North–South divide facts for kids
The North–South divide is a way to talk about the big differences between countries in the northern and southern parts of the world. It mainly looks at how rich or poor countries are, and how developed their economies are.
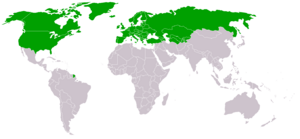
Generally, the 'North' includes richer, more developed countries like those in Europe and North America. The 'South' usually refers to developing countries in places like Africa, Latin America, and Asia. Many powerful countries, like most of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and all members of the G8 group, are considered part of the 'North'.
Contents
What is the North-South Divide?
The North–South divide is a term used in geography and economics. It helps us understand the differences in economic development across the globe. It's not just about being in the northern or southern hemisphere.
Instead, it's about how countries have grown over time. Some countries have strong industries and high incomes. Others are still working to build their economies.
Who is in the 'North'?
The 'North' generally means countries that are economically strong. These are often called developed countries. They usually have:
- High incomes for their citizens.
- Good healthcare and education systems.
- Strong industries and advanced technology.
Examples include countries in North America (like the United States and Canada) and most of Europe. Australia and New Zealand, even though they are in the Southern Hemisphere, are also considered part of the 'North' because they are highly developed.
Who is in the 'South'?
The 'South' usually refers to countries that are still developing. These are often called developing countries. They might have:
- Lower average incomes.
- Less developed industries.
- Challenges with healthcare, education, or basic services.
Many countries in Africa, Latin America, and parts of Asia are considered part of the 'South'. These nations are working hard to improve their economies and living standards.
Why is there a Divide?
The reasons for this divide are complex. They include history, geography, and politics.
Historical Reasons
One big reason is colonialism. For hundreds of years, powerful European countries (from the 'North') controlled many lands in the 'South'. They often took resources from these lands. This made the colonial powers rich but left many colonized countries struggling after they gained independence.
Economic Development
The Industrial Revolution started in the 'North'. This led to factories and new technologies. Countries in the 'North' became very good at making goods and trading them. Many countries in the 'South' did not industrialize as quickly.
Resources and Climate
Sometimes, geography plays a role. Some countries in the 'South' face challenges like harsh climates or lack of easy access to trade routes. However, many 'Southern' countries also have rich natural resources.
Is the Divide Changing?
The North–South divide is not fixed. It is always changing.
Emerging Economies
Today, some countries in the 'South' are growing very fast. These are called emerging economies. Countries like China, India, and Brazil are becoming major players in the world economy. They are lifting many people out of poverty.
Global Cooperation
Organizations like the United Nations work to help bridge the gap. They promote fair trade, provide aid, and support development projects. The goal is to help all countries achieve better living standards.
Even with these changes, the idea of a North–South divide still helps us understand global inequalities. It reminds us that there are still big differences in wealth and development around the world.
Related pages
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |