Stimulus (economics) facts for kids
In economics, a stimulus is when a government or central bank tries to help the economy grow. They do this by using special tools like changing taxes, government spending, or interest rates. Think of it like giving a sleepy plant some water and sunlight to help it perk up and grow!
Sometimes, people call this "priming the pump." This means getting things started so the economy can run on its own again.
Contents
What is Economic Stimulus?
When an economy slows down, like during a recession, businesses might not produce as much, and fewer people might have jobs. This often happens because people aren't buying enough things. A stimulus aims to increase buying and selling to make the economy grow again.
How Governments Use Fiscal Stimulus
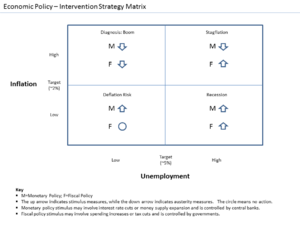
Fiscal stimulus is when the government uses its money to help the economy. It can do this in a few ways:
- Spending more money: The government might build new roads, schools, or other projects. This creates jobs and means companies get paid for their work.
- Lowering taxes: When taxes are lower, people and businesses have more money to spend or invest.
When the government spends more or collects less in taxes, it can increase the country's public debt. However, supporters of this idea, like those who follow Keynesian economics, believe this spending will help the economy grow enough to make up for it. They call this the "multiplier effect" – meaning every dollar spent can lead to even more economic activity.
How Central Banks Use Monetary Stimulus
Monetary stimulus is when a country's central bank (like the Federal Reserve in the United States) tries to make money easier to get. They do this by:
- Lowering interest rates: This makes it cheaper for people to borrow money for things like houses or cars, and for businesses to borrow money to expand.
- Quantitative easing: This is a special way the central bank buys large amounts of government bonds or other assets. This puts more money into the financial system, making it easier for banks to lend.
Why Economists Discuss Stimulus
Economists have different ideas about how well stimulus works. Some, like those who follow Keynesian economics, strongly support it. They believe it's necessary to boost demand during tough times.
Others, like those from the Austrian economic school, are usually against it. They worry that too much government involvement can cause other problems later on.
One common concern is that fiscal stimulus might cause inflation, which means prices go up too quickly. However, if the economy is very slow, some argue that the risk of inflation is low.
Monetary stimulus is sometimes seen as more "neutral." Lowering interest rates can encourage businesses to invest more, but only in projects that are truly good ideas. When the government decides where to spend money, some worry it might lead to decisions based on politics rather than what's best for the economy. However, governments can also consider benefits that aren't just about profit, like how new roads help everyone, not just those who pay for them.
Examples of Economic Stimulus in History
Many countries have used economic stimulus packages to help their economies during difficult times. Here are a few notable examples:
- 1977, United States: The Economic Stimulus Appropriations Act of 1977 was signed by President Jimmy Carter to boost the economy.
- 2008, United States: The Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 was signed by President George W. Bush to help the economy during a slowdown.
- 2008-2009, United Kingdom: The government led by Gordon Brown introduced a package that included bringing forward investment spending, a tax cut, a VAT cut, and loans for businesses.
- 2009, United States: The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 was a large stimulus package signed by President Barack Obama during the Great Recession.
- 2009, Thailand: The Thai Khem Khaeng was an investment program to help Thailand's economy.
- 2008-2009, China: China introduced a huge RMB¥ 4 trillion stimulus program during the global financial crisis.
- 2020, United States: The $2 trillion CARES Act was signed by President Donald Trump to help during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- 221, United States: The $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 was signed by President Joe Biden.
- 2020, Ireland: The July Jobs Stimulus was a €7.4 billion package announced by the Government of Ireland in response to the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Republic of Ireland.
- Taiwan: The Government of the Republic of China issued special vouchers like the ROC consumer voucher during the Great Recession and Triple Stimulus Vouchers during the COVID-19 recession to encourage people to spend money.
See also
- NAIRU
- Policy mix
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |