List of the prehistoric life of Virginia facts for kids
This list explores the amazing ancient creatures and plants whose fossil remains have been found right here in the state of Virginia. These fossils tell us a lot about what life was like millions of years ago!
Contents
Ancient Eras in Virginia
The Precambrian Era: Before Complex Life
The Paleobiology Database doesn't show any known fossils from the Precambrian Era in Virginia. This was a very, very long time ago, before complex life forms with hard parts (like shells or bones) were common.
The Paleozoic Era: Early Ocean Life
The Paleozoic Era was a time when many different kinds of life appeared, especially in the oceans. Virginia has fossils from this era, showing us what ancient seas looked like.
Selected Paleozoic Fossils of Virginia
- †Archimedes: This was a type of bryozoan (say: BRY-oh-zoh-an), which are tiny colonial animals that lived in the ocean. They built unique spiral-shaped skeletons, making them easy to spot as fossils.
- †Bothriolepis: Imagine a fish with a bony head and armor! Bothriolepis (say: Both-ree-oh-LEP-is) was an armored fish from the Late Devonian period. It lived in freshwater and had a flattened body, perfect for living on the bottom.

- †Cincinnetina: These were common brachiopods (say: BRAK-ee-oh-pods), which are marine animals with two shells, similar to clams but different inside. They lived during the Ordovician period.
- †Isotelus: This giant trilobite (say: TRY-loh-bite) was a type of ancient arthropod, like a distant cousin of crabs and insects. Isotelus (say: Eye-so-TEL-us) could grow very large and lived in the Middle to Late Ordovician seas.
- †Lepidodendron: These were huge, ancient trees that looked like giant club mosses. They grew tall during the Carboniferous period, forming vast forests that later became coal.
- †Pentremites: Often called "sea buds," these were blastoids (say: BLAS-toyds), a type of echinoderm related to starfish and sea urchins. They had a unique, bud-like shape and lived in the Carboniferous period.
- †Receptaculites: This ancient organism was a type of benthic alga, meaning it lived on the seafloor. It had a distinctive, often spiral, pattern and lived from the Early Ordovician to the Permian.
- †Tentaculites: These small, cone-shaped creatures were likely a type of mollusc. They lived in the oceans from the Early Ordovician to the Late Devonian.
The Mesozoic Era: The Age of Dinosaurs
The Mesozoic Era is famous for dinosaurs! Virginia has many dinosaur footprints, showing that these amazing creatures once roamed here. This era also saw many new plants and other reptiles.
Selected Mesozoic Fossils of Virginia
- †Anomoepus: This is a type of dinosaur footprint from the Early Jurassic. It was likely made by a small, bird-like dinosaur.
- †Brontopodus: These huge footprints were made by giant, long-necked sauropod (say: SAW-roh-pod) dinosaurs. Finding them in Virginia tells us these massive plant-eaters lived here.
- †Doswellia: This was a unique reptile from the Late Triassic period. It had a flattened body and bony plates, similar to an armored lizard. Its fossils were first found in Virginia.
- †Eubrontes: These are large footprints made by big, meat-eating theropod (say: THEER-oh-pod) dinosaurs, like the ancestors of T. rex. They are common dinosaur tracks found in the Early Jurassic rocks of Virginia.
- †Grallator: These are smaller, three-toed dinosaur footprints, also made by theropods. They are some of the most common dinosaur tracks found.
- †Lissodus: This was a freshwater shark that lived from the Early Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Its fossilized teeth are found in ancient river and lake deposits.
- †Rutiodon: This crocodile-like reptile, called a phytosaur (say: FY-toh-sore), lived during the Late Triassic. It had a long snout filled with sharp teeth, perfect for catching fish.

- †Zamites: These were ancient plants that looked like cycads, with stiff, palm-like fronds. They were common during the Mesozoic Era.
The Cenozoic Era: The Age of Mammals
After the dinosaurs, mammals became the dominant animals on Earth. The Cenozoic Era saw the rise of many familiar animals, including giant sloths, mammoths, and ancient whales.
Selected Cenozoic Fossils of Virginia
- †Aglaocetus: This was an ancient baleen whale from the Miocene epoch. Its fossils help us understand how modern whales evolved.
- †Arctodus: Also known as the short-faced bear, Arctodus (say: ARK-toh-dus) was a massive bear that lived during the Pleistocene epoch. It was one of the largest land predators of its time.

- †Bootherium bombifrons: This was a type of musk ox that lived during the Pleistocene and early Holocene epochs. Its fossils show us that these cold-adapted animals once roamed Virginia.
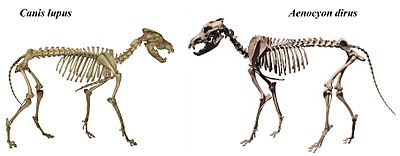
- †Canis dirus: The dire wolf was a large wolf that lived during the Pleistocene epoch. It was bigger and stronger than modern gray wolves.
- †Castoroides: Meet the giant beaver! Castoroides (say: Kas-toh-ROY-deez) was a huge beaver, about the size of a black bear, that lived from the Pliocene to the Pleistocene.
- †Chesapecten jeffersonius: This fossil scallop is so important that it's Virginia's official state fossil! It lived during the Pliocene epoch and is commonly found in the Chesapeake Bay area.
- †Cryptobranchus alleganiensis: This is the hellbender salamander, a large aquatic salamander. Fossils show it has lived in Virginia for a long time.

- †Dasypus bellus: This was a larger, extinct relative of modern armadillos. Its fossils from the Pleistocene epoch show that armadillos once lived much further north.
- †Diplocynodon: This was a type of crocodile that lived from the Paleocene to the Miocene. Its fossils indicate that Virginia had warmer, more tropical climates in the past.
- †Eobalaenoptera harrisoni: This ancient baleen whale was first discovered in Virginia. It lived during the Miocene epoch and is important for understanding whale evolution.

- †Eurhinodelphis: This was a long-snouted dolphin from the Miocene epoch. Its fossils help scientists learn about the diversity of ancient marine mammals.
- †Gavialosuchus: This was a large, extinct relative of modern gavials (a type of crocodile with a very long, thin snout). It lived during the Miocene epoch.
- †Mammut americanum: The American mastodon was a large, elephant-like mammal with long, straight tusks. It lived during the Pleistocene epoch and was a browser, eating leaves and branches.
- †Mammuthus primigenius: The woolly mammoth was another famous elephant-like mammal from the Pleistocene. It had long, curved tusks and a thick coat of fur, adapted for cold climates.

- †Megalonyx jeffersonii: This was Jefferson's ground sloth, a giant ground sloth named after Thomas Jefferson. It lived during the Miocene to Pleistocene epochs and was a massive plant-eater.
- †Metaxytherium: This was an ancient relative of modern manatees and dugongs. It lived in the oceans from the Miocene to the Pleistocene.
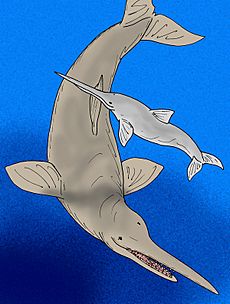
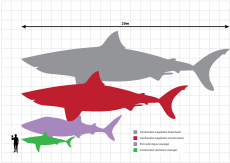
- †Otodus megalodon: Often called just "Megalodon," this was the largest shark that ever lived! It was a massive predator that swam in the oceans during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.
- †Pelagornis: This incredible bird was a "false-toothed" bird, meaning it had bony projections on its beak that looked like teeth. It was one of the largest flying birds ever, living from the Oligocene to the Pleistocene.

- †Platygonus: These were extinct peccaries, which are pig-like mammals. They lived in herds from the Miocene to the Pleistocene.

- †Squalodon: This was a "shark-toothed dolphin" from the Oligocene to the Miocene. It had teeth that looked like those of a shark, even though it was a whale.
- †Tapirus veroensis: This was an extinct species of tapir, a pig-like mammal with a short trunk. Tapirs lived in Virginia during the Pleistocene.

- †Thecachampsa: This was a large, extinct relative of gavials, a type of crocodile. It lived from the Oligocene to the Miocene.
- †Xiphiacetus: This was an ancient whale from the Miocene epoch. Its fossils help scientists understand the early evolution of whales.
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |