Particle detector facts for kids
A particle detector is a special tool that helps scientists "see" tiny, super-fast particles. Think of it like a high-tech camera for things too small to see with your eyes! These particles can come from different places, like when atoms break apart (called nuclear decay), from space (called cosmic radiation), or from powerful machines called particle accelerators that smash particles together.
Scientists use particle detectors in fields like particle physics (studying the smallest building blocks of the universe) and nuclear physics (studying the center of atoms). Modern detectors can also measure how much energy these particles have, and even details like their momentum (how much "push" they have), spin (a bit like how they rotate), or electric charge.
Contents
What Are Particle Detectors?
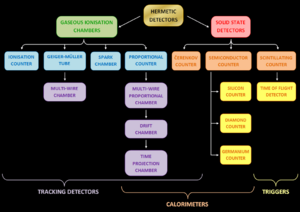
Particle detectors are often very large and can be quite expensive to build. Sometimes, they are simply called counters if their only job is to count how many particles pass by. But most detectors do much more! They can also track ionizing radiation, which is a type of high-energy energy, like powerful photons (light particles) or even visible light.
Different Kinds of Detectors
Many particle detectors work by sensing the "ionization" that particles create. This happens when a particle zips through a material and knocks electrons off atoms, creating an electric signal. Examples include gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors.
Other detectors use a special effect called scintillation. This is when a particle hits a material and makes it glow with tiny flashes of light. Scientists can then "see" these flashes. Some detectors even use Čerenkov radiation, which is a blue glow created when particles travel faster than light can in a specific material.
Some detectors are used to keep people safe by measuring how much radiation is around. Others are used by scientists to learn more about the universe's smallest particles and how atoms work.
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
Cloud chambers help us see particles by making a special misty layer. When particles pass through, they leave trails, just like planes leave condensation trails in the sky!
See also
 In Spanish: Detector de partículas para niños
In Spanish: Detector de partículas para niños