Mechanical efficiency facts for kids
In mechanical engineering, mechanical efficiency is a way to measure how well a machine works. It compares the power put into a machine to the power that comes out of it.
A machine is a device that changes force or motion. When a machine works, force is applied at one point to move a load at another point. The goal is to transfer as much energy as possible from the input to the output.
Mechanical efficiency is usually written as a number between 0 and 1. It can also be written as a percentage up to 100%.
Contents
Understanding Mechanical Efficiency
How Machines Use Power
Every machine needs an input of energy to work. This is called the power input. The machine then does work on a load, which is called the power output.
- Input: The force applied to the machine multiplied by how fast the input point moves.
- Output: The force the machine puts on the load multiplied by how fast the load moves.
The Efficiency Formula
Engineers use math to calculate efficiency. They often use the Greek letter eta (η) to represent it. The formula is a simple dimensionless ratio, which means it does not have units like meters or seconds.
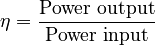
Because of the conservation of energy, a machine cannot create new energy. It also cannot output more power than was put into it. This means the efficiency number can never be higher than 1 (or 100%).
Friction and Energy Loss
Why Real Machines Are Not Perfect
In the real world, no machine is perfect. All machines have moving parts that rub against each other. This creates friction.
Friction turns some of the input energy into heat. This heat energy is usually lost and cannot be used to do work. Because of this loss, the power output is always less than the power input.
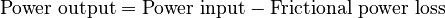
Ideal Machines
Scientists sometimes imagine a machine that has zero friction. This is called an ideal machine.
- An ideal machine would not lose any energy to heat.
- Its power output would be exactly the same as its power input.
- Its efficiency would be exactly 1, or 100%.
While ideal machines do not exist in real life, they help engineers understand how to make real machines better.
Other Types of Efficiency
Different types of machines use different terms for efficiency. For example, when looking at hydropower turbines (machines that get energy from moving water), the efficiency is called hydraulic efficiency.
See also
- Mechanical advantage
- Thermal efficiency
- Electrical efficiency
- Internal combustion engine
- Electric motor
- Velocity ratiohe:נצילות מכנית
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |

