Glossary of chess facts for kids
This glossary of chess terms helps you understand words used in the game of chess. It lists terms in alphabetical order. Some words, like fork and pin, have their own detailed explanations. For different types of chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece. For words used in chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems. If you want to see a list of opening moves, check out List of chess openings. For other games similar to chess, see List of chess variants. For general terms about board games, see Glossary of board games.
A
- Absolute Pin
- An absolute pin happens when a piece is blocked from moving because it would put its own king in check. This piece cannot legally move. It's different from a relative pin.
- Active Piece
- An active piece is one that controls many squares or has many moves available. It can also describe a player who plays aggressively. The opposite is a passive piece.
- Adjournment
- This means pausing a chess game to finish it later. It used to be common in big tournaments. But now, with computers, it's rare. See also sealed move.
- Adjust
- To gently move a piece on its square without actually making a move. You can only do this on your turn. You must say "I adjust" or "J'adoube" first.
- Advanced Pawn
- A pawn that has moved past the middle of the board. For White, this is on the fifth rank or higher. For Black, it's the fourth rank or lower. An advanced pawn can be strong if it limits the enemy's moves. It can also be weak if it's hard to defend.
- Advantage
- Having a better position in the game, which gives you a higher chance of winning. This can be about having more pieces, more space, or better developed pieces.
-
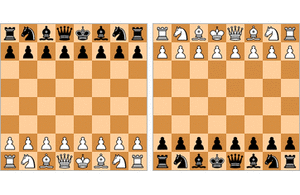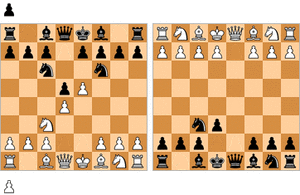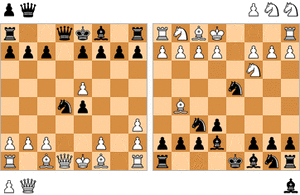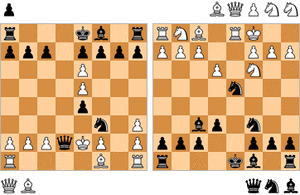
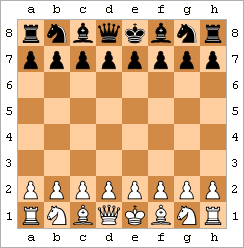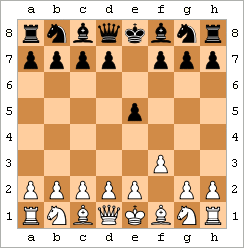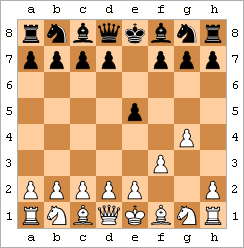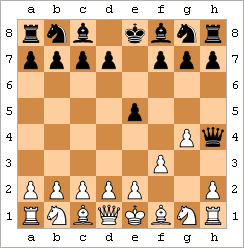
Alekhine vs. Nimzowitsch, 1930
a b c d e f g h 8 


























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Alekhine's Gun - Alekhine's Gun
- A powerful setup where a queen is behind two rooks on the same file. It creates a very strong attack.
- Algebraic Notation
- The standard way to write down chess moves. It uses letters and numbers for each square. For example, "e4" means the pawn moved to square e4. It's also called standard notation.
- Analysis
- Studying a game or position to understand the best moves and ideas. Players often analyze their games after they finish. See also post-mortem.
- Annotation
- Written comments about a chess game or position. It can use words, chess symbols, or notation.
- Antipositional
- A move or plan that goes against good positional play ideas. These moves can create lasting weaknesses, especially with pawns, because pawns can't move backward.
- Anti-Sicilian
- An opening that White plays against the Sicilian Defense (1.e4 c5). It's a way to avoid the most common lines of the Sicilian. Examples include 2.c3 or 2.Nc3.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 



8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Arabian Mate - Arabian Mate
- A checkmate where a knight and a rook trap the enemy king in a corner.
- Arbiter
- An official who makes sure the rules are followed in chess tournaments. They also help settle any disagreements.
- Armageddon Game
- A game designed to have a winner. If the game is a draw, Black wins. To balance this, White gets more time on the clock. For example, White might get five minutes, and Black four.
- Artificial Castling
- When the king and a rook move in several separate turns to reach positions as if they had castled. It's also called castling by hand.
- Attack
- An aggressive move that threatens to capture a piece or pawn. It can also mean putting pressure on a part of the board. The opposite is defense.
-
Example of Attraction
a b c d e f g h 8 






8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White wins with 1.Rd7+! The black king is attracted away from the defense of the black queen with a skewer. - Attraction
- A tactic where you sacrifice a piece to lure an enemy king or other piece to a square where it will be in danger. This often sets up a skewer or other winning combination.
- Automaton
- A machine that seems to play chess by itself, but actually has a hidden human player inside. Famous examples like "The Turk" tricked many people in the 18th and 19th centuries.
B
- B
- The letter used for the bishop when writing down chess moves in English.
- Back Rank
- The row where your pieces start the game. For White, it's the first rank. For Black, it's the eighth rank. Also called home rank.
- Back-Rank Mate
- A checkmate delivered by a rook or queen on the back rank. The enemy king is trapped because its own pawns block its escape squares.
- Back-Rank Weakness
- A situation where a player is in danger of a back-rank mate. They have to keep a rook or queen on the back rank to defend, which limits their other moves.
- Backward Pawn
- A pawn that is behind other pawns of its own color on nearby files. It cannot be moved forward with support from another pawn, making it weak.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White has a bad bishop, Black has a good bishop (Evans 1967, p. 66). - Bad Bishop
- A bishop that is stuck behind its own pawns. It has limited moves and can't do much. The opposite is a good bishop.
- Bare King
- A position where a king is the only piece left of its color on the board.
- Basque Chess
- A type of chess competition where two players play two games at the same time. Each player plays White on one board and Black on the other. This makes sure neither player has an advantage by playing White first.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h A pair of white rooks are aligned along their battery, ready to do some action. - Battery
- Lining up two or more pieces (like rooks and a queen) on the same file or diagonal. This creates a strong attack when the front piece moves, revealing the one behind it. See also Alekhine's Gun.
- Best Play
- The perfect moves in any chess position. It's how a computer would play if it could see every possible outcome.
-
Charousek vs. Maroczy, 1895
a b c d e f g h 8 






















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Example of a "big pawn": the white bishop is doing the work of a pawn and has no bigger prospects. - Big Pawn
- A bad bishop that is stuck behind its own pawns. It acts more like a pawn than a powerful piece.
- Bind
- A strong control over a part of the board, usually with advanced pawns. It makes it hard for the opponent to move their pieces. The Maróczy Bind is a famous example.
- Bishop
- A piece that moves only along diagonals. It cannot jump over other pieces. Each player starts with two bishops, one on light squares and one on dark squares.
- Bishop Pair
- Having both bishops (one for light squares, one for dark squares). In open positions, two bishops are often stronger than two knights or a bishop and a knight.
- Bishops on Opposite Colors
- When one player has only a light-square bishop and the other has only a dark-square bishop. In the endgame, this often leads to a draw, even if one side has more pawns, because the bishops can't attack each other's squares.
- Black
- The player who moves second in a game. Their pieces are usually dark-colored. See also White.
- Blindfold Chess
- A type of chess where one or both players play without seeing the board. They remember the positions in their mind.
- Blitz Chess
- A very fast game of chess. Each player usually gets only three or five minutes for the whole game. Modern chess clocks often add a second or two per move.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 




















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Black has a solid light-square blockade. White's bishop cannot challenge Black's minor pieces. - Blockade
- Placing a piece directly in front of an enemy pawn to stop it from moving forward. A knight is often a good piece for a blockade.
- Blocked Position
- A position where both sides have trouble moving forward. This often happens when pawn chains block the board. See also closed game.
- Blunder
- A very bad mistake in chess, often leading to losing the game or a lot of material. It's usually marked with "??" in game notes.
- Board
- Short for chessboard. It can also mean a player's position in a team match, like "first board" for the strongest player.
-
Schulder vs. Boden, London 1853
a b c d e f g h 8 























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Boden's Mate - Boden's Mate
- A checkmate pattern where the king is trapped by two crisscrossing bishops. It often happens after a queen sacrifice.
- Book Move
- An opening move that is found in standard chess books. A game is "in book" when players follow these known moves. It's "out of book" when someone plays a new move or a mistake.
- Break
- A move that helps a player gain space or open up a blocked position. This is often done by advancing or capturing a pawn. See also pawn break.
- Breakthrough
- Getting past the opponent's defenses, often by making a sacrifice.
- Brilliancy
- A game that includes a surprising, deep, and beautiful idea, combination, or plan. It's often awarded a special prize in tournaments.
- Bronstein Delay
- A way to manage time in chess. When it's your turn, your clock waits for a short delay before it starts counting down your time. This helps prevent running out of time too quickly.
- Bughouse Chess
- A fun chess variant played by teams of two. When you capture a piece, your teammate can place it on their board.
- Bullet Chess
- An extremely fast game of chess. Each player gets only one minute for all their moves.
- Bust
- A way to show that an opening, a line of play, or a tactic is not good and can be defeated. It's like finding a flaw in a plan.
- Bye
- A round in a tournament where a player doesn't have a game. This usually happens when there's an odd number of players. A bye is usually counted as a win.
C
- Caïssa
- The goddess or muse of chess. Her name comes from a poem written in 1763.
- Calculate
- To think ahead and plan a series of moves in your mind, considering what your opponent might do. This is done without actually moving the pieces.
- Candidate Master
- A chess title given by FIDE. It's a step below FIDE Master. Abbreviated as CM.
- Candidate Move
- A move that looks promising when you first see it. It's worth thinking about more deeply to see if it's the best choice.
- Candidates Tournament
- A tournament organized by FIDE. The winner gets to challenge the World Champion for their title.
- Can Opener
- A slang term for attacking the opponent's kingside by pushing the h-pawn. The goal is to open up lines near the enemy king.
- Capture
- To remove an opponent's pawn or piece from the board by moving your own piece to its square. The only exception is en passant.
- Castling
- A special move where the king and a rook move at the same time. It helps make the king safer and brings the rook into the game. You can castle kingside (0-0) or queenside (0-0-0). You can't castle if your king is in check, or if any squares the king crosses or lands on are attacked. Neither the king nor the rook can have moved before.
- Castling into It
- When a player castles, but it actually puts their king in more danger than it was before. This can happen right away or later in the game.
- Castling Long
- Castling on the queenside. In chess notation, it's written as 0-0-0.
- Castling Rights
- The ability to castle according to the rules of chess. Once the king or rook moves, you lose your castling rights for that side.
- Castling Short
- Castling on the kingside. In chess notation, it's written as 0-0.
- Category of a Tournament
- A way to measure how strong a tournament is. It's based on the average FIDE rating of the players. Higher categories mean stronger players.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
















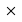
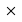
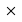
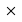
















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The center squares are marked "×". - Center
- The four middle squares of the board (d4, e4, d5, e5). Controlling the center is very important in chess. Sometimes it refers to the pawn center.
- Center Pawn
- A pawn on the d-file or e-file, which are the middle files of the board.
- Centralization
- Moving your pieces towards the center of the board. Pieces are usually strongest and have the most influence when they are in the center. Knights especially benefit from this.
- Cheapo
- Slang for a simple trap, often used when a player is losing. They hope the opponent makes a mistake to get a draw or even a win.
- Check
- A direct attack on the king by an enemy piece or pawn. When your king is in check, you must immediately move it, capture the attacking piece, or block the attack. In casual games, players often say "check!"
- Checkmate
- Also called mate. This is when a player's king is in check and there are no legal moves to escape the check. The player whose king is checkmated loses the game.
- Chess Blindness
- When a player fails to see a good move or a danger that they should have noticed. It's like having a mental block during the game.
- Chessboard
- The square board used for chess. It has 64 squares (8 rows by 8 columns) that alternate between light and dark colors.
- Chess Clock
- A device with two clocks used to keep track of how much time each player uses. After making a move, a player presses a button to stop their clock and start their opponent's. Modern clocks are digital.
- Chessmen
- All the movable figures on the board: the pieces (king, queen, rook, bishop, knight) and the pawns.
- Chess Set
- The 32 pieces and the chessboard needed to play a game.
- Chess Variant
- A game similar to chess but with different rules, pieces, or a different board. Fischerandom and Bughouse Chess are examples.
- Chop Wood
- Slang for capturing or exchanging pieces. See also wood.
- Classical
- 1. A style of opening play that focuses on building a strong pawn center. This style was challenged by hypermodern ideas.
- 2. A game played with a longer time control, like two hours for 40 moves. This is the opposite of fast chess.
- Clearance
- Moving a piece out of the way so another piece can use that square, rank, file, or diagonal. This sometimes involves sacrificing the blocking piece.
- Clock Move
- In some casual games, a move is only complete when the player presses their clock. This means you could touch a piece, then move a different one, as long as you haven't pressed the clock yet.
- Closed File
- A file on the board where both White and Black have a pawn.
- Closed Game
- A game with few open lines (files or diagonals). It often has pawn chains that block the board, making it hard to attack. Players usually maneuver their pieces behind the lines. See also open game.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 

































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The Blackburne Shilling Gambit (1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 Nd4?!), an example of coffeehouse play - Coffeehouse
- Describes a risky, tricky style of play that tries to set traps for the opponent. It's like the kind of games you might see played quickly in a coffee shop.
- Color
- Refers to the white or black pieces, and the light or dark squares on the chessboard. Even if the pieces or squares are other colors, they are called "white" and "black".
- Colorbound
- A piece that can only move on squares of one color. In standard chess, each bishop is colorbound, meaning it only moves on either light or dark squares.
- Colors Reversed
- When White plays an opening that Black normally plays, or vice versa. White usually gets an extra tempo (a move) in these openings.
- Combination
- A series of forced moves, often involving a sacrifice, that leads to a clear advantage for one player.
- Compensation
- What you gain in return for losing material. For example, if you sacrifice a piece, you might get a strong attack or better development as compensation.
- Computer Move
- A move that seems like something a chess computer would play, rather than a human. It might look strange or not make immediate sense, but it's based on deep calculations.
- Connected Passed Pawns
- Two passed pawns of the same color on neighboring files. They are very strong because they can support each other as they move towards promotion.
- Connected Pawns
- Two or more pawns of the same color on neighboring files. They can defend each other. The opposite is isolated pawns.
- Connected Rooks
- Two rooks of the same color on the same rank or file with no other pieces between them. They are strong because they protect each other and work together.
- Consolidation
- Improving your position by moving your pieces to better squares. This often happens after an attack or combination has left your pieces in awkward spots.
- Consultation Game
- A game where two or more players work together as a team to decide the moves for one side.
- Control
- When your pawns or pieces guard squares, files, or ranks. This prevents your opponent from using that area and gives you an advantage.
- Control of the Center
- Having your pieces or pawns attack or occupy the four central squares. This is a very important goal in the opening of a chess game.
- Coordination
- How well your pieces work together, supporting and helping each other. Good coordination means your pieces are in harmony.
- Correspondence Chess
- Chess played over a long distance, where players send their moves to each other. It used to be by mail, but now it's usually online by email or a special server.
- Corresponding Squares
- Pairs of squares where if one king moves to one, the other king must move to the other to keep the position balanced. This is important in endgames.
- Counterattack
- An attack that you make in response to your opponent's attack.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The Falkbeer Countergambit (1.e4 e5 2.f4 d5), a gambit response to the King's Gambit - Countergambit
- A gambit (a sacrifice of a pawn) offered by Black in the opening. Examples include the Albin Countergambit and the Falkbeer Countergambit.
- Counterplay
- The defending player's own aggressive moves. Even when defending, a player tries to create threats and opportunities for themselves.
- Cramped
- When your pieces have very limited mobility and few squares to move to. This is usually a disadvantage.
- Critical Position
- A moment in the game where the situation is about to change a lot. A wrong move here can be very bad, while a good move can lead to a big advantage.
- Cross-Check
- A check that you give in response to your opponent's check. This often happens when you block their check with a piece that also gives a check.
- Crosstable
- A table that shows the results of every game in a tournament. It lists players and their scores against each opponent.
- Crush
- Slang for a quick and overwhelming win, especially when one player plays a very strong attack against weak defense.
D
- Dark-Square Bishop
- One of your two bishops that only moves on the dark-colored squares of the board. For White, it starts on c1. For Black, it starts on f8.
- Dark Squares
- The 32 dark-colored squares on the chessboard, like a1 and h8. The opposite are light squares.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 



8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h A dead draw by means of insufficient material. King versus king and bishop will never lead to checkmate. If for Black, a knight or a light-squared bishop were added to the position (e.g. a Nf3 or Bf3), a mate would be possible in theory for either side, but not with reasonable play, making it a "dead draw" in the broader sense. - Dead Draw
- A drawn position where neither player has any real chance to win. This can be because there aren't enough pieces left to checkmate.
- Dead Position
- A position where it's impossible for either player to checkmate the opponent's king, no matter what moves are made. This position is always a draw.
- Decoy
- A tactic where you trick an enemy piece into moving away from its important defensive spot. See also deflection and attraction.
- Defense
- 1. A move or plan you use to protect against your opponent's attack.
- 2. Part of the name of some openings played by Black, like the Scandinavian Defense.
- Deflection
- A decoy tactic where you lure an enemy piece away from a square where it's defending something important. This leaves another piece or square unprotected.
- Demonstration Board
- A large chess board used to show games or analyze positions to a group of people. It's often used by teachers or commentators.
- Desperado
- A piece that is about to be captured, so it tries to take as much of the opponent's material as possible before it's lost. It might also sacrifice itself to create a stalemate or perpetual check.
- Development
- Moving your pieces (not pawns) from their starting squares to more active positions in the opening. This helps them control more of the board and get ready for attacks.
- Diagonal
- A line of squares of the same color that touch corner to corner. Bishops and queens move along diagonals.
- Discovered Attack
- An attack made by a queen, rook, or bishop when another piece moves out of its way. The piece that moved might also make a threat.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 





8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Once the e4-bishop moves, it is discovered check by the rook. - Discovered Check
- A special type of discovered attack where the hidden piece puts the enemy king in check. This is a very powerful tactic.
- Domination
- In endgame studies, this means controlling all the possible squares an enemy piece can move to, trapping it.
- Double Attack
- When one move creates two attacks at the same time. If the same piece makes both attacks, it's called a fork.
- Double Check
- A check given by two of your pieces at the same time. This always involves a discovered check. The only way to escape a double check is to move the king.
- Doubled Pawns
- Two pawns of the same color on the same file. This is usually a weakness because they can't defend each other as easily.
- Doubled Rooks
- When two rooks of the same color are on the same file or rank with no pieces between them. They are very strong together, especially in the endgame.
- Draw
- A game that ends without either player winning. Most draws happen when players agree to it. Other ways to draw include stalemate, threefold repetition, or insufficient material. A draw is usually scored as ½ point.
- Draw by Agreement
- When both players agree to end the game in a draw.
- Drawish
- An adjective describing a position or game that is very likely to end in a draw.
- Dynamism
- A style of play that focuses on the activity and movement of pieces, even if it means accepting some weaknesses in your position. It's about creating action.
E
- Eat
- Slang for capturing an opponent's piece or pawn.
- ECO
- A big reference book for chess openings. It also has a system of codes (like A00 to E99) to classify different openings.
- Edge
- A small but important advantage in a position. For example, White is often said to have a slight "edge" at the start of the game because they move first.
- Eighth Rank
- The rank where pawns can be promoted. For White, it's the 8th rank. For Black, it's the 1st rank. Also called last rank.
- Elo Rating System
- A system used to calculate the skill level of chess players. Higher numbers mean stronger players. FIDE uses this system for international ratings.
- Endgame
- The final stage of a chess game, when there are only a few pieces and pawns left on the board. It comes after the middlegame.
- Endgame Tablebase
- A computer database that has solved all possible endgames with a small number of pieces. It shows the perfect moves for both players in these positions.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 














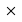


















8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h After 1.d4 c5 2.d5 e5, White can play 3.dxe6, capturing the e-pawn en passant on the next move. The white pawn is placed on e6, and the black pawn on e5 is removed from the board. - En Passant
- A special pawn capture rule. If an enemy pawn moves two squares forward and lands next to your pawn, your pawn can capture it as if it had only moved one square. You can only do this on the very next move.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The pawn on e4 is en prise. - en prise
- A piece or pawn that is left unprotected and can be captured by the opponent for free or for a gain in material.
- Epaulette Mate
- A checkmate where the king is trapped on both sides by its own rooks, which look like epaulettes (shoulder decorations).
- Equalize
- To reach a position where both players have an equal chance of winning. For Black, a common goal in the opening is to achieve equality against White's first-move advantage.
- Escape Square
- A square where a king or other piece can move to escape an attack. Also called flight square.
- Evaluation
- Analyzing a position to see who has the advantage. Chess computers give a number (like +2.50) to show how good a position is. A plus sign means White is better, a minus sign means Black is better. The number shows how many pawns worth of advantage one side has.
- Exchange
- To trade pieces or pawns by capturing them. Usually, the pieces traded are of similar value, like a rook for a rook or a knight for a bishop.
- The Exchange
- The advantage of having a rook instead of a minor piece (a knight or bishop). If you capture a rook and lose a minor piece, you "win the exchange."
- Exhibition
- Chess games played for the public. This can be two masters playing, or one player playing against many opponents at once (a simultaneous exhibition).
- Expanded Center
- The central 16 squares of the chessboard. It's a larger area than just the four center squares.
- Exposed King
- A king that doesn't have enough pawns or pieces protecting it from enemy attacks.
F
- Family Fork
- A fork by a knight that attacks the enemy king (giving check), queen, and possibly other pieces all at once. It's a very strong tactic.
- Fast Chess
- Any form of chess where players have less time to make their moves than in a regular tournament game. This includes rapid chess, blitz chess, and bullet chess.
- Fianchetto
- To develop a bishop to one of the longest diagonals on the board (b2 or g2 for White; b7 or g7 for Black). This is a common opening strategy.
- FIDE
- The World Chess Federation. It's the main international organization that governs chess. FIDE is a French acronym for Fédération Internationale des Échecs.
- FIDE Master
- A chess title given by FIDE. It's a step below International Master. Abbreviated as FM.
- Fifty-Move Rule
- A rule that allows a draw to be claimed if no capture or pawn move has happened in the last 50 moves by both players. This prevents endless games without progress.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 








8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The f-file - File
- A column of squares on the chessboard. Files are named with letters from 'a' to 'h'. For example, the "f-file" is the column from f1 to f8.
- Fingerfehler
- A German word meaning "finger mistake." It's when you accidentally touch the wrong piece or let go of a piece on the wrong square. Because of the touch-move rule, you might be forced to make that unintended move.
- First-Move Advantage
- The small advantage that White has in chess because they get to make the first move. This allows White to start developing and controlling the center first.
- Fischerandom
- Also known as Chess960. A chess variant where the starting position of the pieces on the back rank is random. This makes players rely more on their skills during the game rather than memorizing opening moves.
- Fischer Delay
- A time control method where a small amount of time (e.g., 5 seconds) is added to your clock before each move you make. This helps prevent running out of time in long games.
- Fish
- Slang, often used in a negative way, for a weak or easily defeated chess player. See also woodpusher.
- Fivefold Repetition
- A game is a draw if the exact same position appears five times, with the same player to move and the same legal moves available. This is similar to the threefold repetition rule.
- Flag
- A small indicator on an old-style chess clock that falls when a player's time runs out. To "flag" someone means to win because their time ran out.
- Flank
- The sides of the board, away from the center. The queenside (a-, b-, c-files) and the kingside (f-, g-, h-files). Also called wing.
- Flight Square
- A square where a king can move to escape a check or other attack. Also called escape square. See also luft.
- Fool's Mate
- The shortest possible checkmate in chess, happening in just two moves. It's usually 1.f3 e5 2.g4 Qh4# (or similar).
- Forced Mate
- A series of moves that leads to an unavoidable checkmate for the opponent. The opponent cannot stop it.
- Forced Move
- A move that is the only good option for a player. If they don't make this move, they will be in a much worse position or even lose. It can also describe a sequence of moves that cannot be avoided.
- Fork
- A double attack where one piece attacks two (or more) of the opponent's pieces or important squares at the same time. A knight is very good at giving forks.
- Fortress
- In endgame theory, a position that is impossible for the stronger side to break through. It allows the side with less material to achieve a draw by creating an impenetrable defense.
- Friendly Game
- A game of chess that is not part of a tournament or match. It's played for fun, often without a chess clock. Also called casual game.
G
- Gambit
- An opening move where a player sacrifices a pawn (or sometimes a piece) early in the game. The goal is to gain an advantage in space or time.
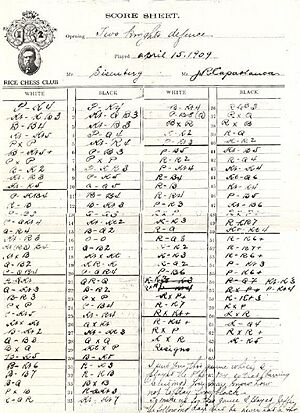
- Game Score
- The written record of all the moves in a chess game, usually using algebraic notation. In tournaments, players write this on a score sheet.
- GM
- An abbreviation for Grandmaster.
- Good Bishop
- A bishop that has a lot of mobility and is not blocked by its own pawns. It's the opposite of a bad bishop.
- Grandmaster
- The highest title a chess player can earn, given by FIDE. It's a lifetime title, unless there are very unusual circumstances.
- Grandmaster Draw
- A game where players quickly agree to a draw, often without much play. It originally referred to games between grandmasters.
- Greek Gift Sacrifice
- A common sacrifice of a bishop (Bxh7+ for White, or ...Bxh2+ for Black) against a castled king. It's used to start a strong mating attack. Also called the classical bishop sacrifice.
H
- Half-Open File
- A file on the board where only one player has pawns. This means the other player's rooks or queen can use that file more easily for attacks. Also called semi-open file.
- Hanging
- Slang for a piece or pawn that is unprotected and can be captured. It's similar to en prise.
- Hanging Pawns
- Two pawns of the same color on neighboring files, but with no other pawns of the same color on the files next to them. This can sometimes be a weakness.
- Hole
- A square in or near a player's territory that cannot be controlled by their own pawns. This creates a weak spot, especially if it's near the center or the king. An enemy knight can be very strong on a hole.
- Home Rank
- The rank where your pieces start the game. For White, it's the first rank. For Black, it's the eighth rank. Also called back rank.
- Horwitz Bishops
- When a player's light-square and dark-square bishops are placed on neighboring diagonals. This creates a powerful attack on the enemy king. Also called raking bishops.
- Human Move
- A move that a human player would typically make, often based on intuition or strategy, rather than just deep calculation like a computer.
- Hypermodernism
- A chess idea that suggests you don't always need to put pawns directly in the center. Instead, you can control the center from the sides of the board with your pieces. This was a new idea that challenged older, classical ways of thinking.
I
- Illegal Move
- A move that is not allowed by the rules of chess. If an illegal move is made, it must be corrected.
- Illegal Position
- A position on the board that could not have been reached by legal moves. This might happen because of an illegal move or a wrong starting setup.
- Imbalance
- Any difference between the positions of White and Black. An imbalanced position means both sides have unique strengths and weaknesses, making the game more complex.
- Inaccuracy
- A move that isn't the best choice, but it's not as bad as a blunder. It might give your opponent a small advantage.
- Increment
- The extra time added to each player's clock before or after each move. For example, "25 minutes plus 10 seconds increment" means you get 10 extra seconds per move.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h In the KID Fianchetto Variation (1.d4 Nf6 2.c4 g6 3.Nf3 Bg7 4.g3 0-0 5.Bg2 d6 6.0-0), both sides have Indian bishops. - Indian Bishop
- A bishop that has been fianchettoed. This is a common feature in openings like the King's Indian Defense.
- Indian Defense
- An opening that starts with 1.d4 Nf6. It often involves fianchettoing one or both of Black's bishops.
- Initiative
- The ability to make attacking moves and control the flow of the game. The player with the initiative is usually forcing the opponent to react.
- Insufficient Material
- An endgame situation where there aren't enough pieces left on the board to force a checkmate. For example, a king and knight against a lone king is a draw because you can't force a mate.
- Interference
- Blocking the line between an attacking piece and its target by moving another piece in between them.
- International Arbiter
- A highly ranked tournament official who settles disputes and makes sure the rules are followed. Abbreviated as IA.
- International Master
- A chess title given by FIDE. It's a step below Grandmaster but above FIDE Master. Abbreviated as IM.
- Internet Chess Server
- A website or program that lets you play, discuss, and watch chess games online over the Internet. Abbreviated as ICS.
- Interpose
- To move a piece in between an attacking piece and its target, blocking the line of attack. This is one way to respond to a check.
- Interzonal Tournament
- A tournament that used to be part of the World Chess Championship cycle. Players who did well in Zonal tournaments would play here, and the top players would move on to the Candidates Tournament.
- Irregular Opening
- An opening that doesn't start with the most common moves (like 1.e4 e5 or 1.d4 d5). Today, these are often called "uncommon" or "unorthodox" openings.
- Isolani
- A pawn on the d-file that has no other pawns of its own color on the c-file or e-file. It's also called an isolated queen pawn. Some players see it as a strength in the middle of the game, but a weakness in the endgame.
- Isolated Pawn
- A pawn that has no other pawns of its own color on the neighboring files. This can make it harder to defend.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Italian bishops in the Giuoco Piano - Italian Bishop
- A White bishop developed to c4, or a Black bishop developed to c5. This is a common feature in the Italian Game.
J
- J'adoube
- A French phrase meaning "I adjust." You say this when you want to straighten a piece on its square without actually making a move, following the touch-move rule.
K
- K
- The letter used for the king when writing down chess moves in English.
- Key Square
- 1. An important square on the board.
- 2. In pawn endgames, a square that, if your king reaches it, guarantees you will achieve a goal, like promoting a pawn.
- Kibitz
- When a spectator makes comments about a chess game that the players can hear. This is considered very rude in serious games.
- Kick
- To attack an enemy piece, usually a knight, with a pawn to force it to move. This can help you gain a tempo or control important squares.
- King
- The most important piece in chess. It can move one square in any direction. If your king is attacked, it's in check. If it's in check and can't escape, it's checkmate, and you lose. If you have no legal moves and your king is not in check, it's a stalemate, which is a draw.
- King Hunt
- A long, continuous attack on the enemy king that forces it to move far from its starting position, usually leading to checkmate.
- Kingside
- The right half of the board from your perspective, where the kings start. It includes the e-, f-, g-, and h-files. The opposite is the queenside.
- Knight
- A unique piece that moves in an "L" shape: two squares in one direction (horizontal or vertical) and then one square perpendicular to that. It's the only piece that can jump over other pieces.
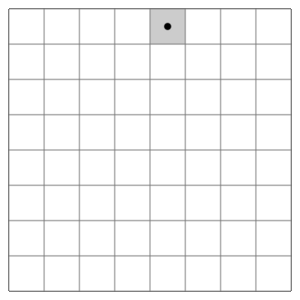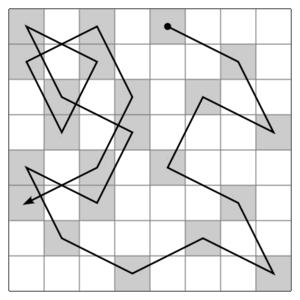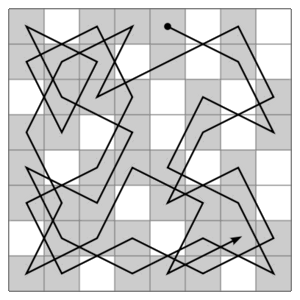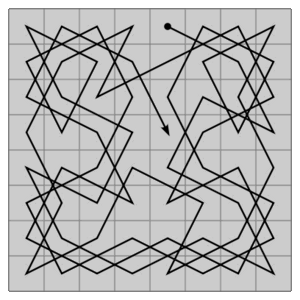
- Knight's Tour
- A puzzle where you try to move a knight around an empty chessboard, visiting every square exactly once. A "closed tour" ends on the starting square. An "open tour" ends on a different square.
- Knockout Tournament
- A tournament where players are eliminated after one loss. The winner of each game or match moves on to the next round, until only one player is left.
- Kotov Syndrome
- A situation where a player thinks for a very long time but can't find a good plan. Then, under time pressure, they make a quick, bad move they haven't thought about enough.
- Kriegspiel
- A chess variant where players can only see their own board, not their opponent's. An umpire tells them what's happening. It's like a "war game" with limited information.
L
- Last Rank
- See eighth rank.
- Laws of Chess
- The official rules that govern how chess is played.
- Lightning Chess
- A very fast game of chess, usually referring to blitz chess or bullet chess.
- Light-Square Bishop
- One of your two bishops that only moves on the light-colored squares of the board. For White, it starts on f1. For Black, it starts on c8.
- Light Squares
- The 32 light-colored squares on the chessboard, like h1 and a8. The opposite are dark squares.
- Line
- 1. A sequence of moves, often in the opening or when analyzing a position.
- 2. An open path on the board (a file or diagonal) that a queen, rook, or bishop can use to move or control squares.
- Line Piece
- A piece that moves in straight lines: the rook, bishop, and queen.
- Long Castling
- See castling long.
- Long Diagonal
- One of the two diagonals that go across the entire board (a1-h8 or h1-a8). Each has eight squares.
- Long-Range Piece
- A bishop, rook, or queen. These pieces can attack or control squares from far away.
- Loose Piece
- A piece that is not defended and is in danger of being captured by the opponent.
- Loss
- When a player is defeated in a game. This can happen by being checkmated, resigning, running out of time, or breaking the rules. A loss means the other player gets a win.
-
Lucena position
a b c d e f g h 8 





8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White wins by 1.Rd1+ Ke7 2.Rd4! Ra1 3.Kc7 Rc1+ 4.Kb6 Rb1+ 5.Kc6 Rc1+ 6.Kb5 Rb1+ 7.Rb4 and the pawn queens. - Lucena Position
- A famous endgame position where a player with a rook and pawn can force a win against a lone rook. It involves cutting off the enemy king and creating a path for the pawn to promote.
- Luft
- A German word meaning "air." In chess, it refers to creating an escape square for a castled king by moving a pawn in front of it. This helps prevent a back-rank mate.
M
- Main Line
- The most common, important, or often played sequence of moves in an opening.
- Majority
- Having more pawns than your opponent on one side of the board (a flank). This can be a strength, as you might be able to create a passed pawn.
- Major Piece
- A queen or a rook. These are the most powerful pieces and can checkmate an enemy king with just their own king's help.
- Man
- A general term for any piece or pawn on the board. It includes both the powerful pieces and the pawns.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 





























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h A typical Maróczy Bind position - Maróczy Bind
- A strong control over the light squares in the center, especially d5, created by White placing pawns on c4 and e4. It's a powerful way to limit Black's moves.
- Master
- A general term for a very strong chess player who would usually beat most amateur players. It can also refer to formal titles like International Master.
- Match
- A competition between two teams or a series of games between two individual players. It's not just one game, but a set of games played until one side wins enough.
- Mate
- Short for checkmate.
- Material
- All the pieces and pawns a player has on the board. Having a "material advantage" means your pieces are worth more points than your opponent's.
- Materialism
- A style of play where a player is very focused on winning material, sometimes even if it means having a worse position. Chess computers used to play this way a lot.
- Mating Attack
- An attack that is aimed at checkmating the enemy king.
- Mating Net
- A position or a series of moves that creates a situation where the enemy king is trapped and will be checkmated.
- Middlegame
- The middle part of a chess game. It comes after the opening (when pieces are developed) and before the endgame (when few pieces are left). This is usually where the main battles happen.
- Miniature
- A very short chess game, usually ending in a win in 20-25 moves or less. Ideally, the losing side doesn't make an obvious blunder. The Opera Game is a famous example.
- Minor Piece
- A bishop or a knight. These pieces are less powerful than major pieces (queens and rooks).
- Minority Attack
- An attack where you advance your pawns on a side of the board where you have fewer pawns than your opponent. The goal is to create weaknesses in their pawn structure.
- Mobility
- How easily your pieces can move around the board. Having good mobility means your pieces have many squares they can go to, giving you more options.
- Mouse Slip
- An accidental mistake made when playing chess online. It happens when you click or drag a piece to the wrong square by mistake, forcing you to make an unintended move.
- Move
- A full turn in chess, which includes one move by White and one move by Black. A single move by either White or Black is called a half-move or ply.
- Move Order
- The specific sequence in which you play your moves in an opening or to carry out a plan. Changing the move order can sometimes have different effects.
- Mysterious Rook Move
- A term coined by Nimzowitsch for moving a rook to a seemingly quiet square on a closed file. The idea is to prepare for the file to open later, or to stop the opponent's plans.
N
- N
- 1. The letter used for the knight when writing down chess moves in English.
- 2. An abbreviation for novelty.
- NN
- Used in old chess records to mean a player whose name is not known. It's like saying "unknown player."
- Norm
- A high-level performance in a chess tournament that helps a player earn a chess title, like Grandmaster or International Master. You usually need three norms to get a title.
- Notation
- Any system used to write down chess moves so games can be replayed and studied later. The most common system today is algebraic notation.
- Novelty
- See theoretical novelty.
O
- Occupation
- When a rook or queen controls an entire rank or file. Or, when a piece or pawn is sitting on a square.
- Octopus
- A slang term for a knight that is very strongly placed deep in enemy territory. It's called an octopus because a knight can attack up to eight squares, like an octopus's tentacles.
- Odds
- When a stronger player gives a weaker player an advantage to make the game more fair. This could be giving them extra pieces, extra moves, or more time on the clock.
- Olympiad
- A big international team chess tournament held every two years. Teams from different countries compete against each other.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 






























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The e-file is open in the French Defense, Exchange Variation after 3.exd5 exd5. - Open File
- A file on the board that has no pawns on it. This makes it a great place for rooks and queens to move and attack.
- Open Game
- A game where many exchanges have happened, creating lots of open lines (files and diagonals). There are usually few pawns in the center. The opposite is a closed game.
- Opening
- The first part of a chess game, usually the first 10-15 moves. In the opening, players develop their pieces, set up their pawn structures, and often castle their king.
- Opening Preparation
- Studying and analyzing chess openings at home. Players do this to prepare for games and find new or better moves to use against opponents.
- Opening Repertoire
- The set of openings that a particular player usually plays. Some players have a wide range of openings, while others stick to just a few.
- Opening System
- An opening where one player's moves are planned out regardless of what the opponent does. The goal is to reach a specific type of middlegame position.
- Open Tournament
- A tournament that anyone can enter, no matter their rating or if they are invited. The opposite is a closed tournament.
- Opposite Castling
- When one player castles on the kingside and the other player castles on the queenside. This often leads to sharp, attacking games.
- Opposition
- A position in the endgame where two kings are on the same rank, file, or diagonal with one empty square between them. The player whose turn it is might be forced to move their king to a worse square.
- Optimal Play
- When both players make the best possible moves at every turn. This is how a perfect chess game would be played.
- Outpost
- A square that is protected by a pawn and is deep in the enemy's territory. It's a great spot to place a piece, especially a knight, to launch an attack.
- Outside Passed Pawn
- A passed pawn that is close to the edge of the board. In the endgame, this pawn can be very strong because it threatens to promote and can distract the opponent's pieces.
- Overextended
- When a player has pushed their pawns too far into the opponent's side without enough support. This can create weaknesses in their own position.
- Overloaded
- A piece that has too many defensive jobs. If it moves to defend one thing, it might leave something else unprotected. This can be used as a tactic to win material.
- Overprotection
- A strategy where you protect an important pawn or square with more pieces than seems necessary. This makes it very hard for the opponent to attack that point.
- Over the Board
- 1. A chess game played in person, face-to-face with your opponent, not online or by mail.
- 2. Analyzing a position during a live game, without the help of computers or outside resources.
P
- P
- The letter used for the pawn when writing down chess moves in English. A lowercase 'p' is sometimes used for a Black pawn.
- Pairing
- How opponents are matched up in a tournament. Common methods are round-robin (everyone plays everyone) and Swiss system (players with similar scores play each other).
-
a b c d e f g h 8 











8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White with a passed pawn on b7. Black has a passed pawn on g6. - Passed Pawn
- A pawn that has no enemy pawns in front of it on its own file or on the neighboring files. This means it has a clear path to queening (reaching the other side of the board).
- Passer
- Short for passed pawn.
- Passive
- Describes a piece or pawn that is not doing much, has few moves, or a position that doesn't offer many attacking chances. The opposite is active.
- Pattern Recognition
- The ability to remember and recognize common chess positions, ideas, and tactics. Experienced players develop this skill, which helps them quickly understand a position without calculating every move.
- Patzer
- A slang term for a weak chess player. See also woodpusher.
- Pawn
- The smallest and most numerous piece in chess. It moves one square forward, or two on its first move. It captures diagonally forward. If it reaches the last rank, it can be promoted to a queen, rook, bishop, or knight.
- Pawn Break
- A pawn move that attacks an enemy pawn to open up lines or change the opponent's pawn structure. See also break.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 

































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White has a large pawn center in the King's Indian Defense, Four Pawns Attack.a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Pawn chains in the French Defense, Advance Variation - Pawn Center
- Your pawns that are in the center of the board. Having a strong pawn center is usually a good thing, giving you space and control.
- Pawn Chain
- Two or more pawns of the same color that are linked diagonally. The weakest part of a pawn chain is its base, as it's not protected by another pawn.
- Pawn Island
- A group of pawns of one color that are separated from other pawns of the same color by empty files. A single pawn island is an isolated pawn.
- Pawn Race
- A situation where both players are trying to push their passed pawns to the other side of the board to promote them first.
- Pawn Roller
- Two connected passed pawns. They are called "rollers" because they can advance together, supporting each other as they move towards promotion.
- Pawn Storm
- An attacking strategy where you advance a group of pawns on one side of the board to break open the opponent's defenses, especially around their king.
- Pawn Structure
- The way the pawns are arranged on the board. Since pawns can't move backward, their positions greatly affect the game and create strengths or weaknesses. Also called pawn skeleton.
- Performance Rating
- A number that shows how well a player performed in a specific tournament or match. It's like a temporary rating for that event.
- Perpetual Check
- When a player can give an endless series of checks to the opponent's king, but cannot checkmate them. This leads to a draw by repetition. It's often used to save a game that would otherwise be a loss.
- Piece
- 1. One of the chessmen used in the game: a king, queen, rook, bishop, or knight. This term usually does not include pawns.
- 2. Sometimes, it refers specifically to a minor piece (bishop or knight).
- Pin
- When a piece is attacked and cannot move (or shouldn't move) because it would expose a more valuable piece (like the king or queen) behind it. See absolute pin and relative pin.
- Playable
- Describes an opening, position, or move that gives a player a reasonable and stable position, even if it's not the best.
- Ply
- A term mostly used in computer chess. It means one single move by either White or Black. So, a full move (White and Black) is two plies.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 





























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Black has accepted the "poisoned" b2-pawn with 8...Qxb2 in the Sicilian Defense, Najdorf Variation. - Poisoned Pawn
- An unprotected pawn that looks tempting to capture, but if you take it, it leads to problems in your position or loss of material.
- Portable Game Notation
- A common computer format for recording chess games. It includes the moves and other game information. Abbreviated as PGN.
- Position
- The arrangement of all the pieces and pawns on the board at any point in the game. If one side has an overall advantage, they are said to have "the better position."
- Positional Play
- A style of play that focuses on long-term plans, gaining small advantages, and understanding the overall position. It's different from tactics, which are about short, forced moves.
- Positional Sacrifice
- A sacrifice where you don't immediately get the material back. Instead, you gain a long-term advantage in your position, like better development or control of important squares.
- Post Mortem
- Analyzing a game after it has finished. Players often do this together, sometimes with spectators, to see what happened and what could have been played better.
- Premove
- In online chess, making a move during your opponent's turn. The move will happen instantly if it's legal once your opponent moves. This is common in fast games like blitz to save time.
- Promotion
- When a pawn reaches the eighth rank (the last row), it must be changed into a queen, rook, bishop, or knight. Most often, it's promoted to a queen. Promoting to anything else is called underpromotion.
- Prophylaxis
- A strategy where you make moves to prevent your opponent's plans or attacks before they can even start. It's about thinking ahead and stopping problems before they happen.
- Protected Passed Pawn
- A passed pawn that is supported and defended by another one of your pawns. This makes it very strong and hard for the opponent to stop.
- Push
- To move a pawn forward.
Q
- Q
- The letter used for the queen when writing down chess moves in English.
- Quad
- A small tournament with four players. Each player plays against every other player once.
- Queen
- The most powerful piece in chess. It can move any number of squares in any straight direction: horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. It cannot jump over other pieces.
- Queening
- The act of promoting a pawn to a queen when it reaches the last rank. This is the most common and usually best choice for promotion.
- Queenside
- The left half of the board from your perspective, where the queens start. It includes the a-, b-, c-, and d-files. The opposite is the kingside.
- Quiet Move
- A move that doesn't immediately attack or capture an enemy piece. These moves often have a hidden, long-term strategic purpose.
R
- R
- The letter used for the rook when writing down chess moves in English.
- Raking Bishops
- Another term for Horwitz bishops, which are two bishops on neighboring diagonals creating a strong attack.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 






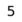


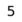
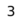
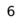






8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White's ranks are indicated on the left (a-file); Black's relative reference to ranks are indicated on the right (h-file). - Rank
- A row of squares on the chessboard. Ranks are numbered 1-8, starting from White's side. So, White's first rank is Black's eighth rank.
- Rapid Chess
- A type of fast chess where each player gets a limited time, usually 30 minutes, for the whole game. It's faster than classical chess but slower than blitz.
- Rating
- See Elo rating system. It's a number that shows a player's skill level.
- Recapture
- To capture an opponent's piece or pawn that just captured one of your pieces. This usually happens on the same square and with pieces of similar value.
- Refute
- To prove that a chess strategy, move, or opening idea is not good or leads to a loss. It's like finding a flaw in a plan.
- Relative Pin
- A pin where the pinned piece *can* legally move, but doing so would expose a more valuable piece (like a queen or rook) behind it to capture. This is different from an absolute pin where the king is behind.
- Resign
- To give up and admit you have lost the game. Players often resign before being checkmated if they see there's no way to win. You can resign by stopping the clock or saying "I resign."
- Reverse Opening
- See colors reversed.
- Romantic Chess
- The style of chess played in the 19th century. It was known for bold attacks, sacrifices, and exciting games.
- Rook
- A piece that moves any number of squares horizontally or vertically along ranks and files. It cannot jump over other pieces. Each player starts with two rooks.
- Rook Lift
- A maneuver where you move a rook forward, often to the 3rd or 4th rank, to make it more active. This helps the rook control half-open files or prepare for attacks.
- Round-Robin Tournament
- A tournament where every player plays against every other player an equal number of times. If they play twice (once with White, once with Black), it's a "double round-robin." This is common for smaller tournaments.
- Royal Fork
- A fork that threatens both the king and the queen at the same time. Since the king must move, the queen will be captured.
- Royal Piece
- In standard chess, this refers to the king and queen. In other chess games, it means any piece that must be protected from capture.
S
- Sac
- Short for sacrifice, often used when a sacrifice leads to a mating attack.
- Sacrifice
- A move where you intentionally give up material (a pawn or piece) to gain something else, like space, faster development, or a strong attack. A sacrifice in the opening is called a gambit.
- Scholar's Mate
- A four-move checkmate that beginners often fall for. White plays 1.e4, then moves their queen and bishop to attack f7, ending with 4.Qxf7#.
- Score
- 1. The written record of moves in a game. See game score.
- 2. A player's points in a tournament. A win is 1 point, and a draw is ½ point.
- Score Sheet
- The paper used to write down the moves of a chess game as it's being played. In formal games, both players usually record the moves.
- Sealed Move
- When a game is paused (adjourned), the player whose turn it is writes their next move on a paper and puts it in a sealed envelope. This prevents them from using the break to analyze the position with computers. This practice is now rare.
- Second
- An assistant who helps a chess player prepare for big matches or tournaments. They help with opening preparation and analysis.
- Semi-Closed Game
- An opening that starts with White playing 1.d4 and Black responding with something other than 1...d5. It's a mix between an open game and a closed game.
- Semi-Open Game
- An opening that starts with White playing 1.e4 and Black responding with something other than 1...e5. It often leads to more open positions than a closed game.
- Seventy-Five-Move Rule
- A rule that says a game is a draw if no capture or pawn move has happened in the last 75 moves by both players. This is an extension of the fifty-move rule.
- Sham Sacrifice
- An offer to sacrifice material that is actually safe. If the opponent takes it, you will either win back equal or more material, or even deliver checkmate. It's a trick.
- Sharp
- Describes a game, position, or move that is risky, complex, and full of tactical possibilities. Sharp positions require very precise play.
- Shot
- Slang for a surprising or sharp move that creates an immediate threat or a difficult challenge for the opponent.
- Silent Move
- A move that doesn't capture or attack an enemy piece directly, but still has a strong hidden effect on the position.
- Simplification
- A strategy of exchanging pieces to make the position less complicated. This can be done to reduce the opponent's attacking forces, reduce their counterplay, or try to get a draw.
- Simul
- Short for simultaneous exhibition.
- Simultaneous Chess
- A type of chess event where one strong player plays against many opponents at the same time. The strong player moves from board to board.
- Skewer
- An attack where a valuable piece is attacked, and when it moves to escape, a less valuable piece behind it is then captured. It's like a pin, but the more valuable piece is in front.
- Skittles
- A casual or informal game of chess, usually played for fun and often without a chess clock. At tournaments, a "skittles room" is where players relax and play informal games.
- Slow
- Describes a strategy or plan that takes too many tempi (moves) to complete. This gives the opponent too much time to react and improve their position.
- Smothered Mate
- A checkmate delivered by a knight where the enemy king is completely surrounded (or "smothered") by its own pieces and cannot move.
- Sofia Rules
- A rule used in some tournaments where players are not allowed to agree to a draw. Draws can only happen through specific rules like stalemate, threefold repetition, or insufficient material.
- Solid
- Describes a move, opening, or style of play that is safe, avoids risks, and focuses on positional play rather than wild tactics.
- Sortie
- When a queen moves out early in the opening, often in front of its own pawns. This is usually done to take advantage of space or an opponent's mistake.
- Sound
- A correct and reliable move or plan. A sound sacrifice has enough compensation. A sound opening has no known way to defeat it. The opposite is unsound.
- Space
- The amount of squares on the board that a player controls. Having a "spatial advantage" means you control more squares, giving your pieces more room to move.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The Spanish bishop on b5 in the Ruy Lopez. - Spanish Bishop
- A White king bishop developed to b5. This is a key feature of the Ruy Lopez opening, also known as the Spanish Opening.
- Speed Chess
- See blitz chess.
- Spite Check
- A check given by a player who is about to lose the game. It doesn't help them, but it delays the checkmate for one move.
- Squeeze
- Making pawn moves that limit the opponent's mobility and options, often leading to zugzwang (where any move makes their position worse).
- Stalemate
- A position where the player whose turn it is has no legal moves, but their king is *not* in check. A stalemate immediately ends the game in a draw.
- Staunton Chessmen
- The standard design of chess pieces used in official competitions. They are easily recognizable.
- Stem Game
- The first known game where a particular opening variation was played. Sometimes the opening is named after this game or the player who played it.
- Strategy
- The overall plan and long-term goals in a chess game. It's about understanding the position and making moves that help you achieve your aims. Strategy is different from tactics, which are short-term calculations.
- Strong
- Describes an effective piece or pawn, a good move, a position with good winning chances, or a highly rated player. The opposite is weak.
- Stronger Side
- The player who has a material or positional advantage in the game.
- Strongpoint
- 1. An opening idea where you defend and keep a central pawn (like on e4 or d4) instead of trading it.
- 2. Any square that is heavily defended and hard for the opponent to attack.
- Strong Square
- A square deep in enemy territory that cannot be attacked by enemy pawns. It's a great place to put one of your pieces, especially a knight.
- Sudden Death
- A time control where each player gets a fixed amount of time for the entire game. If you run out of time, you lose.
- Swindle
- A clever trick or trap played by a player who is in a losing position. They hope to confuse the opponent and turn the game around to a draw or win.
- Swiss Tournament
- A common tournament system where players are matched up based on their scores. Players with similar scores play each other, so the strongest players meet in later rounds. It's different from a round-robin tournament.
-
Example of symmetry
a b c d e f g h 8 
























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h 1.e4 e6 2.d4 d5 3.exd5 exd5 4.Bd3 Bd6 5.Nf3 Nf6 6.0-0 0-0 7.Bg5 Bg4 8.Re1 Nbd7 9.Nbd2 c6 10.c3 Qc7 11.Qc2 Rfe8 12.Bh4 Bh5 13.Bg3 Bxg3 14.hxg3 Bg6 15.Rxe8+ Rxe8 16.Bxg6 hxg6 17.Re1 (diagram). Capablanca–Maróczy, 1926. The game continued 17...Rxe1+ 18.Nxe1 Ne8 19.Nd3 Nd6 20.Qb3 a6 21.Kf1 ½–½ - Symmetry
- When the positions of your pieces are exactly mirrored by your opponent's pieces. This often happens when Black copies White's opening moves. When a player stops copying, they "break symmetry."
T
- Tabia
- A key position in a chess opening that is reached very often. It's like a starting point where many different variations can begin.
- Tactician
- A player who is very good at finding and playing tactical moves and combinations. They often focus on short-term attacks and calculations.
- Tactics
- Short-term attacks, traps, and combinations that require careful calculation. Tactics are often contrasted with strategy, which is about long-term plans.
- Takeback
- In casual games, when both players agree to undo one or more moves that have already been played. This is not allowed in official games.
- Tarrasch Rule
- A general rule that says rooks should usually be placed behind passed pawns, whether they are your own or your opponent's. This helps them support the pawn or stop the enemy pawn.
- Tempo
- A unit of time in chess, meaning one move. You "gain a tempo" if your opponent has to move the same piece twice in the opening. You might "lose a tempo" to gain an advantage in the endgame.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 






























8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h This Scotch Opening position contains tension due to the knights on c6 and d4. Both knights are currently adequately defended, so neither player is forced to release the tension. - Tension
- A position where exchanges are possible, like two pawns facing each other. It creates a feeling of pressure because players have to decide whether to make the capture or not. "Keeping the tension" means avoiding immediate exchanges.
- Theoretical Novelty
- A move in the opening that has never been played before in a recorded game. It's a new idea that can surprise opponents. Also called novelty.
- Threat
- A move or plan that creates a danger for the opponent, like threatening to capture a piece or deliver checkmate. The opponent must respond to the threat.
- Threefold Repetition
- A rule that allows a draw to be claimed if the exact same position appears three times in a game, with the same player to move and the same legal moves available. This prevents games from going on forever.
- Tiebreaks
- Extra rules used in tournaments to decide who wins if two or more players have the same score. They help break ties and determine a single winner.
- Time
- 1. The amount of time each player has to think during a game, measured by a chess clock.
- 2. The number of moves it takes to achieve a goal. If you don't have "enough time," it means you can't reach your goal in the remaining moves.
- Time Control
- The rules about how much time each player has for their moves in a game. It can be a set number of moves per time period (e.g., 40 moves in 2 hours) or a total time for the whole game (e.g., 5 minutes for blitz).
- Time Delay
- A time control method that adds a small delay before your clock starts counting down. This helps players avoid running out of time too quickly. Bronstein delay and Fischer delay are examples.
- Time Pressure
- Also called time trouble or zeitnot. This is when a player has very little time left on their clock (often less than five minutes) to make their remaining moves. It can lead to mistakes.
- Touch-Move Rule
- A very important rule: if you touch one of your pieces, you must move it if it has a legal move. If you move a piece to a square and let go, the move is final. If you touch an opponent's piece, you must capture it if possible. To adjust a piece without moving it, you must say "J'adoube" or "I adjust."
- Tournament
- A competition with more than two players or teams, usually held in one place over a short time. Tournaments have rounds, and opponents are matched using systems like round-robin or Swiss.
- Tournament Director
- The person in charge of a chess tournament. They make sure the rules are followed, handle disputes, and organize the pairings. Abbreviated as TD.
- Transposition
- When you reach a position on the board using a different sequence of moves than is usually played. This can sometimes surprise your opponent or lead to a different type of game.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 

































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h With 4...Nbd7 Black sets a trap in the QGD (1.d4 d5 2.c4 e6 3.Nc3 Nf6 4.Bg5). White cannot win the pawn on d5 due to the Elephant Trap. - Trap
- A move that tries to trick your opponent into making a mistake that will cost them material or even the game. See also List of chess traps.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 






8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h White to move should underpromote the c7-pawn to a rook; promoting to a queen gives stalemate. - Underpromotion
- When a pawn reaches the last rank and is promoted to a rook, bishop, or knight instead of a queen. This is rare, usually done to avoid a stalemate or to deliver a special check with a knight.
- Unsound
- The opposite of sound. Describes a move, plan, or sacrifice that is not correct and can be defeated.
V
- Variation
- 1. A sequence of moves, often an alternative way to play an opening or analyze a position. It's a possible path the game could take.
- 2. A specific named sequence of moves within a larger opening, like the Dragon Variation in the Sicilian Defense.
W
- Waiting Move
- A move made just to pass the turn to the opponent. It's useful when your opponent is in zugzwang, meaning any move they make will make their position worse.
- Weakness
- A pawn or square that can be easily attacked and is hard to defend. Players try to create weaknesses in their opponent's position and protect their own.
- Weak Square
- A square that is hard to defend, often because it cannot be protected by your own pawns (a hole). Opponents can use these squares to place their pieces and launch attacks.
- White
- The player who makes the first move in a game. Their pieces are usually light-colored. See also Black.
- Win
- A victory for one player in a game. This can happen by checkmate, the opponent resigning, the opponent running out of time, or the opponent breaking the rules. A win means the other player gets a loss.
- Windmill
- A powerful combination where two pieces work together to give a series of alternating checks and discovered checks. This forces the enemy king to move each turn, allowing the attacking player to capture other pieces. The Torre–Lasker game is a famous example.
- Wing
- The sides of the board, away from the center. The queenside (a-, b-, c-files) and the kingside (f-, g-, h-files). Also called flank.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 
































8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h Wing Gambit in the Sicilian Defense - Wing Gambit
- The name for openings where a player sacrifices a pawn on the side of the board (a "wing pawn"), usually the b-pawn.
- Winning Position
- A position where one player, by playing perfectly, can force a checkmate against any defense. Also called a won game.
- Woman Grandmaster
- The highest chess title specifically for women, given by FIDE. Abbreviated as WGM.
- Wood
- Slang for chess pieces. If "a lot of wood came off the board," it means many pieces were exchanged.
- Woodpusher
- Slang, often used in a negative way, for a weak chess player. Also called a patzer or duffer.
- World Champion
- The winner of the World Chess Championship, recognized as the best chess player in the world.
- Wrong Bishop
- A bishop that becomes less useful in the endgame because it's on the wrong color squares to help its pawn promote.
- Wrong Rook Pawn
- A rook pawn that, in combination with a bishop, cannot be promoted to a queen because the bishop cannot control the pawn's promotion square. This often leads to a draw.
-
a b c d e f g h 8 





8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h A wrong rook pawn at a5 with a wrong-colored bishop. In this position, White cannot force promotion and Black can force a draw.
X
-
Example of an X-ray defense
a b c d e f g h 8 












8 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 a b c d e f g h The white queen has just put the king in check, and the white rook provides an X-ray defense of the white queen. - X-ray
- When a piece's power (to attack or defend) seems to go *through* an enemy piece. An X-ray attack is like a skewer, where a valuable piece moves, revealing another piece behind it to be captured. An X-ray defense is when one piece protects another through an enemy piece in between.
Z
- Zeitnot
- A German word meaning "time need." It's when a player has very little time left on their clock to finish their moves. Also called time pressure or time trouble.
- Zonal Tournaments
- Tournaments organized by FIDE that are the first step in qualifying for the World Chess Championship. Top players from different regions (zones) compete here.
- Zugzwang
- A German word meaning "compulsion to move." It's a situation where a player is forced to make a move, but any legal move they make will make their position worse. This usually happens in the endgame.
- Zwischenschach
- A German word meaning "in-between check." It's a surprising check played in the middle of a sequence of moves, forcing the opponent to react to the check before continuing their plan.
- Zwischenzug
- A German word meaning "in-between move." It's a move played before an expected reply. Often, it's a threat that forces the opponent to deal with it first, changing their plans.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Términos relacionados con el ajedrez para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Términos relacionados con el ajedrez para niños
- Chess equipment

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Glossary of chess Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.