Leopard gecko facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Leopard gecko |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Eublepharidae |
| Genus: | Eublepharis |
| Species: |
E. macularius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eublepharis macularius (Blyth, 1854)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
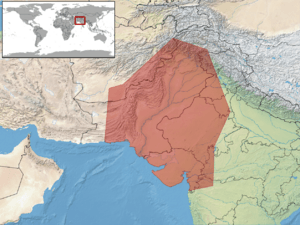
The leopard gecko (its scientific name is Eublepharis macularius) is a type of gecko that lives on the ground. You can find them in rocky, dry grasslands and deserts. Their native homes are in countries like Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan, India, and Nepal.
Leopard geckos are very popular pets. Because many of them are bred by people, some even call them the first "domesticated" lizard. However, no lizards are truly domesticated like dogs or cats.
Contents
About Leopard Geckos
Leopard geckos were first described by a zoologist named Edward Blyth in 1854. The name Eublepharis comes from two Greek words: eu (meaning "good") and blepharos (meaning "eyelid"). This name was chosen because these geckos have eyelids, which is special since most other geckos don't!
The second part of their name, macularius, comes from the Latin word macula. This word means "spot" or "blemish". It refers to the cool spotted patterns you see on these animals.
There are five different types, or subspecies, of Eublepharis macularius:
- Eublepharis macularius afghanicus
- Eublepharis macularius fasciolatus
- Eublepharis macularius macularius
- Eublepharis macularius montanus
- Eublepharis macularius smithi
Where Leopard Geckos Live
Leopard geckos naturally live in dry areas. These include rocky grasslands and deserts in parts of south-Asian Afghanistan, Pakistan, north-west India, western Nepal, and some areas of Iran.
They like places that are dry or semi-dry with not many plants. They also prefer clay or sandy soils. You can often find them hiding in rocky spots. They tend to stay away from areas that are mostly sand.
Sometimes, leopard geckos are found in dry forests in Nepal and Pakistan. In these places, they might hide under the loose bark of trees. During winter, temperatures in their home areas can drop below 10 °C (50 °F). When it gets cold, they go underground. They enter a state called brumation, which is like a semi-hibernation. They live off the fat stored in their tails during this time.
Leopard Gecko Behavior
Wild leopard geckos are mostly active at night. This means they are nocturnal animals. During the day, they hide in burrows or other sheltered spots. They become active when the sun goes down and the temperature is just right.
Famous naturalist David Attenborough said that leopard geckos, like most geckos, are nocturnal. He explained that they get all the heat they need from rocks. Rocks stay warm for several hours after the sun sets.
There is some discussion about how much leopard geckos interact with each other in the wild. Some experts believe they live in loose groups. However, many pet guides say these geckos are solitary. This means they usually prefer to live alone.
What Leopard Geckos Eat
Leopard geckos are hunters. In the wild, they mostly eat invertebrates, like insects. But if they get the chance, they will also eat small vertebrates. This can include baby mice, smaller reptiles, or even other baby leopard geckos.
Leopard Gecko Characteristics
Leopard geckos are small lizards. They get their name from their spotted skin, which looks a bit like a leopard's spots.
When they first hatch, they are about 7 to 10 cm (2.8 to 3.9 in) long. They weigh only about 2 to 5 grams. Adult female geckos are usually 18 to 20 cm (7.1 to 7.9 in) long and weigh 50 to 70 grams. Adult males are a bit bigger. They can be 20 to 28 cm (7.9 to 11.0 in) long and weigh 60 to 80 grams.
Unlike many other geckos, leopard geckos cannot climb smooth vertical walls. This is because their toes do not have sticky pads.
Teeth
Leopard geckos have about 100 teeth. They are special because they can replace each tooth every 3 to 4 months! Next to each full-grown tooth, a tiny new replacement tooth is already growing.
Tails
Leopard geckos have thick tails. These tails are used to store fat. Think of it like a camel's hump, which stores fat for energy. The fat in a gecko's tail acts as an energy reserve. They can use this stored energy if they can't find food for a while.
When a leopard gecko hunts, it might lift its tail. It can twitch or wag its tail as it gets closer to its prey. After it eats, the tail goes back to a relaxed position.
Like many geckos, leopard geckos can drop their tails if they are in danger. This is called autotomy. The tail can even keep wiggling for up to 30 minutes! This distracts the predator, giving the gecko time to escape. The tailbone has special breaks that allow the tail to come off easily with very little blood loss.
After losing a tail, the gecko will start to grow a new one right away. However, the new tail will look different. It will be shorter, wider, and often smoother than the original tail.
Defense Mechanisms
Wild leopard geckos mostly try to avoid being seen by predators. Their spotted colors help them blend in with their surroundings. This is called camouflage. They also stay hidden during the day to avoid the heat and to not be seen by predators that hunt during the day.
If a leopard gecko faces a predator, it might make sounds. This is an attempt to scare the predator away.
Colors of Leopard Geckos
Leopard geckos can be yellow to brownish-orange. They have spots covering most of their back. Their colors come from special cells called chromatophores. These cells contain pigments, which are what give animals their colors.
There are different types of chromatophores:
- Xanthophores make yellow colors.
- Erythrophores make red colors.
- Iridophores create shiny, rainbow-like colors.
- Leucophores make white colors.
- Melanophores make black colors.
- Cyanophores make blue colors.
Wild leopard geckos have xanthophores (yellow) and melanophores (black spots). But pet leopard geckos can have many more colors! This is because people have selectively bred them to create new color patterns.
Telling Males and Females Apart
You can tell if a leopard gecko is male or female by looking at its underside. Males have special pores and bumps near their tail. Females have smaller pores and no external bumps.
Male geckos can tell the sex of other geckos by smelling chemicals called pheromones on their skin. If a male smells another male, he will act aggressively. He will raise himself up, stretch his legs, and arch his back. He might also make quick, strong bites. If he smells a female, he will show courtship behavior instead.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Leopard geckos usually breed in the summer. A female can lay about six to eight groups of two eggs each. Eggs are laid about 21 to 28 days after mating. It takes about 35 to 89 days for the babies to hatch, but usually closer to the longer time.
Baby leopard geckos have a tiny "egg tooth" on their snout. This helps them break out of their eggshell. The "egg tooth" falls off within a day or two. Also, their skin usually sheds within 24 hours of hatching. A baby gecko cannot eat until after its first skin shed.
The temperature during incubation can determine if a baby gecko will be male or female.
- If eggs are kept mostly cool (around 26–29 °C [79–84 °F]), they will develop into females.
- If eggs are kept very warm (around 34–35 °C [93–95 °F]), they will also develop into females.
- If eggs are kept at middle temperatures (around 31–33 °C [88–91 °F]), they will develop into males.
The sex is usually set during the first two weeks of incubation. Females born in warmer temperatures can act more aggressively. These are sometimes called "hot females" and might not be able to have babies.
Leopard Geckos as Pets
Leopard geckos are one of the most popular pet lizards. They are second only to the bearded dragon. They might even be the first lizard species to be "domesticated" by humans.
It's easy to breed them in captivity. This means most pet leopard geckos are born in captivity, not caught from the wild. Because people have been breeding them for so long, pet geckos come in many different colors and patterns. Wild geckos usually have more plain colors than the ones kept as pets.
See also
 In Spanish: Gecko leopardo para niños
In Spanish: Gecko leopardo para niños
- Chinese cave gecko
- African fat tail gecko