Mainland China facts for kids
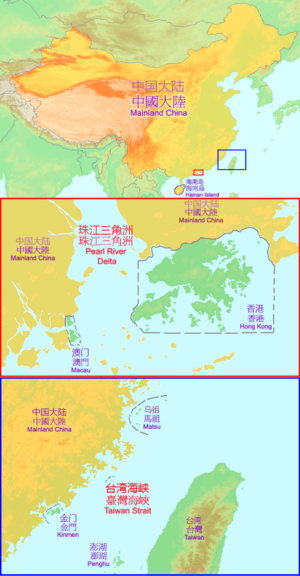
Mainland China is the main part of China. It's the large land area that makes up most of the country. When people talk about Mainland China, they usually mean the parts controlled by the People's Republic of China.
This term helps us understand that some areas are not included. For example, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau are not considered part of Mainland China. These places have different histories and ways of being governed.
Contents
What is Mainland China?
Mainland China is the biggest part of the country. It includes the land on the continent of Asia. It also includes many small islands very close to the mainland. The largest island that is part of Mainland China is Hainan.
Areas Not Included
The term "Mainland China" helps to make a clear difference. It does not include several places:
- Taiwan: This island is governed separately by the Republic of China.
- Kinmen and Matsu: These are small islands near Taiwan.
- Pescadores: These islands are also near Taiwan.
- Hong Kong: This city is a special administrative region.
- Macau: This city is also a special administrative region.
These places are part of China in a broader sense. However, they have their own governments or special rules. This is why they are not called "Mainland China."
A Brief History of Mainland China
The history of this region is long and interesting. It helps explain why some areas are separate today.
The Qing Dynasty
Long ago, during the Qing Dynasty, China was a huge empire. This empire included all of what we now call Mainland China. It also included Taiwan, Hong Kong, Macau, and even Mongolia.
However, some parts of this empire were later taken over by other countries.
- Taiwan was controlled by Japan.
- Hong Kong was controlled by the British.
- Macau was controlled by the Portuguese.
Changes After the Empire
After the Qing Dynasty ended, China went through many changes. In 1945, Taiwan became part of China again. This was under the government called Nationalist China, also known as the Republic of China.
Later, a big change happened. The Communists took control of most of China. This new government was called the People's Republic of China. The Nationalists then moved to Taiwan. They kept control of Taiwan and a few nearby islands like Kinmen and Matsu.
Mongolia also became an independent country. This meant it was no longer part of China.
Hong Kong and Macau Return
Much later, Hong Kong and Macau were returned to China. This happened in the late 1990s. However, they were given a special status. They became "special administrative regions."
This means they have their own laws and systems. This idea is called "one country, two systems." Because of this, Hong Kong and Macau are still not considered part of Mainland China. They are unique areas within China.
See also
 In Spanish: China continental para niños
In Spanish: China continental para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |

