Open system (systems theory) facts for kids
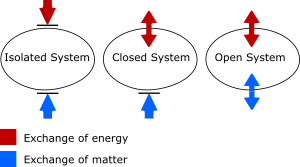
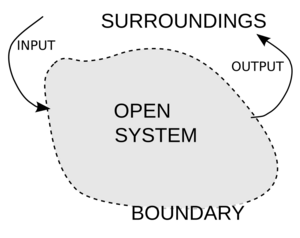
An open system is like anything that interacts with its surroundings. It takes things in, such as information, energy, or materials, and also lets things out. Think of it as a system that's always connected to the outside world. This is different from an isolated system, which doesn't exchange anything at all. An open system is also sometimes called a flow system.
The idea of open systems became important when scientists started connecting ideas from biology (how living things work), thermodynamics (how energy moves), and evolution. Later, it was further developed with information theory and systems theory. Today, the concept of open systems is used in many areas, including natural sciences and social sciences.
Open Systems in Nature
In the natural sciences, an open system is one where its border lets both energy and mass pass through. For example, a living plant is an open system. It takes in sunlight (energy) and water and nutrients (mass) from its environment. It also releases oxygen and water vapor.
A closed system, on the other hand, lets energy pass through but not matter. Imagine a sealed greenhouse: sunlight can enter and warm it (energy), but the plants inside can't exchange air or water with the outside (matter).
The definition of an open system often assumes there's a huge supply of energy that won't run out. In real life, this energy comes from the environment around the system. For example, a system that uses radiant energy gets its power from solar radiation (sunlight). The sun's energy can be thought of as endless for most studies.
Open Systems in Society
In the social sciences, an open system is a process that exchanges materials, energy, people, money, and information with its environment. For example, a country's economy is an open system. It trades goods and services with other countries, people move in and out, and money flows across borders.
The philosopher Kostas Axelos suggested that seeing the world as an open system could help solve many problems in social studies. He believed that if different social sciences worked together, they could understand the world better. He argued that thinking of a system as closed can actually make it act more closed, which is a less flexible way of thinking.
David Harvey used the idea of open systems to explain why systems like capitalism can face crises. He said that problems can come from many different parts of the system, such as gender roles, how we treat nature, or issues with how wealth is collected. For example, when too much money is held by a few people and can't move freely in the market, things like foreign direct investment (money invested in other countries) or privatization (selling state-owned things to private companies) can act as ways to release this pressure.
Sociologists like Talcott Parsons have used system theory to describe how society and its different parts work together. The sociology of religion also looks at both open and closed systems within the field of religion.
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema abierto para niños
In Spanish: Sistema abierto para niños
- Business process
- Complex system
- Dynamical system
- Glossary of systems theory
- Ludwig von Bertalanffy
- Maximum power principle
- Non-equilibrium thermodynamics
- Open system (computing)
- Open System Environment Reference Model
- Openness
- Open and Closed Systems in Social Science
- Phantom loop
- Thermodynamic system
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |