Linux Mint facts for kids
 |
|
Linux Mint 22 "Wilma" using Cinnamon 6.2.7
|
|
| Company / developer | Clément Lefèbvre, Linux Mint Teams and community |
|---|---|
| OS family | Unix-like |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | 27 August 2006 |
| Latest stable release | |
| Available language(s) | Multilingual |
| Package manager | APT (dpkg) · Flatpak |
| Supported platforms | x86-64 · IA-32 (LMDE) |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux) |
| Userland | GNU |
| Default user interface | |
| License | Mainly GPL and other free software licenses, minor additions of proprietary software |
Linux Mint is a popular computer operating system. It is a type of Linux distribution, which means it is built using the Linux kernel. Linux Mint is mostly based on Ubuntu, another well-known Linux system. There is also a special version called Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE), which is based on Debian.
Linux Mint works on most modern computers. It was first released in 2006. People often like Linux Mint because it is easy to use. It also comes with many useful programs already installed. The main look and feel, called the desktop environment, is Cinnamon. However, you can also choose MATE or Xfce.
Contents
The Story of Linux Mint
Early Years: 2006 to 2013
Linux Mint started in 2006 with a test version called 'Ada'. This first version was based on Kubuntu. It used the KDE desktop.
Later, Linux Mint 2.0, named 'Barbara', switched to using Ubuntu as its main base. It used the GNOME desktop. More people started using Linux Mint after version 3.0, 'Cassandra', came out.
At first, Linux Mint released new versions twice a year. This was usually about a month after Ubuntu released its new versions. In 2008, Linux Mint started following Ubuntu's release schedule. Every fourth release was a Long Term Support (LTS) version. This meant it would get updates for a longer time.
In 2010, the Linux Mint team created Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE). This version was different because it was based directly on Debian. It did not rely on Ubuntu. LMDE was designed to get continuous updates. This meant users did not have to reinstall the system often.
Recent Developments: Since 2014
In 2014, the team announced that Linux Mint was no longer tied to Ubuntu's exact release schedule. This meant they could release new versions whenever they were ready.
In February 2016, the Linux Mint website faced a security issue. Hackers briefly changed download links for one version. They replaced it with a version that had harmful software. The hackers also got into the website's user forum. Linux Mint quickly took its servers offline. They then improved their website's security.
Starting with Linux Mint 18, some special versions were stopped. This was done to make it easier to manage the different versions.
Since Linux Mint 20, the main versions only work on 64-bit computers. This is because Ubuntu, which Linux Mint is based on, stopped supporting 32-bit computers. However, the Debian-based LMDE still supports older 32-bit processors.
What Linux Mint Offers
Linux Mint mainly uses free and open-source software. This means the software can be used, changed, and shared by anyone. Before version 18, some special software was included. This included things like drivers for hardware and codecs for playing MP3s and DVDs. Now, when you install Linux Mint, you get an option to install this extra software.
Linux Mint comes with many useful programs already installed. These include LibreOffice for documents, Firefox for browsing the web, and VLC media player for videos. You can get more programs using the Software Manager.
Linux Mint has a firewall to help keep your computer safe. It lets you control which connections are allowed. The main desktop environments, Cinnamon and MATE, support many different languages. You can even run some programs made for Microsoft Windows on Linux Mint. This is possible using a tool called Wine.
You can choose from different desktop environments when you install Linux Mint. The main ones are Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce. You can also install other desktop environments later.
Linux Mint uses a security feature called AppArmor. This helps protect your computer by controlling what programs can do. Most of the software for Linux Mint is made using the Python programming language. The code is available for anyone to see and use on GitHub.
Software Made by Linux Mint
The Linux Mint team creates its own special software. These tools help make the operating system easy to use.
Cinnamon Desktop
Cinnamon is the main desktop environment for Linux Mint. It was created by the Linux Mint team. It first appeared as an add-on for Linux Mint 12. Since Linux Mint 13, it has been the default desktop.
Hypnotix
Hypnotix is a program for watching IPTV. IPTV lets you watch TV over the internet. The Mint team developed Hypnotix. The first test version was released in 2020.
MintTools: Helpful Programs
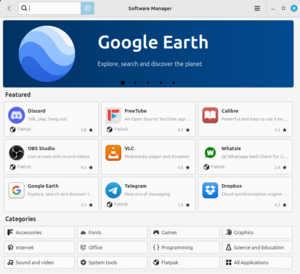
- Software Manager (mintInstall): This tool helps you find and install new programs. You can also remove programs you don't need. It can get software from different places, including Flatpak.
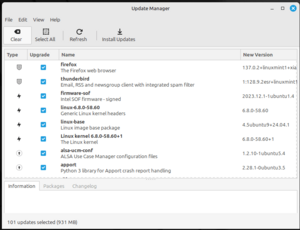
- Update Manager (mintUpdate): This tool helps you keep your system updated. It makes sure you get the latest security fixes and improvements. It also helps prevent problems when installing updates.
- Main Menu (mintMenu): This is the menu you use to find programs and settings. It is designed for the MATE desktop.
- Backup Tool (mintBackup): This program lets you save copies of your important files. You can use it to restore your data if something goes wrong.
- USB Image Writer/USB Stick Formatter (mintStick): This tool helps you put a Linux Mint installation onto a USB drive. It can also format (erase) USB drives.
- System Reports (mintReport): This tool helps you see and manage reports when programs crash. It can also suggest actions, like installing drivers.
Different Versions of Linux Mint
Linux Mint comes in several versions. Most are based on Ubuntu. They offer different desktop environments. There is also the special Debian-based edition.
Ubuntu-Based Editions
Since Linux Mint 13, there are two main versions. One uses Linux Mint's own Cinnamon desktop. The other uses the MATE desktop. There is also a version that uses the Xfce desktop. All three of these versions are released at the same time.
The KDE edition was stopped after Linux Mint 19. However, older KDE versions were supported for a while.
LMDE: Debian-Based Edition
The Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE) uses Debian as its base. This is different from the other versions that use Ubuntu. LMDE aims to look and feel the same as the Ubuntu-based versions.
The first LMDE version (LMDE 1) received updates in 'Update Packs'. This meant users did not have to reinstall the system often. LMDE 2, called 'Betsy', was released in 2015. It was based on Debian Jessie. It also got automatic updates for Mint's own software. LMDE 2 was available with both MATE and Cinnamon desktops.
LMDE 3, named 'Cindy', came out in 2018. It was based on Debian Stretch and only came with Cinnamon. The newest version of LMDE is version 6, called 'Faye'. It was released in 2023 and is based on Debian Bookworm.
How Linux Mint is Developed
Linux Mint is developed by a community of users and developers. People who use the system can donate money or become sponsors. Linux Mint listens to its users to decide what to work on next. The official blog often asks users for their ideas and opinions.
Users can also help by translating the operating system into different languages. They can also report any problems or bugs they find. Most of the development work is done using the Python programming language. The code is organized online using GitHub.
Release Schedule
Linux Mint does not have fixed release dates. Instead, new versions are released "when ready". This means they can come out earlier if everything is finished. They can also be delayed if important problems are found.
Every version of Linux Mint has a number and a special code name. The code names are usually feminine first names ending in 'a'. The first letter of the name goes up with each major version. For example, version 17 was 'Qiana', and version 18 was 'Sarah'.
In 2014, with Linux Mint 17, the team changed its release plan. All future versions would use a Long Term Support (LTS) version of Ubuntu as their base. This plan was set to continue until 2016.
X-Apps
In 2016, the Linux Mint team created the X-Apps. This is a collection of applications designed to work well across different desktop environments. These apps often have a traditional look. For example, they use a menu bar instead of a header bar. The team wanted to make sure these apps worked everywhere.
The Linux Mint team is now working to make X-Apps a separate project. This means they will be developed independently from Linux Mint itself. Many of these X-Apps are based on parts of GNOME Core Applications.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Linux Mint para niños
In Spanish: Linux Mint para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |