Luna programme facts for kids
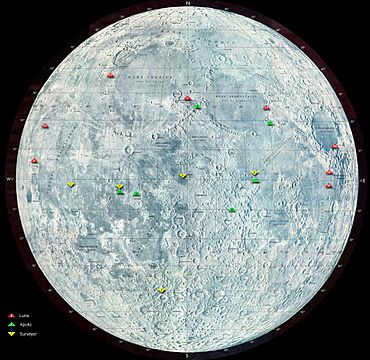
Locations of Luna landings on the Moon are marked in red; Apollo missions in green, and Surveyor in yellow.
|
|
| Country | Soviet Union, Russia |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Uncrewed exploration of the Moon |
| Status | Operational |
| Program history | |
| Duration | 1958–present |
| First flight |
|
| Last flight |
|
| Successes | 15 |
| Failures | 29 |
| Partial failures | 0 |
| Launch site(s) | Baikonur Cosmodrome |
| Vehicle information | |
| Launch vehicle(s) |
|
The Luna programme (which means "Moon" in Russian) is a series of robotic spacecraft missions. These missions were sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union and later Russia. They took place between 1959 and 2023.
Out of many missions, fifteen were successful. Each Luna spacecraft was designed to either orbit the Moon or land on it. These missions achieved many "firsts" in space exploration. They also did many experiments. They studied the Moon's chemical makeup, gravity, temperature, and radiation.
Twenty-four spacecraft were officially named Luna. However, more were launched. Missions that failed to reach orbit were not publicly announced back then. They were not given a Luna number. Those that failed in low Earth orbit were often called Cosmos missions.
Contents
Exploring the Moon: Mission Types
The name Luna was used for different spacecraft designs. Each design aimed to achieve a specific type of mission:
Impactors: Hitting the Moon
Impactor spacecraft were built to crash into the Moon's near side. Luna 1 (January 1959) missed the Moon. It became the first spacecraft to leave the Earth-Moon system. Luna 2 (September 1959) successfully hit the Moon's surface. This made it the first human-made object to reach the Moon. This was Luna's only successful impact out of six tries.
Flybys: Flying Past the Moon
A flyby is the simplest type of lunar spacecraft. It doesn't need special engines to slow down or a super-accurate guidance system to hit the Moon. Its main job is to send photos back to Earth. Luna 3 (October 1959) flew around the Moon later that year. It sent back the first pictures of the Moon's far side. This side can never be seen from Earth. This was Luna's only successful flyby mission.
Soft Landers: Gentle Touchdowns
Soft landers need rocket power to slow down. This prevents the spacecraft from crashing. They can keep sending pictures from the Moon's surface. They might also dig into the lunar soil or gather other information.
Luna program landers were generally called Ye-6 (or E-6). Two successful soft landings happened out of thirteen attempts.
Luna 9 became the first probe to make a soft landing on another planet (the Moon) in February 1966. It sent back five black and white panoramic images. These were the first close-up pictures of the lunar surface.
Orbiters: Circling the Moon
Orbiter spacecraft need less power than landers. But they still need enough to get into orbit around the Moon. Luna 10 (March 1966) became the first artificial satellite of the Moon. The Luna program had six successful orbiters out of eight attempts.
Rovers: Driving on the Moon
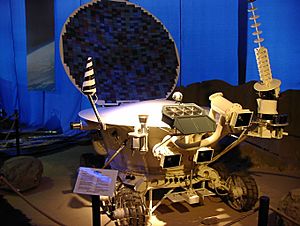
More advanced soft landers can release wheeled vehicles. These "rovers" can explore a wider area of the Moon's surface. The first attempt to launch a Lunokhod rover failed in February 1969. Luna 17 (November 1970) and Luna 21 (January 1973) carried Lunokhod vehicles. These were the first robotic wheeled vehicles to explore the Moon's surface.
Lunokhod 1 traveled about 10.5 kilometers (6.5 miles) in 322 days. It sent back over 20,000 TV images and 206 high-quality panoramas. Lunokhod 2 worked for about four months. It covered 42 kilometers (26 miles) of terrain. A third Lunokhod was built but never flew.
Sample Return: Bringing Moon Rocks Home
More complex soft lander craft can robotically pick up a small amount of lunar material. Then, they lift off from the surface and bring the material back to Earth. Luna 16 (September 1970), Luna 20 (February 1972), and Luna 24 (August 1976) all brought samples of lunar soil back to Earth. A total of 301 grams (10.6 ounces) of soil was returned from these three missions.
Luna 15 (July 1969) flew at the same time as the Apollo 11 mission. Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin had already landed on the Moon. Luna 15 then began its descent but crashed into a mountain.
Mission Success Rates: How Luna Compared
When the Luna program was active, the Soviet Union usually did not share details about missions that failed. Because of this, people in Western countries often gave their own names to these missions. For example, a failed mission from 1958, which NASA thought was part of the Luna program, was called Luna 1958A.
Here's a look at how Luna missions compared to similar US programs:
| Luna | Competing United States programmes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | First attempt | Attempts | First success | Successes | Rate | First attempt | Attempts | First success | Successes | Rate |
| Impactor | 23 Sep 1958 | 6 | Luna 2 Sep 13, 1959 |
1 | 16.7% | Ranger 1 23 Aug 1961 |
9 | Ranger 7 31 July 1964 |
3 | 33.3% |
| Flyby | Luna 3 6 Oct 1959 |
3 | Luna 3 | 1 | 33.3% | Pioneer 3 6 Dec 1958 |
2 | Pioneer 4 6 Mar 1959 |
1 | 50.0% |
| Soft lander | 4 Jan 1963 | 13 | Luna 9 3 Feb 1966 |
2 | 15.4% | Surveyor 1 2 Jun 1966 |
7 | Surveyor 1 | 5 | 71.4% |
| Orbiter | 1 Mar 1966 | 8 | Luna 10 3 Apr 1966 |
6 | 75.0% | Pioneer 0 17 Aug 1958 |
12 | Lunar Orbiter 1 18 Aug 1966 |
5 | 41.7% |
| Rover | 19 Feb 1969 | 3 | Luna 17 17 Nov 1970 |
2 | 66.7% | Apollo 15 31 July 1971 |
3 | Apollo 15 | 3 | 100.0% |
| Sample return | 14 Jun 1969 | 11 | Luna 16 24 Sep, 1970 |
3 | 27.3% | Apollo 11 24 Jul 1969 |
7 | Apollo 11 | 6 | 85.7% |
| Total | 44 | 15 | 34.1% | Total | 40 | 24 | 60.0% | |||
Luna Missions: A Closer Look
This table lists the different Luna missions, their types, and what happened during each one.
| Public name | Internal name | Photo | Mission | Launch date | Carrier rocket | Outcome | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | E-1 No.1 | Impactor | 23 September 1958 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| N/A | E-1 No.2 | Impactor | 11 October 1958 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| N/A | E-1 No.3 | Impactor | 4 December 1958 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 1 | E-1 No.4 | Impactor | 2 January 1959 | Luna | Launch failure | Also known as Mechta; flew past the Moon; first spacecraft to escape geocentric orbit | |
| N/A | E-1A No.1 | Impactor | 18 June 1959 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 2 | E-1A No.2 | Impactor | 12 September 1959 | Luna | Successful | First human-made object to reach the Moon. | |
| Luna 3 | E-2A No.1 | Flyby | 4 October 1959 | Luna | Successful | Took first photographs of the far side of the Moon. | |
| N/A | E-3 No.1 | Flyby | 15 April 1960 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| N/A | E-3 No.2 | Flyby | 16 April 1960 | Luna | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| N/A | E-6 No.2 | Lander | 4 January 1963 | Molniya-L | Launch failure | Never left LEO | |
| N/A | E-6 No.3 | Lander | 3 February 1963 | Molniya-L | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 4 | E-6 No.4 | Lander | 2 April 1963 | Molniya-L | Spacecraft failure | Flew past the Moon | |
| N/A | E-6 No.6 | Lander | 21 March 1964 | Molniya-M | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| N/A | E-6 No.5 | Lander | 20 April 1964 | Molniya-M | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Kosmos 60 | E-6 No.9 | Lander | 12 March 1965 | Molniya-L | Launch failure | Never left LEO | |
| N/A | E-6 No.8 | Lander | 10 April 1965 | Molniya-L | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 5 | E-6 No.10 | Lander | 9 May 1965 | Molniya-M | Spacecraft failure | Crashed on the Moon | |
| Luna 6 | E-6 No.7 | Lander | 8 June 1965 | Molniya-M | Spacecraft failure | Flew past the Moon | |
| Luna 7 | E-6 No.11 | Lander | 4 October 1965 | Molniya | Spacecraft failure | Crashed on the Moon | |
| Luna 8 | E-6 No.12 | Lander | 3 December 1965 | Molniya | Spacecraft failure | Crashed on the Moon | |
| Luna 9 | E-6 No.13 | Lander | 31 January 1966 | Molniya-M | Successful | First soft landing on the Moon. | |
| Kosmos 111 | E-6S No.204 | Orbiter | 1 March 1966 | Molniya-M | Launch failure | Never left LEO | |
| Luna 10 | E-6S No.206 | Orbiter | 31 March 1966 | Molniya-M | Successful | First artificial satellite of the Moon. | |
| Luna 11 | E-6LF No.101 | Orbiter | 24 August 1966 | Molniya-M | Successful | ||
| Luna 12 | E-6LF No.102 | Orbiter | 22 October 1966 | Molniya-M | Successful | ||
| Luna 13 | E-6M No.205 | Lander | 21 December 1966 | Molniya-M | Successful | Landed on the Moon. | |
| N/A | E-6LS No.112 | Orbiter | 7 February 1968 | Molniya-M | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 14 | E-6LS No.113 | Orbiter | 7 April 1968 | Molniya-M | Successful | ||
| N/A | E-8 No.201 | Rover | 19 February 1969 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | First attempt to launch Lunokhod. | |
| N/A | E-8-5 No.402 | Sample return | 14 June 1969 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 15 | E-8-5 No.401 | Sample return | 13 July 1969 | Proton-K/D | Spacecraft failure | Crashed on the Moon while Apollo 11 was on the surface. | |
| Kosmos 300 | E-8-5 No.403 | Sample return | 23 September 1969 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | Never left LEO | |
| Kosmos 305 | E-8-5 No.404 | Sample return | 22 October 1969 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | Never left LEO | |
| N/A | E-8-5 No.405 | Sample return | 6 February 1970 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 16 | E-8-5 No.406 | Sample return | 12 September 1970 | Proton-K/D | Successful | First robotic sample return from the Moon. | |
| Luna 17 | E-8 No.203 | Rover | 10 November 1970 | Proton-K/D | Successful | Deployed Lunokhod 1, the first robotic wheeled vehicle on the Moon. | |
| Luna 18 | E-8-5 No.407 | Sample return | 2 September 1971 | Proton-K/D | Spacecraft failure | Crashed on the Moon. | |
| Luna 19 | E-8LS No.202 | Orbiter | 28 September 1971 | Proton-K/D | Successful | ||
| Luna 20 | E-8-5 No.408 | Sample return | 14 February 1972 | Proton-K/D | Successful | Returned a sample to Earth. | |
| Luna 21 | E-8 No.204 | Rover | 8 January 1973 | Proton-K/D | Successful | Deployed Lunokhod 2. | |
| Luna 22 | E-8LS No.206 | Orbiter | 29 May 1974 | Proton-K/D | Successful | ||
| Luna 23 | E-8-5M No.410 | Sample return | 28 October 1974 | Proton-K/D | Spacecraft failure | Landed but fell over. | |
| N/A | E-8-5M No.412 | Sample return | 16 October 1975 | Proton-K/D | Launch failure | Failed to orbit | |
| Luna 24 | E-8-5M No.413 | Sample return | 9 August 1976 | Proton-K/D | Successful | Returned a sample to Earth. | |
| Luna 25 | E-8-5M No.414 | Lander | 10 August 2023 | Soyuz 2.1b | En route |
See also
 In Spanish: Programa Luna para niños
In Spanish: Programa Luna para niños
- Luna (rocket)
- Luna-Glob
- Soviet crewed lunar programs
- Soviet space program
- Surveyor program
- Pioneer program
- Ranger program