No. 2 Squadron RAAF facts for kids
Quick facts for kids No. 2 Squadron RAAF |
|
|---|---|

No. 2 Squadron's crest
|
|
| Active | 1916–1919 1922 1937–1982 2000–current |
| Country | Australia |
| Branch | Royal Australian Air Force |
| Role | Airborne Early Warning and Control |
| Part of | No. 42 Wing, Surveillance & Response Group |
| Base | RAAF Base Williamtown |
| Motto(s) | Consilio et manu ("To Advise and to Strike") |
| Engagements | World War I
World War II Malayan Emergency |
| Decorations | Presidential Unit Citation (United States) Vietnam Gallantry Cross Unit Citation (South Vietnam) USAF Outstanding Unit Commendation (United States) |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders |
Oswald Watt (1916–18) Alan Charlesworth (1939) Peter Raw (1953–55) |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Electronic warfare |
Boeing 737 AEW&C "Wedgetail" |
No. 2 Squadron is a special unit of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). It is based at RAAF Base Williamtown, which is near Newcastle, New South Wales.
Since it was formed in 1916, this squadron has flown many different types of aircraft. These include fighters, bombers, and planes for Airborne Early Warning & Control (AEW&C).
During World War I, the squadron fought on the Western Front. They flew missions to attack enemy ground forces. After the war, the squadron was temporarily closed in 1919.
It was briefly restarted in 1922, then closed again. In 1937, it was reformed for good. During World War II, it was a bomber unit in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II.
Later, with English Electric Canberra jets, it fought in the Malayan Emergency and the Vietnam War. The squadron was closed again in 1982 when the Canberra jets were retired.
In 2000, No. 2 Squadron was reformed to fly the Boeing 737 AEW&C "Wedgetail" aircraft. One of these planes was sent to the Middle East in 2014. This was part of Australia's help in the fight against ISIS.
Contents
History of No. 2 Squadron
World War I Missions
No. 2 Squadron was created on 20 September 1916. It was part of the Australian Flying Corps (AFC). The unit was formed in Kantara, Egypt. Most of its members came from Australian Light Horse units.
Soon after forming, the squadron moved to the United Kingdom. They trained there from February to September 1917. They were given Airco DH.5 fighter planes. To avoid confusion, the British called them "No. 68 Squadron RFC." However, the Australians always used the AFC name.
In late September 1917, the squadron flew to St Omer, France. They then moved to Baizieux. A month later, they began their first combat missions on the Western Front. Their first big action was during the Battle of Cambrai in November and December. They attacked German trenches from low altitudes. This caused them to suffer many losses.
On 22 November, the squadron shot down its first German aircraft. This happened during a ground attack mission. After this, they shot down several more German planes. In December, the squadron stopped operations to get new Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.5a fighters. In January 1918, they moved to Savy. The next month, they had their first victories with the new planes.
In early 1918, Germany launched a big attack called the Spring Offensive. The squadron had to move its airfields back as German forces advanced. They moved to Bertangles, La Bellevue, Fouquerolles, and then Liettres. They supported the French during the Marne offensive.
The squadron flew many missions during this time. They fought in air-to-air battles and attacked German ground forces. After the German attack stopped, the Allies launched their own offensive. The squadron attacked German airfields and retreating troops. They moved three more times in October to keep up with the advance. By November, they were based at Pont-a-Marq.
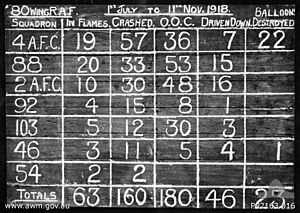
After the war ended, the squadron returned to the UK in March 1919. They were disbanded on 6 May, and their members went back to Australia. During the war, No. 2 Squadron had 18 flying aces. These pilots shot down many enemy planes. The squadron destroyed 94 enemy aircraft. They lost 25 personnel and had eight wounded.
No. 2 Squadron in World War II
In 1922, No. 2 Squadron was briefly reformed. It was part of the new Royal Australian Air Force. But it was closed again a few months later. It was reformed again on 3 May 1937 at Laverton.
When World War II started, the squadron flew Avro Anson planes. They patrolled the seas and protected ships off Australia's east coast. In May and June 1940, they received Lockheed Hudson planes.
In December 1941, the squadron moved to Darwin, Northern Territory. They continued their sea patrols. They also sent small groups of planes to islands north of Australia, like Ambon.
After Japan entered the war, the squadron bombed Japanese ships and bases. They damaged a Japanese ship on 8 December. But they also suffered heavy losses early on. In early 1942, their groups on the islands returned to Australia. This was because Japanese forces were advancing.
The squadron continued its missions from Australia. They bombed Japanese ships and bases on islands like Timor and Ambon. For their brave service, the squadron received a US Presidential Unit Citation.
From 1942 to 1943, the squadron kept flying missions with their Hudsons. They also dropped supplies for Australian forces fighting on Timor. In late 1943, they started training on the Bristol Beaufort plane. They used it briefly before switching to the North American B-25 Mitchell in May 1944.
They restarted combat missions in late June. They focused on attacking enemy ships and airfields. Late in the war, No. 2 Squadron moved to Balikpapan in Borneo. They dropped supplies to Allied troops in Japanese prisoner-of-war camps. After the war ended, they helped with transport duties. The squadron returned to Australia in December 1945. It was disbanded in May 1946. During the war, 176 squadron members were killed.
Cold War Operations
After World War II, the squadron was briefly reformed in 1947. It was a communications squadron. In 1948, it became No. 34 Squadron. Another unit, No. 21 Squadron, became No. 2 Squadron. This new No. 2 Squadron flew Avro Lincoln bombers.
In 1953, the squadron received GAF Canberra jets. In 1958, they moved to RAAF Butterworth in Malaysia. They took over from No. 1 Squadron RAAF during the Malayan Emergency. The squadron bombed communist forces. After the conflict, they stayed in Malaysia during the Confrontation.
In April 1967, eight Canberras were sent to South Vietnam. This was part of Australia's help in the Vietnam War.
The unit was based at Phan Rang Air Base. It became part of the United States Air Force 35th Tactical Fighter Wing. From April 1967 to June 1971, the Canberras flew about 12,000 missions. They mostly flew low-level daylight attacks. The squadron was very successful. They dropped over 76,000 bombs. They were credited with destroying many enemy structures and personnel.
On 24 April 1969, a squadron aircraft responded to a distress call. It bombed a site in Cambodia where US special forces were trapped. This was against operational orders.
During their time in Vietnam, two squadron members were killed. Two others died from illness, and three from accidents. Two Canberras were shot down in 1970 and 1971. One was hit by a missile, but the crew safely escaped. Another was lost near the Laos border. The crew of this plane, Flying Officer Michael Herbert and Pilot Officer Robert Carver, were missing in action. Their plane's wreckage was found in 2009, and their remains were returned to Australia.
The squadron received two awards for its service in Vietnam. These were the Vietnam Gallantry Cross Unit Citation and a United States Air Force Outstanding Unit Commendation. The squadron's planes used the callsign "Magpie" in Vietnam. This was because of the squadron's emblem.
The squadron returned to Australia in 1971. They had been overseas for 13 years. After Vietnam, No. 2 Squadron was based at Amberley. They briefly returned to bombing training. But in later years, their Canberra bombers were used for target towing. They also took survey photos for mapping Australia and other places. These included Papua New Guinea and the Cocos and Christmas Islands. In July 1982, the squadron was disbanded as the Canberra bombers were retired.
Recent Activities
No. 2 Squadron was reformed in January 2000. It now operates Boeing 737 Airborne Early Warning & Control (AEW&C) aircraft. These planes were bought as part of Project Wedgetail. The squadron operates from RAAF Base Williamtown and RAAF Base Tindal.
On 26 November 2009, the RAAF received the first two of six Boeing 737s. By the end of 2010, the squadron began training. In 2011, they took part in Exercise Talisman Sabre with US and Australian forces.
The squadron is part of the Surveillance & Response Group's No. 42 Wing. This group is in charge of the RAAF's AEW&C abilities.
On 14 September 2014, the Australian government sent one of the squadron's Boeing 737s to Al Minhad Air Base in the United Arab Emirates. This was part of a group of countries fighting Islamic State forces in Iraq. The aircraft started its missions in Iraq on 1 October.
In July 2023, the Australian Government announced another deployment. A Wedgetail aircraft and up to 100 personnel will go to Germany for six months starting in October. This is part of Australia's help after the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The aircraft will help protect supplies going to Ukraine.
Aircraft Used by No. 2 Squadron
| Type | Origin | Class | Role | Introduced | Retired | Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D.H.5 | UK | biplane | fighter | 1916 | 1917 | 80 | First Australian fighter plane. |
| S.E.5a | UK | biplane | fighter | 1918 | 1919 | ||
| Anson | UK | prop | maritime patrol | 1937 | 1940 | ||
| Hudson | USA | prop | patrol bomber | 1940 | 1943 | ||
| Beaufort | UK | prop | torpedo bomber | 1943 | 1944 | ||
| B-25 Mitchell | USA | prop | bomber | 1944 | 1946 | ||
| Lincoln | UK | prop | heavy bomber | 1947 | 1953 | ||
| Canberra | AUS | jet | bomber | 1953 | 1982 | ||
| E-7A Wedgetail | USA | jet | AEW&C | 2009 | Active |