Refraction facts for kids
Refraction is when a wave changes direction because its speed changes. This often happens when a wave moves from one transparent material (called a medium) to another. Think of light moving from air into water. Sound waves can also refract!
Contents
How Light Bends
You see light refraction all the time! It's why things underwater look closer than they really are. It's also how lenses work in things like glasses, cameras, binoculars, microscopes, and even your own eyes. Refraction also creates amazing natural sights like rainbows and mirages.
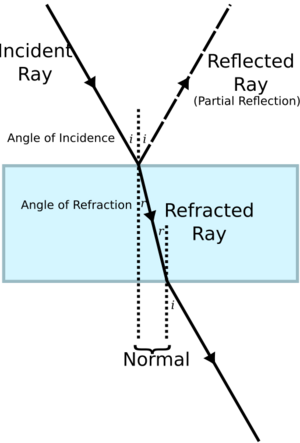
When light moves from one clear material to another, it changes both its speed and its direction. For example, when light travels from air into water, it slows down and bends.
Imagine light hitting a denser material, like water from air. The light ray will "bend" towards an imaginary line called the "normal" (which is straight up from the surface). If it then goes back into a less dense material, it will bend back again.
A great example is putting a straw in a cup of water. The straw looks bent at the water's surface! This happens because light rays from the straw change speed and direction as they move from the water into the air before reaching your eyes.
Think of light like a car driving. If one side of the car hits a patch of gravel (a new "medium") before the other side, that tire slows down first. This makes the car turn. Similarly, when light hits a new material at an angle, one part of the light wave slows down before the other, causing the whole wave to bend. The amount of bending is described by something called Snell's law.
What is Refractive Index?
The refractive index (or n) of a material is a number that tells us how much light slows down and bends when it goes through that material. It's found by dividing the speed of light in empty space (a vacuum) by the speed of light in the material. Materials with a higher refractive index bend light more.
Colors and Prisms
Refraction is also why we see rainbows! It's also why a glass prism can split white light into all the colors of the rainbow. Glass has a higher refractive index than air. When white light enters a prism, each color (which has a slightly different frequency) bends by a different amount. This effect is called dispersion, and it separates the colors so you can see them individually.
Light Bending in the Air
The air's refractive index changes with its density, which depends on temperature and pressure. Higher up in the atmosphere, the air is thinner, so its refractive index is lower. This causes light rays to bend towards the Earth's surface when they travel long distances through the atmosphere. This is why stars appear slightly higher in the sky than they actually are when they are near the horizon. It also makes the sun visible to us a little bit before it truly rises above the horizon during a sunrise!

Differences in air temperature can also make light bend. You might see this as a heat haze shimmering over a hot road, or above a fire, or from engine exhaust. When hot and cold air mix, objects viewed through them can seem to shimmer or move around. This is because the light rays are constantly bending in different ways as they pass through the moving pockets of hot and cold air. This effect can even make images from powerful telescopes look blurry if they don't use special technology to correct for it.

Another cool effect of air temperature changes near the ground is a mirage. On a hot sunny day, the air right above a road gets very hot. This hot air bends light coming from the sky at a shallow angle towards your eyes. It makes the road look like it's reflecting the sky, giving the illusion that there's water covering the road!
Images for kids
-
The Golden Gate Bridge image is bent and distorted by many different water drops.
See also
 In Spanish: Refracción para niños
In Spanish: Refracción para niños