Luna 1 facts for kids
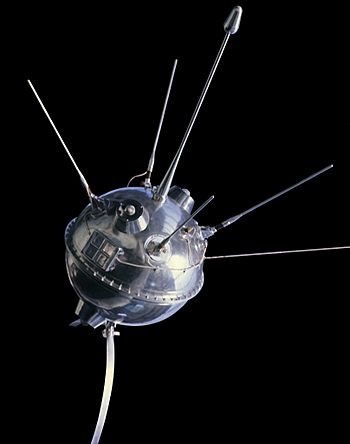
A museum replica
|
|
| Mission type | Lunar impactor |
|---|---|
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Harvard designation | 1959 Mu 1 |
| Mission duration | Approximately 62 hours |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | Ye-1 |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
| Launch mass | 361.3 kilograms (797 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 2 January 1959, 16:41:21 UTC |
| Rocket | Luna 8K72 |
| Launch site | Baikonur, Site 1/5 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | 5 January 1959 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Heliocentric |
| Semi-major axis | 1.146 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.14767 |
| Perihelion | 0.9766 AU |
| Aphelion | 1.315 AU |
| Inclination | 0.01° |
| Period | 450 days |
| Epoch | 1 January 1959, 19:00:00 GMT |
| Lunar flyby (failed impact) | |
| Closest approach | 4 January 1959 |
| Distance | 5,995 kilometres (3,725 mi) |
|
|
|
Luna 1 was a space probe launched by the Soviet Union in 1959. It is also known as Mechta (which means "Dream" in Russian). It was the first spacecraft to fly close to the Moon. It was also the first human-made object to leave Earth's orbit and circle the Sun.
The mission was originally designed to crash-land on the Moon. However, a problem with the rocket caused it to miss its target. Instead of hitting the Moon, it flew past it. Because it traveled so fast, it broke away from Earth's gravity. It became a "new planet" orbiting the Sun.
Contents
The Luna 1 Spacecraft
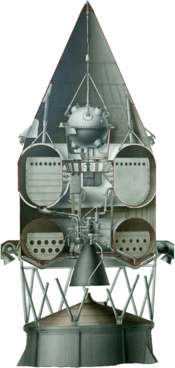
The spacecraft was a sphere, shaped like a ball. It weighed 361.3 kilograms (797 lb). It had five antennas sticking out of it to send radio signals back to Earth.
Design and Instruments
Luna 1 carried special equipment to study space. It had no engines to move itself once it separated from the rocket. It relied on batteries for power.
The probe carried several scientific instruments:
- A magnetometer to look for the Moon's magnetic field.
- Radiation detectors to measure high-energy particles in space.
- Micrometeorite detectors to count tiny space rocks that hit the spacecraft.
- Ion traps to measure the solar wind, which is a stream of particles coming from the Sun.
The spacecraft also carried two metal balls filled with liquid. These balls contained metal flags (pennants) with the Soviet coat of arms. The plan was for these flags to be scattered on the Moon's surface when the spacecraft landed.
Launch and Journey
Luna 1 launched on January 2, 1959. It blasted off from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on a large rocket.
Why it Missed the Moon
The launch went well at first. However, the engineers on the ground made a small mistake. They sent a radio signal to turn off the rocket's engine a little too late.
Because the engine burned for too long, the rocket went faster than planned. It gained extra speed. This caused Luna 1 to miss the Moon by about 5,995 kilometres (3,725 mi).
Even though it missed, the mission achieved something amazing. It reached escape velocity. This is the speed needed to break free from Earth's gravity. On January 6, 1959, Luna 1 left Earth's orbit forever. It began to orbit the Sun, located between Earth and Mars.
Scientific Experiments
Luna 1 sent back important information about outer space. Scientists learned new things about the environment between Earth and the Moon.
The Artificial Comet
On January 3, 1959, the spacecraft did a special experiment. It released 1 kilogram (2.2 lb) of sodium gas into space. This created a large, glowing orange cloud behind the spacecraft.
This cloud acted like an artificial comet. It was very bright and could be seen from Earth over the Indian Ocean. Astronomers took photos of the glowing trail. This helped them track exactly where the spacecraft was located.
Discoveries in Space
Luna 1 made several key discoveries:
- It measured the solar wind for the first time. It found that the Sun sends out a strong stream of plasma particles.
- It studied the Van Allen radiation belt. It found that there are high-energy particles in the outer belt around Earth.
- It looked for a magnetic field around the Moon but did not find a strong one.
The batteries ran out of power on January 5, 1959. This happened when the probe was about 597,000 kilometres (371,000 mi) away from Earth. After that, scientists could no longer talk to the spacecraft.
Reaction and Legacy
At the time, the "Space Race" was happening between the United States and the Soviet Union. Some people in the West doubted that the Soviets had really launched the probe. However, scientists in the United States were eventually able to pick up signals from the spacecraft, proving it was real.
The mission was a big step forward for space exploration. It showed that humans could send objects beyond Earth. Later in 1959, another mission called Luna 2 successfully hit the Moon.
See also
 In Spanish: Mechta para niños
In Spanish: Mechta para niños
- Pioneer 4 – A similar American mission launched a few months later.
- List of missions to the Moon
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |