Point-contact transistor facts for kids
The point-contact transistor was the very first type of transistor ever shown to work! It was created by scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They were part of a team led by physicist William Shockley. Their goal was to find a way to replace large, power-hungry vacuum tubes with something much smaller and more efficient.
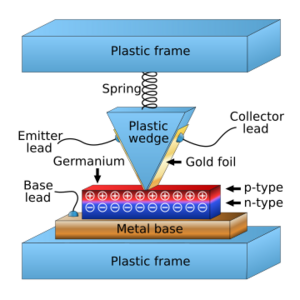
Their big breakthrough happened on December 16, 1947. They used a special material called germanium, which is a semiconductor. A semiconductor is a material that can sometimes conduct electricity and sometimes not, which makes it very useful for electronics. They placed two tiny gold contacts very close together on the germanium block.
Walter Brattain made the contacts by putting a thin strip of gold foil over a plastic triangle. He then carefully cut the gold at the tip. This created two separate gold contacts that were extremely close to each other.
The germanium they used had extra electrons on its surface. When an electric signal went into one of the gold contacts, it created "holes" where electrons were missing. This made a thin area with fewer electrons.
A small current put into one contact could control a much larger current flowing out of the other contact. This meant the device could make a small signal much stronger, acting like an amplifier. The input for the point-contact transistor was called the emitter. The outputs were the base and collector. This was a bit different from how transistors work today.
The point-contact transistor was sold by companies like Western Electric. However, it was soon replaced by a newer type called the bipolar junction transistor. This new transistor was easier to make and much tougher. Even so, point-contact transistors were still made until about 1966. By then, the silicon planar transistor had become the most popular type.
Contents
How the First Transistor Worked
The scientists used a special material called germanium to build their first transistor. Germanium is a semiconductor, meaning it can control how much electricity flows through it. This is key for making electronic devices.
They placed two tiny gold wires, called contacts, very close together on the germanium. One contact was the "emitter," and the other was the "collector." The germanium itself was connected to a "base."
When a small electric signal went into the emitter, it changed how the germanium worked. This small change then controlled a much bigger electric current flowing between the collector and the base. It was like a tiny switch or a volume knob for electricity.
This ability to control a large current with a small one is called "amplification." It meant that the point-contact transistor could make weak signals stronger. This was a huge step forward for electronics!
Why the Point-Contact Transistor Was Important
The invention of the point-contact transistor was a massive breakthrough. Before transistors, electronic devices used vacuum tubes. These tubes were big, fragile, used a lot of electricity, and got very hot.
Transistors changed everything. They were:
- Much smaller: They could fit into tiny spaces.
- More reliable: They didn't break as easily as vacuum tubes.
- Used less power: They didn't need as much electricity to work.
- Produced less heat: They stayed cooler.
This invention opened the door for all modern electronics. Without the transistor, we wouldn't have computers, smartphones, or any of the digital devices we use every day!
Making Them Work Better
Early point-contact transistors sometimes needed a special trick to work their best. This trick was called 'electrical forming'. It involved sending a short, strong burst of electricity through the collector contact.
This quick pulse would change the properties of the contact, helping the transistor work more efficiently. However, this process didn't always work perfectly, and some transistors had to be thrown away. Even though they knew it helped, scientists didn't fully understand exactly why it worked.
Interestingly, it was possible for people at home to make their own point-contact transistors. They could start with a germanium point-contact diode and even fix them if they got damaged.
Key Features of Point-Contact Transistors
Point-contact transistors had some unique features compared to later types of transistors:
- Current Gain: They could make the output current 2 to 3 times stronger than the input current. This is called "current gain."
- Speed: For a while, point-contact transistors were the fastest transistors available. Some could work at very high frequencies, which was amazing for their time.
- Moisture: They were less affected by moisture than other early transistors.
- Digital Use: When used in some digital circuits, they would sometimes stay "on" even when they should turn "off." This meant the power had to be briefly cut to reset them.
See also