Malwa Sultanate facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Malwa Sultanate
Mālwā Salṭanat
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1401–1562 | |||||||||
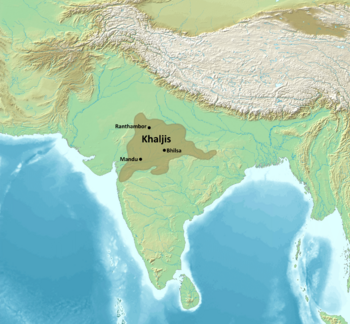
Malwa Sultanate at their height under the Khalji dynasty.
|
|||||||||
| Capital | Dhar (initially) Mandu |
||||||||
| Common languages | Persian (official) | ||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | ||||||||
| Sultan | |||||||||
|
• 1401 - 1406
|
Dilawar Khan (first) | ||||||||
|
• 1555 - 1562
|
Baz Bahadur (last) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
|
• Established
|
1401 | ||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1562 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||||
The Malwa Sultanate was a powerful kingdom in India during the Middle Ages. It existed from 1401 to 1562. This kingdom was located in the Malwa region. Today, this area covers parts of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Dilawar Khan started the Malwa Sultanate in 1401. He made Malwa an independent state. This happened after Timur's invasion weakened the Delhi Sultanate.
Later, in 1519, a large part of the Sultanate was briefly controlled by Rana Sanga of Mewar. He put his trusted helper, Medini Rai, in charge. In 1562, the Mughal Empire took over the Sultanate. Its last ruler was Baz Bahadur. Malwa then became a province (called a subah) of the Mughal Empire.
Most of the time, the Malwa Sultanate was ruled by Afghan or Turco-Afghan families.
Contents
How the Malwa Sultanate Began
Dilawar Khan was a governor for the Delhi Sultanate. He was either Afghan or of Turkic and Afghan background. Dilawar Khan stopped paying taxes to Delhi after 1392.
In 1437, Dilawar Khan's family, the Ghurid dynasty, was overthrown. Mahmud Khan took over. He was from the Khalji family, who were also Turko-Afghan.
After the Khaljis, Shujaat Khan ruled Malwa. He was an Afghan governor under Sher Shah Suri. His son, Baz Bahadur, declared Malwa independent in 1555. He ruled until the Malwa Sultanate ended.
Key Events in Malwa's History

The Ghurid Dynasty (1401–1436)
Dilawar Khan Ghuri founded the Malwa Sultanate. He was a governor for the Delhi Sultanate. He became independent in 1392. However, he officially became king in 1401.
At first, Dhar was the capital city. Soon, the capital moved to Mandu. Mandu was renamed Shadiabad, meaning "the city of joy."
After Dilawar Khan died, his son Alp Khan became king. He took the title Hoshang Shah.
The Khalji Dynasty (1436–1531)
The Ghurid dynasty was replaced by Mahmud Shah I. He declared himself king on May 16, 1436. The Khalji dynasty ruled Malwa until 1531.
The Sultanate became much weaker after 1519. This was due to repeated attacks by the Rajput chief Rana Sanga of Mewar.
Mahmud Khalji I was followed by his oldest son, Ghiyas-ud-Din. Ghiyas-ud-Din's last years were difficult. His two sons fought for the throne. Nasir-ud-Din won and became king on October 22, 1510.
The last Khalji ruler was Mahmud Shah II. He surrendered to Bahadur Shah. Bahadur Shah was the sultan of Gujarat. This happened after the fort of Mandu fell on May 25, 1531.
Gujarat Takes Over (1531–1537)
From 1518, Mahmud Shah II was under the control of the Gujarat Sultan. After Mahmud Shah II surrendered, Gujarat ruled Malwa from 1531 to 1537.
The Mughal emperor Humayun captured Malwa for a short time in 1535–36. But the Gujaratis soon took it back. They remained loyal to Bahadur Shah until 1542.
Malwa's Last Rulers (1537–1562)
In 1537, Qadir Shah took control of part of the old kingdom. He was a former officer of the Khalji dynasty.
But in 1542, Sher Shah Suri conquered Malwa. He defeated Qadir Shah and made Shuja'at Khan the new governor. Shuja'at Khan's son, Baz Bahadur, declared himself independent in 1555.
In 1561, Emperor Akbar sent the Mughal army to Malwa. The army was led by Adham Khan and Pir Muhammad Khan. They defeated Baz Bahadur in the Battle of Sarangpur on March 29, 1561. This led to the Mughal conquest of Malwa.
Akbar soon called Adham Khan back. Pir Muhammad took command. Pir Muhammad attacked Khandesh. But he was defeated by a group of three rulers. These were Miran Mubarak Shah II of Khandesh, Tufal Khan of Berar Sultanate, and Baz Bahadur. Pir Muhammad died while retreating.
The combined army chased the Mughals out of Malwa. Baz Bahadur got his kingdom back for a short time. In 1562, Akbar sent another army. This army was led by Abdullah Khan. They finally defeated Baz Bahadur. He fled to Chittor.
Malwa then became a top-level province (a subah) of the Mughal Empire. Its main city was Ujjain. Abdullah Khan became its first governor.
Art and Culture
Many amazing illustrated books were made during the Sultanate's time. One example is an illustrated book called Kalpa Sutra (1439). It was made in Mandu during the rule of Mahmud Shah I. You can see it today in the National Museum, Delhi.
Another interesting book is the Nimat Nama. This book is about the art of cooking. It has many pictures of Ghiyas-ud-Din Shah. Other important illustrated books from this time include the Miftah-ul-Fuzala, the Bustan (1502), and the Aja'ib-us-San'ati (1508).
Rulers of Malwa
The Ghurid Dynasty (1401–1436)
- Dilawar Khan (1401–1406)
- Husam-ud-Din Hoshang Shah (1406–1435)
- Taj-ud-Din Muhammad Shah I (1435–1436)
The Khalji Dynasty (1436–1531)
- Ala-ud-Din Mahmud Shah I (1436–1469)
- Ghiyas-ud-Din Shah (1469–1500)
- Nasir-ud-Din Shah (1500–1510)
- Shihab-ud-Din Mahmud Shah II (1510–1531)
Other Rulers and Periods
- Medini Rai (as a helper of Mewar's ruler Maharana Sanga) (1519–1528)
- Bahadur Shah (the sultan of Gujarat) (1531–1537)
- Humayun (Mughal emperor) (1535–1540)
- Qadir Shah (1540–1542)
- Shuja'at Khan (governor for Sher Shah Suri) (1542–1555)
- Baz Bahadur (1555–1562)
Images for kids
See Also
- Malwa
- Mandu
- List of Sultans of the Malwa Sultanate
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |






