Solar power in Australia facts for kids
Solar power is a big part of how Australia gets its electricity. As of December 2023, Australia had over 3.69 million solar power systems installed. These systems can produce a total of 34.2 gigawatts (GW) of electricity.
In 2019, many new solar projects were being built or planned. Solar energy made up 12.4% of Australia's total electricity in 2021. This shows how much Australia has grown in using solar power.
Australia has quickly become a world leader in solar power. It now has the most solar capacity per person, with over 1 kilowatt (kW) for every person. The amount of solar power installed in Australia grew very fast between 2009 and 2016.
The first large solar power plant, the 1 MW Uterne Solar Power Station, opened in 2011. The Greenough River Solar Farm opened in 2012 with 10 MW of power. Solar panels have also become much cheaper. In 2013, it cost less to use solar power than to buy electricity from the main grid.
Most solar panels in Australia come from China.
Contents
Types of Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems in Australia are divided into different types.
| Off grid (MW) |
Grid-connected distributed (MW) |
Grid-connected centralized (MW) |
Total (MW) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 173 | 4,580 | 356 | 5,109 |
| 2016 | 210 | 5,329 | 446 | 5,985 |
| 2017 | 247 | 6,115 | 740 | 7,103 |
| 2018 | 284 | 8,030 | 3,272 | 11,586 |
| 2020 | 10,700 | |||
| 2021 | 361 | 16,760 | 9,008 | 26,129 |
| 2022 | 395 | 19,588 | 10,385 | 30,368 |
The most common type in 2018 was grid-connected distributed solar. These are mostly solar panels on roofs of homes, businesses, and factories. Residential systems are usually small (under 9.5 kW). Commercial systems are medium-sized (9.5 to 99.9 kW), and industrial systems are larger (100 kW to 5 MW).
The next biggest type was grid-connected centralized plants. These are very large solar farms built on the ground, usually producing more than 5 MW of power. Off-grid solar, which means systems not connected to the main electricity grid, was the smallest type.

By the end of 2018, Australia had over 2 million rooftop solar systems. More than 200,000 new systems were installed in 2018 alone. Australia leads the world in how many homes have solar panels, with over 20% of houses having them. By 2021, Australia had 13 GW of rooftop solar.
New solar inverters (devices that change solar power into usable electricity) must have special features. These features help the local electricity grid stay stable and improve power quality.
Solar Power Potential
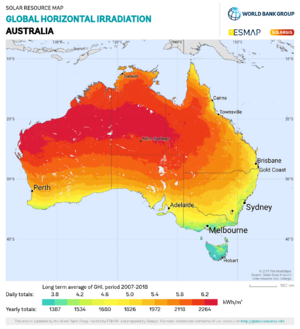
Australia has a huge amount of sunshine, which is perfect for making solar energy.
How Much Sun Australia Gets
Australia's dry weather and location mean it gets a lot of sunshine. Most of the country receives more than 4 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of sunlight per square metre each day in winter. Some northern areas get over 6 kWh per square metre daily. Western and Northern Australia have the best potential for solar power.
Australia gets much more sunlight than places like Europe or North America. Only desert areas in Africa, the southwestern U.S., and parts of South America get similar amounts. However, the sunniest parts of Australia are far from where most people live.
Rooftop Solar Potential
Experts believe Australia could install 179 GW of solar power on roofs across the country. At the end of 2018, Australia only had about 8 GW of rooftop solar. This means the country was using less than 5% of its possible rooftop solar power.
| Type of roof top solar PV | Potential GW |
|---|---|
| Residential | 96.0 |
| Rural / Primary production | 33.9 |
| Industrial / Utilities | 19.0 |
| Commercial / Business | 9.3 |
| Special use | 6.7 |
| Mixed use | 4.0 |
| Community use | 3.9 |
| Unknown | 2.2 |
| Conservation / National park | 2.1 |
| Recreational / Open space | 1.7 |
| Transport / Infrastructure | 0.6 |
If all this rooftop solar potential were used, it could produce more electricity than Australia currently uses each year.
Help and Support for Solar
Rebates and Incentives
The Australian Government used to offer rebates, like the Solar Homes and Communities Plan, to help people install solar panels. This program ended in 2009 and was replaced by the Solar Credits Program. This new program gave people more Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) for their solar systems.
Schools could also get grants to install solar panels through the National Solar Schools Program. Over 2,870 schools have installed solar panels through this program.
The Victorian state government helps homeowners by offering rebates and interest-free loans for solar panels.
The Australian Government also has financial incentives called Small-Scale Technology Certificates (STCs). The number of STCs you get depends on where you live in Australia and the size of your solar system. Each STC is worth money, which can save you about 25-30% on the cost of solar panels. This program will slowly reduce the number of STCs given out each year until it ends on December 31, 2030.
Similar help is available in some states for installing solar batteries and solar hot water systems.
Selling Excess Solar Power
Many states have programs that let people with solar panels sell any extra electricity they produce back to the main electricity grid. This is called a "feed-in tariff." The price paid for this electricity, how long payments are guaranteed, and the size of the system allowed can vary.
For example, in the Australian Capital Territory (ACT), a program started in 2009 paid a good price for solar electricity for 20 years. South Australia also introduced a solar feed-in tariff and installed solar panels on major public buildings. In 2018, the Queensland government offered interest-free loans for solar panels and storage.
South Australia has the highest number of homes with solar power per person in Australia.
Renewable Energy Goals
In 2001, the Australian government set a goal to have 20% of its electricity come from renewable sources by 2020. This goal was called the mandatory renewable energy target (MRET). It aimed to increase new renewable energy generation. The MRET required electricity buyers to purchase Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro. This helps support these technologies.
Later, the MRET was split into large-scale and small-scale goals. Australia now aims for 33,000 GWh of renewable energy from large sources by 2020, which is about 23.5% of its electricity.
Funding for Solar Projects
The Solar Flagships program set aside $1.6 billion to help build large solar power plants. This funding was for four new solar plants that could produce as much power as a coal plant (up to 1000 MW). These projects also needed funding from the companies building them.
Major Solar Projects
Australia has many large solar farms across different states. Here are some of the biggest ones, producing over 100 MW of power.
| State | Project/ |
Nameplate capacity (MWac) |
Commissioning | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSW | New England Solar | 520 | 2023 | Very large photovoltaic farm. |
| Qld | Western Downs Green Power Hub | 400 | 2023 April | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Vic | Glenrowan West Solar Farm | 149 | 2020 December | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Limondale Solar Farm | 313 | 2020 January | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Darlington Point Solar Farm | 275 | 2020 November | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| SA | Bungala Solar Power Farm | 220 | 2018 May | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Sunraysia Solar Farm | 200 | 2020 November | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Wellington Solar Farm | 174 | 2020 November | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Daydream Solar Farm | 168 | 2018 October | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Suntop Solar Farm | 150 | 2021 August | Uses special two-sided panels that track the sun. |
| NSW | Coleambally Solar Farm | 150 | 2018 September | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Finley Solar Farm | 133 | 2019 August | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Sun Metals Solar Farm | 124 | 2018 May | Uses thin-film panels that track the sun. |
| Qld | Ross River Solar Farm | 116 | 2018 September | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Gunnedah Solar Farm | 110 | 2021 July | Uses two-sided panels that track the sun. |
| Vic | Glenrowan West Solar Farm | 110 | 2021 June | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Darling Downs Solar Farm | 110 | 2018 May–September | Next to a power station. |
| SA | Tailem Bend Solar Power Farm | 108 | 2019 March | Photovoltaic, fixed panels. |
| NSW | Nevertire Solar Farm | 105 | 2019 December | |
| NSW | Nyngan Solar Plant | 102 | 2015 June | Was the largest solar PV plant in the Southern Hemisphere when built. |
| WA | Merredin Solar Farm | 100 | 2020 July | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Bomen Solar Farm | 100 | 2020 June | Uses two-sided panels that track the sun. |
| Qld | Yarranlea Solar Farm | 100 | 2020 January | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Vic | Numurkah Solar Farm | 100 | 2019 May | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Haughton Solar Farm | 100 | 2019 May | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Lilyvale Solar Farm | 100 | 2019 March | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| Qld | Clare Solar Farm | 100 | 2018 May | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
| NSW | Metz Solar Farm | 115 | 2022 September | Photovoltaic, panels track the sun. |
Australian Capital Territory
A 20 MW solar power plant was built in Royalla, near Canberra. It has 83,000 solar panels and can power 4,400 homes. It opened in 2014 and was the largest solar plant in Australia at the time.
New South Wales
Solar farms in New South Wales often produce more electricity for their size than those in other states. New solar farms are being built that could power 50,000 homes.
Northern Territory
The Northern Territory has solar concentrator dishes in three remote areas: Hermannsburg, Yuendumu, and Lajamanu. These dishes focus sunlight to generate electricity.
Together, these solar stations produce enough power to save a lot of diesel fuel and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The project cost A$7 million and won an award in 2005. The government has also funded many small solar systems for remote Indigenous communities.
Queensland
By 2018, over 2 GW of solar farms were finished or being built in Queensland.
The 100 MW Clare Solar Farm started sending electricity to the grid in May 2018. The 50 MW AC Kidston Solar Project was built on an old gold mine site. This is the first part of a plan to combine solar energy with pumped hydro storage.
The Lilyvale Solar Farm, with 130 MW AC capacity, is also being built. It will be located near Emerald. Other solar farms like Hamilton Solar Farm, Hayman Solar Farm, and Daydream Solar Farm have also come online in Queensland.
South Australia
The Bungala Solar Power Project near Port Augusta is a major solar farm in South Australia. Stage 1 can produce 110 MW.
Sundrop Farms has a special solar thermal power plant that can generate 40 MW. It was finished in 2016. There's also a floating solar panel array at a wastewater treatment plant.
The largest rooftop solar array in South Australia was installed at Yalumba Wine Company in 2017. Other big installations include those at Flinders University and Adelaide Airport. The Adelaide Showground had the first 1 MW solar power station in Australia.
In 2017, the state government announced new funding for renewable energy projects. These include a solar PV and battery project at a distribution centre and solar panels at the University of South Australia.
South Australia sometimes produces more solar power than it needs. New solar systems in South Australia must have special features to help manage the grid.
Victoria
The 100 MW PV Mildura Solar Concentrator Power Station was planned but later cancelled. It was meant to be a very efficient solar power station.
The Gannawarra Solar Farm is a 60 MW DC project and was the first large-scale solar farm built in Victoria. The Bannerton Solar Park is another large project that generates up to 88 MW of electricity.
Western Australia
Western Australia's first big solar farm, the Greenough River Solar Farm, opened in 2012. It has 150,000 solar panels. The 20 MW Emu Downs Solar Farm became the largest in WA when it opened in 2018. It is located next to a wind farm.
The largest rooftop solar array in Western Australia was completed in 2021 at Ellenbrook city shopping centre, with a total capacity of 2.8 MW.
A huge project called the Asian Renewable Energy Hub is planned. It will combine solar and wind power to produce up to 26 gigawatts of energy.
Solar Cities Program
The Solar Cities program was a project to show how solar power, smart meters, and saving energy could work in Australian cities. Townsville, Queensland, was one of these cities.
Renewable Energy Master Plan 2030
The Council of Sydney aims to make the city run 100% on renewable energy by 2030. This plan was announced in 2014 and won an award for its efforts.
Solar Power Facts
| Year | Capacity (MW) |
Watts per person |
Electricity generation % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 510 | 23 | 0.4% |
| 2020 | 20,741 | 809 | 9.0% |
| 2022 | 30,379 | 1,155 | 14.2% |
See also
 In Spanish: Energía solar en Australia para niños
In Spanish: Energía solar en Australia para niños
- Australia–ASEAN Power Link
- Building-integrated photovoltaics
- Centre for Appropriate Technology (Australia)
- List of countries by electricity production from renewable sources
- List of renewable energy topics by country
- List of solar farms in South Australia
- Australian Renewable Energy Agency