Polar bond facts for kids
A polar bond is a special type of covalent bond in chemistry. It happens between two or more different atoms. In a polar bond, the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms. A covalent bond is a strong connection that holds atoms together to form a molecule.
Electrons have a negative charge. If two atoms share electrons equally, the negative charge is spread out evenly. This makes the whole molecule neutral. This is called a non-polar bond, and it forms a non-polar molecule. But sometimes, one atom is "greedier" for electrons than the other. This "greediness" is called electronegativity. When one atom is greedier, its side of the bond gets more electrons. This makes that side slightly negative. The other side, with fewer electrons, becomes slightly positive.
This difference in charge turns the bond into an electrical dipole. A dipole acts a bit like a tiny magnet. If other bonds that are also dipoles are nearby, they will react to each other.
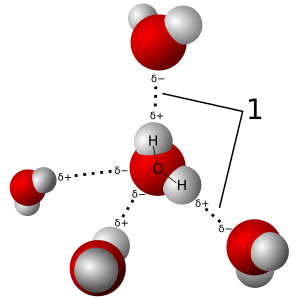
In some molecules, these polar bonds line up together. When this happens, the entire molecule becomes a dipole. This means the whole molecule can attract other dipoles. Water is a great example of this. In the image, you can see that the hydrogen atoms (small and white) are slightly positive. The oxygen atom (big and red) is slightly negative. This picture shows how tiny water dipoles line up. It's like when you toss a bunch of small magnets into a box; they will naturally line up.
This idea of polar bonds is one of the most important differences between chemical bonds. It also affects how molecules behave. Scientists can easily predict if a bond will be polar. This is because the electronegativity of all atoms is known from the periodic table. This small difference in how electrons are shared makes a huge difference in how molecules act.
Contents
What Makes a Bond Polar?
A bond becomes polar when there's an uneven sharing of electrons. Imagine two friends sharing candy. If they share it perfectly, everyone gets the same amount. That's like a non-polar bond. But if one friend always grabs more candy, that's like a polar bond. One atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself. This creates a slightly negative side and a slightly positive side.
Electronegativity: The Electron "Greediness"
The "greediness" of an atom for electrons is called electronegativity. Every atom has an electronegativity value. Atoms with high electronegativity pull electrons strongly. Atoms with low electronegativity don't pull as hard. When two atoms with different electronegativity values bond, the one with higher electronegativity pulls the shared electrons closer. This causes the bond to be polar.
Why are Polar Bonds Important?
Polar bonds are super important in chemistry and in life. They affect how molecules interact with each other. For example, water's polar bonds are why it can dissolve so many things. This is also why water has a relatively high boiling point. Without polar bonds, life as we know it might not exist!
How Polarity Affects Molecules
When a molecule has polar bonds, it can become a "dipole." This means the whole molecule has a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end. These charged ends can attract other molecules. This attraction is called an intermolecular force. These forces are weaker than the bonds inside a molecule. But they are very important for how substances behave. They affect things like boiling points, melting points, and solubility.
Water: A Perfect Example
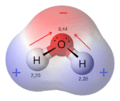
Water (H₂O) is a classic example of a polar molecule. It has two polar bonds between oxygen and hydrogen. The oxygen atom is much more electronegative than hydrogen. So, oxygen pulls the electrons closer. This makes the oxygen side of the water molecule slightly negative. The hydrogen sides become slightly positive. These positive and negative ends allow water molecules to attract each other. This attraction is called hydrogen bonding. It gives water its unique properties.
Related pages
- Chemical polarity
- Covalent bond
- Electronegativity
Images for kids
-
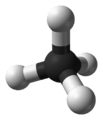
In methane, the bonds are arranged symmetrically in a pyramid shape. This means there is no overall dipole for the molecule.
-
This molecule has several polar parts (which like water) on the right side. It also has a long nonpolar chain (which likes fats) on the left side. This gives it properties like a surfactant, which helps mix oil and water.
-
Phospholipids are natural surfactants. They have important jobs in living things, like forming cell membranes.