Staphylococcal infection facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Staphylococcal infection |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
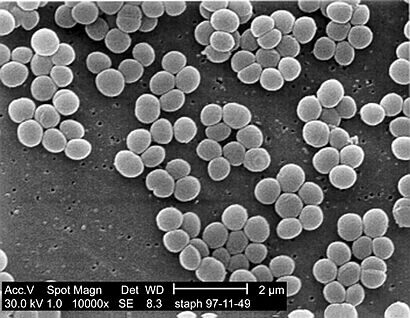
| SEM micrograph of S. aureus colonies; the grape-like clustering is common to Staphylococcus species. |
A staphylococcal infection, or staph infection, is an illness caused by tiny germs called Staphylococcus bacteria. These bacteria are very common.
They often live harmlessly on our skin and inside our noses. But if they get into the body through a cut or scrape, they can cause problems. Once inside, these bacteria can spread to different body parts. They can even make toxins (poisons) that can harm organs like the heart.
If doctors find staph bacteria are causing an illness, they often treat it with antibiotics. They might also drain any infected areas. However, some staph germs have become antibiotic resistant. This means certain medicines don't work against them anymore. For these tough infections, your body's own immune system is the main defense. If your immune system is weak, the infection can get serious quickly. Anyone can get a staph infection, but some people, like children, are more likely to get them.
Contents
What Are Staph Infections?
Staph infections can show up in many ways. They can affect your skin, bones, or even your blood. Here are some common types:
| Main Staphylococcus aureus Infections | |
|---|---|
| Type of Infection | Examples |
| Skin infections (small areas) | |
| Skin infections (spread out) |
|
| Deep infections |
|
| Other infections | |
| Toxin-related illnesses |
|
Other types of staph infections include:
- Infections around fingernails, called paronychia.
- Staph might also play a role in atopic dermatitis (eczema).
How Do People Get Staph Infections?

Staph infections can start in many ways. Here are some common causes:
- Open Wounds: This is a major way staph gets in. Any cut, even a tiny paper cut, can be a way for bacteria to enter. It's important to clean and cover wounds.
- Contact with Infected People or Surfaces: Staph infections are very easy to catch from someone who has one. They can also spread by touching surfaces where the bacteria live. This is why staph can spread in sports like wrestling or in locker rooms.
- Weak Immune System: If your body's defense system is weak, you might get staph more easily. Your body won't be able to fight off the germs as well.
- Unwashed Linens: Staph bacteria are tough. They can live on things like towels, blankets, and clothes. Washing these items regularly helps stop the spread of germs.
- After Surgery: Hospitals can sometimes have staph bacteria. During surgery, if an incision (cut) is made, staph can sometimes get into the body.
- Medical Devices: Devices that go into the body, like tubes for feeding or breathing, can create an easy path for staph to enter.
Signs and Symptoms of Staph Infections
Staph infections often cause redness, swelling, and tenderness. You might also see pus in the infected area. But the exact symptoms depend on where the infection is.
Here are some common skin infections caused by staph:
- Boils: These are the most common type. A boil is a red, tender pocket of white pus. It usually starts where a hair grows or an oil gland is.
- Impetigo: This is common in children. It often appears around the mouth, nose, hands, and feet. It looks like a rash of painful blisters that turn yellowish and crust over.
- Cellulitis: This infection makes the skin red, swollen, and warm to the touch. It often affects the lower legs but can also be on the face or arms.
- Staphylococcus Scalded Skin Syndrome: This serious condition happens when staph toxins cause a fever, rash, and blisters that make the skin look "scalded" or peeled.
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): MRSA is a type of staph that is harder to treat because it resists many common antibiotics. It can cause rashes, boils, sores, and other pus-filled bumps.
How Are Staph Infections Treated?
The way a staph infection is treated depends on how serious it is and what type it is. Common treatments include antibiotics (medicines that kill bacteria). Doctors might also use special creams or clean and drain infected wounds.
Where Does the Name "Staphylococcus" Come From?
The name Staphylococcus comes from ancient Greek words. "Staphyle" means "bunch of grapes," and "kokkos" means "granule" or "berry." If you look at these bacteria under a microscope, they really do look like tiny bunches of grapes!
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |

