Ubuntu facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Ubuntu |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
Ubuntu 25.10 "Questing Quokka"
|
|
| Developer | Canonical Ltd. |
| OS family | Linux (Unix-like), Debian-based |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open-source |
| Initial release | 20 October 2004 |
| Latest release | Regular: Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1571: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). / 9 October 2025 LTS: Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1571: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). / 7 August 2025 |
| Repository |
|
| Marketing target | Cloud computing, personal computers, servers, supercomputers, IoT |
| Available in | More than 55 languages by LoCos |
| Update method | Software Updater, Ubuntu Software, apt |
| Package manager | GNOME Software, dpkg (APT), Snap – graphical front-end: Snap Store |
| Supported platforms | |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux kernel) |
| Userland | uutils (formerly GNU) |
| Default user interface |
GNOME |
| License | Free software + some proprietary device drivers, excluding trademarks |
Ubuntu is a popular computer operating system. It is based on Linux and is mostly made of free and open-source software. This means many people can use, change, and share it. A company called Canonical Ltd. and a large community of people help create Ubuntu.
The name "Ubuntu" comes from an African idea. It means "humanity to others" or "I am what I am because of who we all are." This name shows how important community and working together are to Ubuntu.
Contents
- Discovering Ubuntu: A Friendly Computer System
- The Story of Ubuntu's Beginning
- Key Features of Ubuntu
- Keeping Ubuntu Safe
- Getting Ubuntu on Your Computer
- How Software is Organized in Ubuntu
- Extra Software and Apps
- Ubuntu Versions and Updates
- Different Kinds of Ubuntu
- Ubuntu Community: LoCos
- Computers with Ubuntu
- Ubuntu and Windows Working Together
- Images for kids
- See also
Discovering Ubuntu: A Friendly Computer System
Ubuntu is a special kind of computer operating system. Think of it like the brain of your computer. It helps you run programs, browse the internet, and do many other tasks. Ubuntu is built on something called Linux, which is a very powerful and flexible computer core.
Ubuntu is developed by a British company called Canonical. Many people from all over the world also help make it better. They work together to create different versions of Ubuntu. These include versions for desktop computers, servers (which are powerful computers that store websites and data), and even small devices like those used in smart homes.
The Story of Ubuntu's Beginning
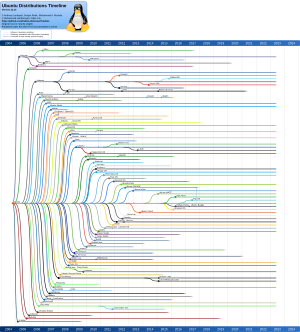
Ubuntu started in April 2004. A person named Mark Shuttleworth invited some computer experts to London. They wanted to create a new, easy-to-use computer system. Mark chose the name "Ubuntu" because of its meaning about community. He wanted everyone to be able to use it.
To help the project, Mark Shuttleworth created Canonical Ltd. This company hired developers to work on Ubuntu. The first version of Ubuntu was released in October 2004. It was called "Warty Warthog."
In 2005, the Ubuntu Foundation was created. Its goal is to make sure Ubuntu continues to be supported and developed. This helps keep Ubuntu available for everyone. Over time, Ubuntu's look has changed. It used to have a desktop called GNOME 2, then Unity, and now it uses GNOME 3 again.
Key Features of Ubuntu
Ubuntu uses a lot of the same building blocks as Debian, another Linux system. When you install Ubuntu, it comes with useful programs. These include the Firefox web browser and basic tools for your computer.
You can find many more programs in the built-in Ubuntu Software store. This store lets you easily install new apps. Ubuntu also supports special "snap packages" and "Flatpaks." These allow you to install software that works on many different Linux systems.
All the main programs that come with Ubuntu are free software. This means you can use, share, and change them. Some parts, like certain hardware drivers, might not be free. These are needed to make Ubuntu work with all kinds of computer parts.
Long-Term Support (LTS) Versions
Ubuntu releases new versions every six months. Every two years, a special version called a Long-Term Support (LTS) release comes out. LTS versions get updates and support for five years. This makes them very stable and reliable for a long time.
Keeping Ubuntu Safe
Ubuntu is designed to be safe from the start. Your programs usually run with limited permissions. This stops them from accidentally changing important system files. When you need to do something important, like install a new program, Ubuntu asks for your password. This uses a tool called sudo to give you temporary power. It helps keep your computer secure.
Ubuntu also has a built-in firewall. This acts like a guard for your computer's network connections. It helps block unwanted access from the internet. You can easily control this firewall to protect your computer. Ubuntu also lets you encrypt your entire hard drive. This means your files are scrambled and can only be read with a special key, keeping your information private.
Getting Ubuntu on Your Computer
To run Ubuntu, your computer needs at least a 2 GHz dual-core processor, 4 GB of RAM, and 25 GB of free space. If your computer is older or less powerful, there are other Ubuntu versions like Lubuntu and Xubuntu. These versions use less memory and processing power.
You can try or install Ubuntu using a "live image." This is a special file you can put on a DVD or a USB flash drive. When you start your computer from this DVD or USB, you can try Ubuntu without installing it. If you like it, you can then install it onto your computer's hard drive. This process does not change your computer until you choose to install.
How Software is Organized in Ubuntu
Ubuntu organizes its software into different groups. This helps people understand what kind of software it is and how much support it gets.
| Free software | Non-free software | |
|---|---|---|
| Officially supported by Canonical | Main | Restricted |
| Community supported/Third party | Universe | Multiverse |
- Free software means you can use, change, and share the program.
- Non-free software means there are more rules about how you can use or share it.
The Main category has software that Canonical officially supports. The Restricted category has important non-free software, like some device drivers. These drivers help your computer hardware work with Ubuntu. The Universe and Multiverse categories have software supported by the community.
Personal Package Archives (PPAs)
A Personal Package Archive (PPA) is like a special online folder. It lets developers share their software with Ubuntu users. This makes it easy to get new or updated programs that are not yet in the main Ubuntu software store.
Extra Software and Apps
You can find even more software for Ubuntu. The ubuntu-restricted-extras package adds support for things like playing DVDs and many common audio and video files. It also includes popular fonts.
Many other apps and games are available through the Ubuntu Software store and the Snap Store. You can find games like Minecraft and other useful programs there.
Ubuntu Versions and Updates
Ubuntu releases new versions every six months. Each standard version gets nine months of free updates and security fixes.
Every two years, a Long-Term Support (LTS) version is released. These LTS versions get five years of free support. You can even get extended support for up to ten years with Ubuntu Pro, which is free for personal use.
Ubuntu version numbers show the year and month it was released. For example, Ubuntu 4.10 came out in October 2004. Each release also has a fun code name, like "Bionic Beaver" or "Jammy Jellyfish."
| Version | Code name | Release date | General support until | Security support (ESM) until |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.04 LTS | Xenial Xerus | 2016-04-21 | 2021-04-30 | 2026-04 |
| 18.04 LTS | Bionic Beaver | 2018-04-26 | 2023-05-31 | 2028-04 |
| 20.04 LTS | Focal Fossa | 2020-04-23 | 2025-05-29 | 2030-04 |
| 22.04 LTS | Jammy Jellyfish | 2022-04-21 | 2027-06-01 | 2032-04 |
| 24.04 LTS | Noble Numbat | 2024-04-25 | 2029-05 | 2034-04 |
| 25.04 | Plucky Puffin | 2025-04-17 | 2026-01 | - |
| 25.10 | Questing Quokka | 2025-10-09 | 2026-07 | - |
|
Legend:
Old version
Older version, still maintained
Latest version
Future release
|
||||
Different Kinds of Ubuntu
Ubuntu has many different versions, often called "flavors." Each flavor offers a slightly different look or set of tools. This means you can choose the one that best fits your needs or computer.
- Ubuntu Desktop is the most common version. It's great for everyday use on laptops and desktop computers.
- Some flavors, like Lubuntu and Xubuntu, are designed for older computers. They use less power and memory.
Official Ubuntu Flavors
These are the versions officially recognized and supported by Ubuntu. They all share the same main software but have different desktop styles.
| Distribution | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Edubuntu | Edubuntu is made for schools and learning. It comes with many educational programs for all ages. | |
| Kubuntu | Kubuntu uses the KDE desktop, which has a different look and feel than standard Ubuntu. | |
| Lubuntu | Lubuntu is a very lightweight version. It's perfect for older computers or if you want a super-fast system. | |
| Ubuntu Core | Ubuntu Core is for small, smart devices and robots. It doesn't have a graphical screen and uses special "Snap" packages. | |
| Ubuntu Budgie | Ubuntu Budgie uses the Budgie desktop, known for being modern and easy to use. | |
| Ubuntu Cinnamon | This flavor uses the Cinnamon desktop, which is also found in Linux Mint. | |
| Ubuntu Kylin | Ubuntu Kylin is designed for users in China, with special features for that region. | |
| Ubuntu MATE | Ubuntu MATE uses the MATE desktop. It looks and feels like older computer desktops, which some people prefer. | |
| Ubuntu Server | Ubuntu Server is for powerful computers that run websites or store lots of data. It doesn't have a graphical desktop by default, making it very efficient. It supports many different computer architectures. | |
| Ubuntu Studio | Ubuntu Studio is for creative people. It includes many free programs for making music, videos, and graphics. | |
| Ubuntu Unity | Ubuntu Unity uses the Unity 7 desktop, which was once the main desktop for Ubuntu. | |
| Xubuntu | Xubuntu uses the Xfce desktop. It's known for being fast and light, great for older or less powerful computers. | |
Some official Ubuntu versions, like Gobuntu and Ubuntu Touch, are no longer actively developed by Canonical. However, volunteers often continue to maintain them.
Unofficial Ubuntu Flavors
These are other Ubuntu versions that are still growing. They hope to become officially recognized in the future.
Ubuntu Community: LoCos
Ubuntu has a worldwide community of users and helpers. These groups are called "LoCos," which stands for Local Communities. LoCos help new users, organize events, and promote Ubuntu in their areas. They are a big part of what makes Ubuntu special.
Computers with Ubuntu
Many computer makers offer computers with Ubuntu already installed. Companies like Dell, Lenovo, and HP sometimes sell laptops and desktops with Ubuntu. This gives people an alternative to computers that come with Windows. Smaller companies also sell computers with Ubuntu.
Ubuntu and Windows Working Together
If you use Windows, you can still try Ubuntu. Many Windows programs can run on Ubuntu using a tool called Wine. For gamers, Steam has a special tool called Proton that helps many Windows games run on Ubuntu.
You can also run Windows inside Ubuntu using a virtual machine. This lets you have both operating systems running at the same time. Sharing files between Ubuntu and Windows is easy with a tool called Samba.
Microsoft has also created something called the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). This allows you to run many Linux tools and even graphical Linux apps directly on Windows. It's a great way for developers to use both systems together.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ubuntu para niños
In Spanish: Ubuntu para niños
- Comparison of Linux distributions