Sieges of Ceuta (1694–1727) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sieges of Ceuta |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Spanish–Moroccan conflicts | |||||||
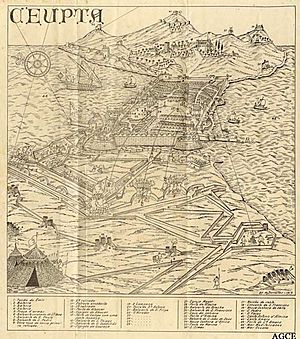 The city of Ceuta in 1700 during the siege |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Combatants | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
up to 40,000 | ||||||
The Sieges of Ceuta were a very long series of attacks on the city of Ceuta. This city is located on the North African coast and was controlled by Spain. Moroccan forces tried to take control of Ceuta for many years.
The first siege started on October 23, 1694. It lasted for a very long time, finally ending in 1720. During these 26 years, Ceuta changed a lot. It lost many of its old Portuguese traditions. Most of the fighting happened around the city walls. However, Spanish forces also made small attacks on the Moroccan coast. They also captured ships in the Strait of Gibraltar.
After a short break, a second siege began in 1721. This siege lasted until April 22, 1727. These attacks are known as one of the longest sieges in history.
Contents
Why Did the Sieges Happen?
Ismail bin Sharif was a powerful leader in Morocco. He had built a strong new country. This country was powerful enough to challenge European nations. It also challenged the Ottoman Empire in what is now Algeria.
Ismail's forces had already captured several important cities. These included Mehdya, Tangier, and Larache. In 1692, they took Asilah. In 1694, he gave his governor, Ali bin Abdallah, a new mission. This mission was to conquer Ceuta.
What Happened During the Sieges?
The First Siege Begins
After surrounding Ceuta, the Moroccan soldiers started building homes. They also began farming the land around the city. This helped them to feed themselves during the long siege.
The governor of Ceuta asked for help from Spain. Troops were sent from towns in Andalusia and even from Portugal. However, the Portuguese troops caused some problems. Ceuta had been controlled by Portugal before. Because of this, some people worried that Portugal wanted to take Ceuta back. The Portuguese soldiers left without fighting.
During this time, there were many attacks and counterattacks. Both sides gained and lost positions around the city walls. In July 1695, a thick fog covered Ceuta. Moroccan troops used this fog to launch a surprise attack. They attacked during a change of guard. The Moroccan soldiers captured the central square, called the Plaza de Armas. Many Spanish defenders were killed trying to escape. Later, the Spanish fought back and took the Plaza de Armas again.
Gibraltar Is Captured
In 1704, English and Dutch forces captured Gibraltar. This was a big problem for Ceuta. Gibraltar was a key point on the supply route from Spain. Getting supplies through Tarifa became hard due to strong winds. Other nearby Spanish cities were busy fighting in the War of the Spanish Succession. This made them unable to help Ceuta.
On August 7, 1704, Prince George of Hesse-Darmstadt sent a message to Ceuta. He sent Juan Basset with part of the English and Dutch fleet. They asked Ceuta to surrender. They promised that the siege would end if the city surrendered. However, the governor and the people of Ceuta refused. They strengthened the Almina peninsula to protect against attacks. No English attack happened. The fleet had to go fight a French and Spanish fleet (Battle of Málaga). This fleet was trying to retake Gibraltar.
Once Gibraltar was controlled by the English, it became a supply source. But it supplied the Moroccan forces attacking Ceuta, not the Spanish defenders.
The Marquis of Lede Arrives
The siege continued for several more years without major changes. Then, in 1720, 16,000 soldiers arrived. They were led by the Marquis of Lede. These troops were returning from another war. Spain had not done well in that war. After losing land in Italy, Ceuta became very important for Spain's defense in the Mediterranean.
The Marquis launched a successful attack against the Moroccan forces. The Moroccans had to retreat to Tetuán. However, a few months later, a disease broke out in 1721. The Marquis decided to leave Ceuta. He saw no way to capture Tetuán or Tangier.
The Second Siege
After the Marquis left, the Moroccan forces quickly started attacking again. Another siege began in 1721. More battles took place until the death of Mawlay Ismail in 1727. After his death, a fight for the throne broke out among his sons. On April 22, a Spanish scouting team from Ceuta confirmed it. The Moroccan forces had finally left.
What Happened After the Sieges?
During the long sieges, many buildings in Ceuta were destroyed. They had to be rebuilt. The Almina area, which was almost empty before the siege, started to get more people.
Another big change was that Ceuta slowly lost its Portuguese identity. The Portuguese language and money were replaced by the Spanish language and money. Many families left Ceuta because of the long siege. Also, many soldiers who defended the city were from Andalusia in Spain. Other people were drawn to the city because of the large number of troops there. This helped Ceuta become more Spanish.
Images for kids
See Also
 In Spanish: Sitio de Ceuta (1694-1727) para niños
In Spanish: Sitio de Ceuta (1694-1727) para niños




