Sarpo Laggo Glacier facts for kids
The Sarpo Laggo Glacier is a huge river of ice found in the Karakoram mountains. These mountains are part of the larger Himalaya mountain range, which is one of the biggest in the world! This glacier is located in a part of China called Xinjiang. The name Sarpo Laggo actually means "young husband."
Contents
What is the Sarpo Laggo Glacier?
The Sarpo Laggo Glacier is a long, slow-moving river made of ice. It sits north of a mountain range called the Baltoro Muztagh. Glaciers like Sarpo Laggo are important because they store a lot of the world's fresh water. They also help shape the land around them over thousands of years.
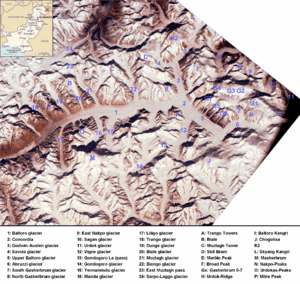
Where is Sarpo Laggo Located?
This glacier is in the Xinjiang region of China. It's nestled within the mighty Karakoram mountains. These mountains are known for having some of the tallest peaks in the world, including K2, the second-highest mountain.
How to Reach the Glacier
There are a couple of ways to get to the Sarpo Laggo Glacier.
- One way is from the Pakistani side of the Karakorams. You would start near the Baltoro Glacier and cross a path called the Old Muztagh Pass. This pass is northeast of the famous Trango Towers, which are giant rock pillars popular with climbers.
- However, it's usually easier to reach the glacier from the Chinese side. This involves a long journey starting from a city called Kashgar on the Karakoram Highway. Along the way, you would even pass by the northern base camp of K2, the huge mountain.
Who is Sarpo Laggo Named After?
The Sarpo Laggo Glacier is named after a famous explorer named Francis Younghusband. He was the very first person to travel through the Old Muztagh Pass. By doing so, he was the first to explore the area where the Sarpo Laggo Glacier is found.
Another Glacier Named Younghusband
Interestingly, there's another glacier nearby that is also named after Francis Younghusband. This one is simply called the Younghusband glacier, but it's also known as the Biango glacier. It flows from a mountain called Muztagh Tower and moves towards the Baltoro Glacier.