Quinine bark facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Quinine bark |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Cinchona |
| Species: |
C. officinalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cinchona officinalis |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
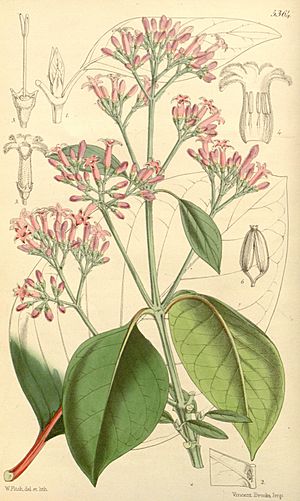
Cinchona officinalis is a tree from South America. It belongs to the plant family called Rubiaceae. You can find this tree growing in wet mountain forests in countries like Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. It usually grows at high altitudes, between 1,600 and 2,700 meters above sea level.
What it Looks Like
The Cinchona officinalis is a shrub or a tree. It has rough bark and its small branches are covered in tiny hairs. The leaves are usually about 10 centimeters (4 inches) long and 3.5 to 4 centimeters (1.4 to 1.6 inches) wide. They can be shiny on top and sometimes have small hairs underneath, especially on the veins.
The flowers grow in clusters at the ends of the branches. They are often pink or red. Each flower has a tube shape, about 1 centimeter (0.4 inches) long. After the flowers, the tree produces a fruit. This fruit is a long, oval-shaped capsule, about 1.5 to 2 centimeters (0.6 to 0.8 inches) long.
Different Names for the Tree
This tree has many different names around the world:
- English: quinine, red cinchona, cinchona bark, Jesuit’s bark, loxa bark, Jesuit’s powder, countess powder, Peruvian bark.
- Spanish: quina, cascarilla, cargua cargua, corteza coja.
- French: quinquina, écorce du Pérou.
How it is Used
The Cinchona officinalis tree is very important for medicine. It is one of several Cinchona species used to make a special medicine called quinine. Quinine is known for helping to reduce fevers.
It is especially useful in preventing and treating a serious disease called malaria. Malaria is a disease spread by mosquitoes that causes high fevers and chills. Besides quinine, other helpful medicines like cinchonine, cinchonidine, and quinidine are also taken from this tree.
See also
 In Spanish: Cinchona para niños
In Spanish: Cinchona para niños

