Muon facts for kids
The muon is a tiny particle, even smaller than an atom! It's a basic building block of the universe, also known as an elementary particle. Muons have a negative electric charge, just like an electron. Their special symbol is "μ-". Muons belong to a family of particles called leptons.
A muon is quite similar to an electron, but it's much heavier – about 200 times heavier! Unlike electrons, muons don't last forever. They are unstable and quickly change into other particles. A muon lives for a very short time, on average about 2.2 micro-seconds, which is 0.0000022 seconds. Scientists even have a special name for a possible "super-muon" called a "smuon."
Contents
How Are Muons Created?
Muons are made in different ways, both naturally and by scientists.
Making Muons in Labs
Scientists can create muons using special machines called particle accelerators. These machines smash tiny particles together with a lot of energy. To make muons, the accelerators need energy levels above 105.7 MeV.
Muons from Space
Muons are also constantly being made in Earth's atmosphere by Cosmic rays. These rays are high-energy particles that come from space, often from the Sun. Here's how it happens:
- Powerful photons (light particles) from cosmic rays crash into air molecules high above us.
- This collision creates new particles called pions.
- These pions are unstable and quickly break down, or undergo atomic decay. When they decay, they turn into neutrinos and muons.
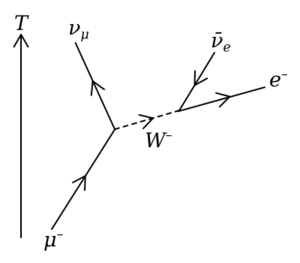
What Happens When Muons Decay?
Muons are unstable, meaning they don't last long. They are heavier than electrons and neutrinos but lighter than most other particles. Muons decay, or break down, into other particles. This process happens through something called the "weak interaction," which is one of the fundamental forces of nature.
When a muon decays, it always produces at least three new particles:
- An electron (which has the same negative charge as the original muon).
- An electron-type antineutrino.
- A muon-type neutrino.
This is the most common way a muon decays. Sometimes, other particles that have no charge or spin might also be created, like a pair of photons.
Antimuons are like the opposite version of muons. They have a positive charge. When an antimuon decays, it usually turns into a positron (which is like a positive electron), an electron-type neutrino, and a muon-type antineutrino.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Muon para niños
In Spanish: Muon para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |