MATE (desktop environment) facts for kids
 |
|
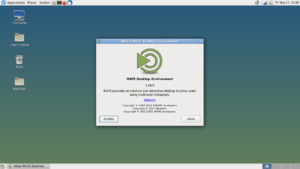
Fedora Linux with MATE version 1.26
|
|
| Developer(s) | Clement Lefebvre, Perberos, Stefano Karapetsas, et al. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 19, 2011 |
| Stable release | |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Unix-like, Unix |
| Type | Desktop environment |
| License | GPLv2+, LGPLv2+ |
MATE (pronounced MAH-tay) is a special kind of computer program. It creates the look and feel of your computer screen, like the background, icons, and menus. This is called a desktop environment. MATE is made from free and open-source software, which means anyone can use it, share it, and even change it. It works on computers that use Linux and other similar systems like Unix-like ones (for example, BSD and illumos).
Contents
What Does MATE Mean?
MATE is named after a plant from South America called yerba mate. People use this plant to make a special tea, also called mate. The name MATE is written in all capital letters. This is like how other free software desktop environments, such as KDE Plasma and LXDE, are named.
Later, people came up with a fun, longer name for MATE. They called it "MATE Advanced Traditional Environment." This is a recursive acronym, which means the first letter of each word spells out the name itself. It's a bit like the name GNU, which stands for "GNU's Not Unix!" Using a new name helped avoid confusion with other computer programs.
How MATE Started
MATE was created by a user named Perberos from Argentina. This person used a computer system called Arch Linux. MATE was started because many people did not like the changes in a program called GNOME 3. GNOME 3 had replaced its old-style taskbar with something new called GNOME Shell.
So, Perberos decided to "fork" GNOME 2. This means they took the old GNOME 2 code and started a new project with it. The goal of MATE was to keep the familiar look and feel of GNOME 2. It also aimed to continue improving its core programs and tools.
MATE was first announced on November 8, 2013. It became an official part of the Arch Linux community in January 2014.
MATE's Main Programs
MATE has many programs that help you use your computer. Many of these programs were originally part of GNOME. The MATE developers gave these programs new names. Most of the new names come from Spanish words.
Here are some of the main programs in MATE:
| Application name | Spanish translation | Original program | What it does |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atril | lectern | Evince | Lets you view documents |
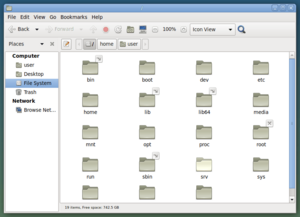
| Caja | box | GNOME Files (Nautilus) | Helps you manage your files |
| Engrampa | staple | Archive Manager (File Roller) | Helps you open and create compressed files |
| Eye of MATE | Eye of GNOME | Lets you view images | |
| MATE Calculator | GNOME Calculator | A calculator for your computer | |
| MATE Control Center | GNOME Control Center | Helps you change MATE desktop settings | |
| MATE System Monitor | GNOME System Monitor | Shows how your computer is using its resources | |
| MATE Terminal | GNOME Terminal | A program for typing commands to your computer | |
| marco | frame | Metacity | Manages how windows appear on your screen |
| Mozo | waiter | Alacarte | Helps you edit your computer's menus |
| Pluma | pen | Gedit | A simple program for writing text |
How MATE Is Developed
MATE works well with a modern program framework called GTK 3. The project gets help from important people. This includes Martin Wimpress, who leads the Ubuntu MATE project. The Linux Mint development team also supports MATE. They believe MATE is an important desktop environment, just like others. They are dedicated to helping it get better.
New features have been added to MATE's programs. For example, the Caja file manager now lets you undo and redo actions. It also helps you see differences when replacing files. MATE has also been updated to use newer technologies. This means it has moved away from older parts of its code.
One of the main goals for MATE developers is to offer a classic computer experience. But they also want to use the newest technologies. For example, MATE 1.20, released in February 2018, added support for HiDPI screens. These screens show very clear images. The GTK version was also updated to 3.22. In MATE 1.22, released in March 2019, many programs were updated. They moved from an older version of Python to a newer one. They also updated how programs talk to each other. Future versions of MATE will also support Wayland. This is a new way for computers to show graphics.
MATE Release History
MATE has been updated many times since it first started. Each new version brings improvements and new features.
| Date | Version |
|---|---|
| 2011-06-18 | Announced at Arch Linux forum |
| 2011-08-19 | Initial release |
| 2012-04-16 | 1.2 |
| 2012-07-30 | 1.4 |
| 2013-04-02 | 1.6 |
| 2014-03-04 | 1.8 |
| 2015-06-11 | 1.10 |
| 2015-11-05 | 1.12 |
| 2016-04-08 | 1.14 |
| 2016-09-21 | 1.16 |
| 2017-03-13 | 1.18 |
| 2018-02-07 | 1.20 |
| 2019-03-18 | 1.22 |
| 2020-02-10 | 1.24 |
| 2021-08-03 | 1.26 |
| 2024-02-12 | 1.28 |
Who Uses MATE?
Many different computer systems use MATE. The MATE website lists 27 different Linux distributions. These are like different versions of the Linux operating system. It also lists 5 Unix-like operating systems that support the MATE desktop environment. This shows that MATE is used by many people around the world.
See also
 In Spanish: MATE para niños
In Spanish: MATE para niños
- Budgie
- Cinnamon
- GNOME Flashback
- LXDE
- LXQt
- Xfce