials like ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic. These materials help them connect to electricity.
Contents
Types of Lamps
There are many kinds of electric lamps. Each type works a bit differently to create light. Some common types include:
- Incandescent light bulbs: These have a thin wire (called a filament) inside a glass bulb. The wire gets very hot and glows.
- Halogen lamps: These are a special type of incandescent lamp. They use a strong glass bulb filled with a gas called halogen.
- LED lamps: These are modern lamps that use tiny electronic parts called light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to make light.
- Arc lamps: These lamps make light by creating a bright spark (an electric arc) between two points.
- Gas-discharge lamps: These lamps create light by sending electricity through a special gas. This gas then glows.
- Fluorescent lamps: A common type of gas-discharge lamp.
- Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs): These are smaller fluorescent lamps designed to fit where old incandescent bulbs used to go.
- Neon lamps: These use neon gas to make a bright glow, often seen in signs.
- Mercury-vapor lamps: These use mercury gas.
- Sodium-vapor lamps: These use sodium gas.
- Fluorescent lamps: A common type of gas-discharge lamp.
Different lamps create light in various ways. They also use different amounts of energy and produce different colors of light. For example, some lamps are very good at turning electricity into light, while others waste a lot of energy as heat.
The most energy-efficient electric lamp is the low-pressure sodium lamp. It makes a very specific orange-yellow light. Because of its unique color, it's mostly used for outdoor street lighting. Astronomers like these lights because their light pollution is easy to filter out.
Incandescent Light Bulbs

The incandescent light bulb we know today has a coiled wire made of tungsten. It became popular in the 1920s. It was an improvement on earlier lamps from the 1880s that used a carbon wire. Besides regular home bulbs, there are many small incandescent lamps used in equipment. However, LEDs are now replacing many of these.
Some countries have started to ban or phase out old incandescent bulbs. For example, Australia began phasing them out in 2009. Sri Lanka has already stopped importing them. This is because these bulbs are not very energy-efficient. Less than 3% of the energy they use becomes light. Most of the energy turns into heat. In warm places, this heat makes buildings hotter, so you need more energy for air conditioning. In cold places, the heat can be helpful during winter.
Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps are usually much smaller than regular incandescent bulbs. They need to get very hot (over 200°C) to work well. Because of this, their bulbs are often made of a special strong glass called quartz. Sometimes, they have an extra layer of glass around them for safety. This outer glass helps block harmful UV light and protects you if the inner bulb breaks. Halogen bulbs can sometimes explode if they get oily fingerprints on them. They also get very hot, so they can cause burns or fires if not used carefully.
Halogen lamps designed for 12 or 24 volts have small wires that are good for directing light. They are also more energy-efficient and last longer than non-halogen bulbs. Their light stays bright and constant throughout their life.
Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent lamps are glass tubes filled with mercury vapor or argon gas at low pressure. When electricity flows through the tube, these gases create ultraviolet energy. The inside of the tube is coated with special powders called phosphors. These phosphors glow and make visible light when hit by the ultraviolet energy.
Fluorescent lamps are much more energy-efficient than incandescent lamps. They use about one-quarter to one-third the power to make the same amount of light. While fluorescent light fixtures cost more at first because they need a special part called a ballast, they save money on electricity bills over time. Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are now available in sizes that fit regular light sockets. They are a popular energy-saving choice for homes.
Because fluorescent lamps contain a small amount of mercury, they need to be recycled properly. The United States Environmental Protection Agency suggests keeping them separate from regular trash. Some places even require you to recycle them.
LED Lamps

Tiny LEDs have been used as indicator lights in electronics since the 1970s. In the 2000s, LEDs became much brighter and more efficient. Now, they are used in many lighting applications, like car headlights, flashlights, bike lights, and holiday decorations.
Indicator LEDs are known for lasting a very long time, sometimes up to 100,000 hours. However, LEDs used for general lighting are often pushed harder, so they might not last quite as long. LED technology is great for lighting because it uses little power, doesn't get very hot, turns on and off instantly, and keeps its color over time. The lifespan of an LED lamp depends a lot on how hot the diode gets. If it gets too hot inside, the lamp's life can be much shorter.
Carbon Arc Lamps

Carbon arc lamps have two carbon rods that act as electrodes. When electricity flows between them, a bright electric spark (arc) forms, heating the carbon tips until they glow white-hot. These lamps are more efficient than filament lamps. However, the carbon rods burn away quickly and need to be adjusted often. They also produce a lot of ultraviolet light, so they need good ventilation indoors and should not be looked at directly.
Invented by Humphry Davy around 1805, the carbon arc lamp was the first practical electric light. They were used for lighting large buildings and streets starting in the 1870s. By the early 1900s, incandescent lights replaced them for most uses. Carbon arc lamps are very powerful and make a bright white light from a small point. They were still used in specific applications like movie projectors, stage lighting, and searchlights until after World War 2.
Discharge Lamps
A discharge lamp has a glass or silica bulb with two metal electrodes separated by a gas. Common gases used include neon, argon, xenon, sodium, and mercury. The basic idea is similar to a carbon arc lamp, but the term 'arc lamp' usually refers to the older carbon type. More modern gas discharge lamps are called discharge lamps.
Some discharge lamps need a very high voltage to start the arc. This requires a special electrical part called an igniter, which is part of the ballast system. Once the arc starts, the lamp's resistance drops, and the ballast then limits the electric current to the correct operating level. Without a ballast, too much current would flow, quickly destroying the lamp.
Some lamps, like low-pressure sodium lamps, contain a little neon. This allows them to start at normal voltage without needing a separate igniter. The simplest ballasts are just a coil of wire and are used when cost is the main concern, like in street lighting. More advanced electronic ballasts can keep the light output constant as the lamp ages. They can also make the light completely flicker-free and shut down if there's a problem.
How Long Lamps Last
The "life expectancy" for many lamps means the number of hours they operate before half of them stop working. This is like the average lifespan. Even small differences in how lamps are made can change their life by a lot. So, some lamps will fail sooner than expected, while others will last much longer. For LEDs, lamp life is often defined as the time when 50% of the lamps have lost 70% of their original brightness.
Some lamps are also affected by how often they are turned on and off. Lamps in rooms where they are switched on and off frequently, like bathrooms, might not last as long as the box says. Compact fluorescent lamps are especially sensitive to frequent switching.
Public Lighting
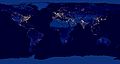
The total amount of artificial light, especially from street lights, is so much that cities are easily seen from the air and from space at night. This light creates light pollution, which can make it harder for astronomers to see the stars and for others to enjoy the night sky.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Luz eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Luz eléctrica para niños