Urheimat facts for kids
Urheimat is a special word from the German language. It means the "original homeland" or "ancient home." In language studies, it refers to the place where a very old language, called a proto-language, was first spoken. Imagine a family tree for languages; the Urheimat is where the first "parent" language of that family lived.
It's tricky to find an exact Urheimat because people have moved around a lot throughout history. But scientists try to figure out where big language families, like the Indo-European family, might have started. This family includes languages like English, Spanish, Hindi, and Russian!
Contents
What is a Proto-Language?
A proto-language is like the great-great-grandparent of many modern languages. We don't have written records of these very old languages. Instead, experts study how different languages are similar today. They look at words, grammar, and sounds to guess what the original language might have been like.
For example, many languages in Europe and parts of Asia have similar words for "mother" (like "mama," "mater," "matr"). This suggests they all came from one older word in a proto-language.
Finding the Original Homeland
Finding an Urheimat is like being a detective! Scientists use clues from language, archaeology (studying old objects), and even genetics (studying DNA). They look for places where the oldest forms of a language family seem to have been spoken.
It's not always easy because people move, trade, and sometimes conquer new lands. This spreads their language far and wide.
Indo-European Urheimat Ideas
The Indo-European language family is one of the biggest in the world. Many ideas exist about where its Urheimat was. Here are some of the main ones:
The Kurgan Hypothesis
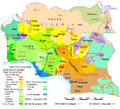
The Kurgan hypothesis suggests that the Indo-European homeland was in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe. This area is a large grassland north of the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. People here were known for riding horses and herding animals. They built burial mounds called "kurgans." This idea suggests that these people spread their language as they moved across Europe and Asia.
The Anatolian Hypothesis
The Anatolian hypothesis proposes a different origin. It suggests the homeland was in Anatolia, which is modern-day Turkey. This idea links the spread of Indo-European languages to the spread of farming. As farming spread from Anatolia into Europe and other regions, so did the language of the farmers.
The Armenian Hypothesis
The Armenian hypothesis is a newer idea. It suggests that the Indo-European homeland was in the Armenian Highlands. This area is in the Caucasus Mountains, near modern-day Armenia. This theory also uses genetic evidence to support its claims.
The Out of India Theory
The Out of India theory suggests that the Indo-European languages originated in India. This idea is less accepted by most linguists. It proposes that the languages spread from India to the west.
Why is Urheimat Important?
Studying the Urheimat helps us understand human history. It tells us about how people moved, traded, and interacted thousands of years ago. It also helps us see how languages change and develop over time. It's like piecing together a giant puzzle of human migration and culture.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Urheimat para niños
In Spanish: Urheimat para niños