Dormancy facts for kids

Dormancy is a special time in an organism's life cycle. During this period, growth, development, and physical activity (for animals) temporarily stop. This helps the organism save energy by slowing down its body processes, called metabolism. Dormancy often happens because of changes in the environment.
There are two main kinds of dormancy:
- Predictive dormancy happens when an organism goes into a resting phase before bad conditions arrive. For example, many plants use the shorter day length and colder temperatures to know that winter is coming. They start their dormancy before the cold weather hits.
- Consequential dormancy happens when organisms go into a resting phase after bad conditions have already started. This type is common in places where the weather changes suddenly. If conditions change too fast, animals using this strategy might not survive. However, it can also be helpful because organisms stay active longer. This lets them use more of the available food and resources.
Contents
How Animals Cope: Different Types of Dormancy
Hibernation: Winter Sleep for Animals
Hibernation is a way many mammals save energy and survive when food is scarce in winter. It can be either predictive or consequential.
Animals get ready for hibernation by eating a lot. They build up a thick layer of body fat in late summer and autumn. This fat gives them energy during their long sleep. While hibernating, an animal's body changes a lot. Its heart rate can drop by as much as 95%. Its body temperature also goes down.
Animals that hibernate include bats, ground squirrels, and other rodents. Mouse lemurs, the European hedgehog, and some marsupials also hibernate. Most hibernators are mammals, but a few birds, like the common poorwill, can also hibernate.
Diapause: Insect's Resting Time
Diapause is a predictive way for insects to rest. It is very common for them to do this between autumn and spring.
Aestivation: Escaping Heat and Dryness
Aestivation is a type of dormancy that happens when it's very hot or dry. It's common in small creatures without backbones (invertebrates). It also happens in lungfish, salamanders, desert tortoises, and crocodiles.
Brumation: Reptile's Slowdown
Brumation is a type of dormancy for reptiles. It is similar to hibernation, but the body processes are different. Reptiles usually start brumation in late autumn. They often wake up to drink water, then go back to sleep. They can go for months without eating food.
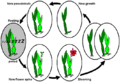
How Plants Cope: Resting and Growing
Seeds: Tiny Plants in Waiting
A seed might look inactive, but it's a tiny living thing. Inside, it holds the embryo of a future plant. This embryo is not growing or changing; it is dormant. Many people think a seed "sleeps" until it gets what it needs to wake up. But it's a bit more complex than that. Different seeds have different ways of resting, which fit their habitat.
There are two main resting stages for seeds:
- Seed dormancy: This means the seed will not grow for a while, even if conditions are good. This delay lets the seed spread out to new places. Changes happen inside the seed that will eventually make it grow. How this happens is very different for each species.
- Seed "hibernation": This means the seed does not grow because the conditions are not right. Growth is started by specific events in the environment. For some seeds, we know what these triggers are, like rain, fire, or ground temperature. Many seeds only grow after an animal has eaten them and they have passed through its digestive system. This also helps them spread.
When a seed grows, or "wakes up," it starts to become a tiny plant called a seedling. It uses the soft, fleshy material inside the seed for food. It does this until it can make its own food using sunlight, water, and air.
Most seeds grow underground where there is no sunlight. The young plant does not need nutrients from the soil for a few days or weeks. This is because the seed has everything it needs to start growing. Later, it will need sunlight. If there is sunlight, the plant will grow strong and healthy. If there is no light, the plant will still grow for a while. But its green parts (plastids) will not fully develop. The chlorophyll will not turn green. If the plant does not get enough light, it will eventually die. It needs light to make its own food when the food stored in the seed runs out.
- The oldest carbon 14-dated seed that grew into a plant was a Judean date palm seed. It was about 2,000 years old. This seed was found during digs at Herod the Great's palace in Masada, Israel. It sprouted in 2005.
- The largest seed comes from the Coco de mer, also known as the "double coconut palm." The whole fruit can weigh up to 23 kilograms (50 pounds). It usually has only one seed inside.
Trees: Overcoming Winter's Chill
Typically, woody perennial plants that live in places with changing seasons need cold temperatures to end their winter dormancy. For some species, this resting period can be broken in just a few hours.
Tree species that really need a cold period can be tricked a little, but not completely. If a plant goes through an "eternal summer" without cold, it becomes stressed. This usually kills the plant. The death rate becomes 100% if the plant does not get enough cold. Most plants need a certain number of "chilling" hours. These are hours at temperatures between about 0 °C and 10 °C. This cold period is needed for them to break dormancy.
Bacteria: Tiny Survivors
Many bacteria can survive bad conditions. They do this by forming endospores or cysts. They can also enter states where their body activity is very low. Up to 80% of bacteria in nature seem to be inactive. Many of these can be brought back to life. This kind of dormancy helps keep many different types of life in natural ecosystems.
Viruses: Not Truly Dormant
Dormancy does not apply to viruses. This is because viruses are not metabolically active on their own. However, some viruses, like poxviruses, can become latent after entering a host. They can stay hidden for long periods, or even forever, until something activates them.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Dormancia para niños
In Spanish: Dormancia para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |