Scottish Parliament facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Scottish Parliament
|
|
|---|---|
| 6th Scottish Parliament | |
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 12 May 1999 |
| Preceded by |
|
|
New session started
|
13 May 2021 |
| Leadership | |
|
Charles III
Since 8 September 2022 |
|
|
Presiding Officer
|
Alison Johnstone
Since 13 May 2021 |
|
Deputy Presiding Officer
|
|
|
John Swinney, SNP
Since 8 May 2024 |
|
|
Deputy First Minister
|
Kate Forbes, SNP
Since 8 May 2024 |
|
Minister for Parliamentary Business
|
Jamie Hepburn, SNP
Since 8 May 2024 |
|
Russell Findlay, Conservative
Since 27 September 2024 |
|
| Structure | |
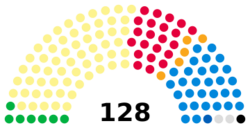
| Seats | 129 |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Government (60)
Opposition (68)
Other (1)
|
| Elections | |
| Additional-member system (Mixed-member proportional representation) | |
|
Last election
|
6 May 2021 |
|
Next election
|
On or before 7 May 2026 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Scottish Parliament Building Edinburgh, Scotland |
|
The Scottish Parliament (Scottish Gaelic: Pàrlamaid na h-Alba Scots: Scots Pairlament) is Scotland's law-making body. It is located in Edinburgh, the capital city. People often call it Holyrood because of the area where it stands.
This Parliament is chosen by the people of Scotland. Its main job is to check on the Scottish Government. It also makes laws for Scotland on many topics. These topics are called "devolved matters." Some other topics are "reserved" for the Parliament of the United Kingdom in London.
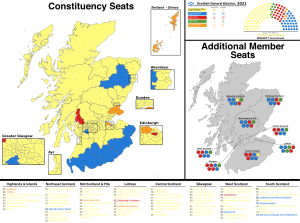
The Scottish Parliament has 129 members. They are called Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs). MSPs are elected for five-year terms. They are chosen using a special voting system. This system combines electing members for local areas and for larger regions. The last election was on 6 May 2021. The Scottish National Party won the most seats.
Contents
- What is the Scottish Parliament?
- See also
What is the Scottish Parliament?
The Scottish Parliament is a modern law-making body. It helps Scotland manage its own affairs. It works to improve life for everyone in Scotland.
How Did the Scottish Parliament Start?
Scotland has a long history of having its own parliament.
Scotland's First Parliament
Before 1707, Scotland was an independent country. It had its own parliament. This first Parliament of Scotland existed from the 13th century. In 1707, Scotland joined with England. They formed a new country called Great Britain. At that time, Scotland's parliament stopped existing. All laws were then made by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in London.
Why a New Parliament?
For almost 300 years, Scotland did not have its own parliament. But many people in Scotland wanted more control over their own country. They wanted a "devolved" parliament. This means a parliament with powers to make decisions for Scotland.
In 1997, people in Scotland voted in a special election called a referendum. They voted to bring back the Scottish Parliament. This new Parliament would have powers to make laws and even change some taxes. The Scotland Act 1998 set out these new powers. The first meeting of the new Parliament was on 12 May 1999.
Building the Parliament's Home
When the Parliament first started, it met in a temporary building. This was the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland in Edinburgh.
Since September 2004, the Parliament has its own special building. It is in the Holyrood area of Edinburgh. A Spanish architect named Enric Miralles designed it. The building has unique features. These include leaf-shaped parts and walls made of stones. Queen Elizabeth II officially opened the new building on 9 October 2004. In September 2024, the Scottish Parliament celebrated its 25th anniversary. The King and Queen attended the celebration.
Who Leads the Parliament?

After each election, MSPs choose a Presiding Officer. This person is like a speaker in other parliaments. They lead the meetings and make sure rules are followed. Two Deputy Presiding Officers are also chosen.
The Presiding Officer (currently Alison Johnstone) must be fair to all parties. They help the Parliament work well. They also represent the Scottish Parliament to other countries.
Inside the Parliament Chamber
The main meeting room is called the debating chamber. It has seats arranged in a semicircle. This design helps encourage everyone to work together. There are 131 seats in total. 129 seats are for the elected MSPs. The other two seats are for Scotland's top lawyers, called Law Officers. They can speak but cannot vote.
MSPs usually sit with members of their own political party. The First Minister and other government ministers sit in the front row. The Presiding Officer sits opposite them.
A special ceremonial mace is displayed in the chamber. It is made of silver and gold. It has words like Wisdom, Compassion, Justice, and Integrity. The mace shows that the Parliament has the power to make laws.
How Does the Parliament Work?
The Parliament usually meets on Tuesdays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays. These meetings happen from January to June and September to December. The public can watch debates and committee meetings. You can also watch them online or on TV.
Making Decisions and Voting

At "Decision Time," MSPs vote on new ideas and changes. A bell rings to call all MSPs to the chamber. They vote using electronic consoles at their desks. This means results are known very quickly.
Political parties usually tell their MSPs how to vote. These instructions are given by party members called "whips." Sometimes, parties allow "free votes." This means MSPs can vote however they wish, often on important moral issues.
Working in Committees

A lot of the Parliament's work happens in smaller groups called committees. These committees are very important. They look closely at specific topics like health or education. They also check new laws and suggest changes. Committees can investigate issues and publish their findings.
What Laws Can the Parliament Make?
The Scotland Act 1998 explains what the Scottish Parliament can do. It lists the areas where it can make laws. These are called "devolved matters."
Powers for Scotland
The Scottish Parliament can make laws on many important topics for Scotland. These include:
- Farming, fishing, and looking after animals
- Protecting the environment and managing land
- Food safety and standards
- Water supply and cleaning
- Growing Scotland's economy
- Some taxes, like income tax and council tax
- Education (from nursery to university)
- Scottish and Gaelic languages
- Health and social care
- Scotland's legal system, courts, and police
- Fire and rescue services
- Prisons and parole
- Rules for things like air guns and alcohol sales
- Recording births, deaths, and marriages
- Local government
- Culture, sports, arts, and tourism
- Roads, buses, trains, and ferries within Scotland
- Housing and building standards
- Charities
- Some energy topics, like onshore oil
- Bank holidays and Sunday trading
- Support for pregnant women and children
Powers Kept by the UK Parliament
Some matters are "reserved" for the UK Parliament in London. The Scottish Parliament cannot make laws on these. These include:
- The UK's constitution
- Foreign affairs (how the UK deals with other countries)
- Broadcasting (TV and radio)
- The UK's armed forces and national security
- Overall UK money and economic policy
- Most taxes, like VAT and corporation tax
- Pensions and financial services
- Drug policy
- Data protection
- Firearms
- Immigration and nationality
- Betting and lotteries
- Competition rules and intellectual property
- Product standards and weights
- Telecommunications and postal services
- Electricity, coal, oil, gas, and nuclear energy
- Employment rules and health and safety at work
- Most transport safety rules
- Many UK-wide social security benefits
The United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 also affects the Parliament's powers. It aims to ensure goods and services can move freely across the UK. This law has led to discussions about how much freedom the Scottish Parliament has to make different economic choices.
How Does the Parliament Check the Government?

The political party (or parties) with the most MSPs forms the Scottish Government. The Parliament chooses a First Minister. This person leads the Scottish Government. The First Minister then chooses other ministers to help run different government departments.
MSPs can ask the First Minister and other ministers questions. This happens during special "Question Time" sessions. It is a way to make sure the government is doing its job well. For example, "First Minister's Question Time" happens every Thursday. This allows MSPs to ask the First Minister directly about important issues.
Who Are the Members of Parliament?
There are 129 MSPs in the Scottish Parliament. They represent people from all over Scotland.
How Members Are Chosen
Scotland uses a special voting system called the "Additional Member System." When you vote, you get two votes:
- One vote is for a specific person to represent your local area (constituency). 73 MSPs are chosen this way.
- The second vote is for a political party in a larger region. 56 MSPs are chosen from these party lists. This helps make sure the number of seats each party gets is fair.
If an MSP leaves Parliament, a new election is held for constituency seats. For list seats, the next person on the party's list takes their place.
Who Can Be a Member?
To be an MSP, you must be at least 18 years old. You also need to be a citizen of the UK, Ireland, a Commonwealth country, a British overseas territory, or an EU citizen living in the UK. People working in the police or armed forces cannot be MSPs. Also, you must be mentally capable to serve.
When Are Elections Held?
Regular elections for the Scottish Parliament happen every five years. The last election was on 6 May 2021. Sometimes, an extra election can happen if the Parliament votes for it.
Who Can Vote?
To vote in Scottish Parliament elections, you must live in Scotland. You also need to be a citizen of the UK, Ireland, an EU country, or another country with permission to live in the UK. The voting age in Scotland is 16. This means 16 and 17-year-olds can vote in Scottish Parliament elections.
See also
 In Spanish: Parlamento Escocés para niños
In Spanish: Parlamento Escocés para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |