Volhynia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Volhynia
Волинь
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Historical region
|
||
|
||
|
||
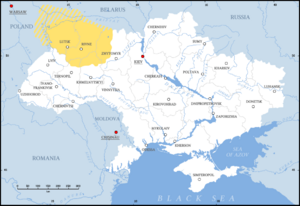
Location of Volhynia (yellow) in Ukraine
|
||
| Country | ||
| Region | Southeastern Poland, Southwestern Belarus, Western Ukraine | |
| Parts | Volyn Oblast, Rivne Oblast, Zhytomyr Oblast, Ternopil Oblast, Khmelnytskyi Oblast, Lublin Voivodeship, Brest Region | |
| Demonym(s) | Volhynian | |
Volhynia, also called Volynia, is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe. It is located between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and western Ukraine. The exact borders of Volhynia have changed many times over history. Today, the area still known as Volhynia is mostly in the Volyn Oblast of western Ukraine.
This region has been part of many different countries throughout history. For hundreds of years, it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Later, it became part of the Russian Empire. Important cities in Volhynia include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "Volhynia" is spelled differently in various languages:
- Ukrainian: Волинь (Volynʹ)
- Polish: Wołyń
- Lithuanian: Voluinė or Volynė
- German: Wolhynien or Wolynien
Another old name for the region is Lodomeria. This name comes from the city of Volodymyr, which was once an important political center in the Middle Ages.
Some historians believe the region is named after an ancient city called Volin or Velin. This city might have been located near the Southern Bug River. Its name could come from an old Slavic word meaning "wet." Other ideas suggest the city was west of Volodymyr, near the Huczwa River.
Where is Volhynia Located?
Volhynia is in the northern part of the Volhynian-Podolian Upland and the western part of the Polesian Lowland. It stretches along the Pripyat River valley, which is part of the large East European Plain. To the west, it reaches the Western Bug River. To the east, it extends to the upper parts of the Uzh and Teteriv rivers.
The region is mostly made up of lowlands. It also has the Kremenets Hills, which are part of the Podolian Upland. Most of Volhynia's rivers flow north or west because they are in the basins of the Western Bug and Pripyat rivers.
Volhynia is northeast of Galicia, east of Lesser Poland, and northwest of Podolia. Its borders are not always clear, and it often overlaps with other regions like Polesia and Podlasie.
Today, parts of historical Volhynia are in several Ukrainian regions: Volyn, Rivne, and parts of Zhytomyr, Ternopil, and Khmelnytskyi. It also includes parts of Poland. Major cities include Lutsk, Rivne, Kovel, Volodymyr, Kremenets, and Starokostiantyniv. Before World War II, many Jewish shtetls (small towns) were important parts of the region.
Volhynia's Past: A Journey Through Time
The first records of Volhynia come from old Ruthenian writings, like the Primary Chronicle. These writings mention ancient Slavic tribes living there. Some historians believe that in very old times, the people of Volhynia were seen as the most important Slavic group.
Early History and Kingdoms
Volhynia became part of the Grand Duchy of Kyiv (also known as Ruthenia) around the 900s. In 983, Vladimir the Great made his son Vsevolod the ruler of the Volhynian principality. In 988, he founded the city of Volodymer.
Later, the duchies of Galicia and Volhynia joined together to form the powerful Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. This kingdom existed between the 12th and 14th centuries.
Polish-Lithuanian Rule
Around 1340, the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia broke apart. The Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania then divided Volhynia between them. Poland took the western part, and Lithuania took the eastern part.
After 1569, Volhynia became a province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During this time, many Polish people and Jewish people moved to the area. Different Christian churches, like the Roman and Greek Catholic churches, also became established.
Russian Empire and Changes
In 1795, after the Third Partition of Poland, Volhynia was taken over by the Russian Empire. It became known as the Volhynian Governorate. The Russian government made big changes to the religions in the area. They forced the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church to close and gave its buildings to the Russian Orthodox Church. Many Roman Catholic churches were also given to the Russian Church.
By 1897, Volhynia had almost 3 million people. Most were East Slavs (mainly Ukrainians), but there were also many Jewish people, Poles, and Germans. A smaller number of Czech people also lived there. Even though the area was growing, it was still mostly rural before World War I.
Volhynia in the 20th Century
After the February Revolution in Russia, Ukrainian nationalists declared the Ukrainian People's Republic. Volhynia was split by a war front. Later, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk brought some peace. This period saw a rebirth of Ukrainian culture. After the war, Poles and Russians fought for control of Volhynia.
After the Polish–Soviet War ended in 1921, the Peace of Riga treaty divided Volhynia. Poland took a larger part, creating the Volhynian Voivodeship. The eastern part became part of the Ukrainian SSR (Soviet Ukraine).
From 1935 to 1938, the Soviet Union moved many people from Volhynia to Siberia and Central Asia. This was part of a plan to control farmers in the region.
World War II and After
In 1939, after the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, the Soviet Union invaded and took over the Polish part of Volhynia. Many ethnic Germans living in Volhynia were moved to areas of Poland taken by Nazi Germany. By 1943, only a small percentage of the population in Volhynia were ethnic Poles.
During the German invasion, about 460,000 Jewish people lived in Volhynia. Sadly, about 400,000 to 450,000 Jewish people and 100,000 Poles were killed by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army and others. Most of the Jewish people were shot and buried in large pits. Only about 1.5% of the Jewish population survived these terrible events.
After World War II, the Soviet Union officially made Volhynia part of Ukraine. Most of the remaining Polish people were moved to Poland in 1945. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the 1990s, Volhynia has been an important part of independent Ukraine.
Important Historical Items
- Peresopnytsia Gospel: A very old and important book from the region.
Famous People from Volhynia
- Sergei Korolev (1907–1966): A famous Soviet rocket engineer who designed spacecraft.
- Hayim Nahman Bialik: A well-known literary figure.
- Dov Ber of Mezeritch: A respected rabbi.
See Also
- Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia
- Galicia (Eastern Europe)
- Massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia
- Historiography of the Volyn tragedy
- Polish Autonomous District
- Kresy Wschodnie
- Volhynian folk costume
- Heinrich Peyer
Literature
- Andriyashev, Alexander (1887). Очерк истории Волынской земли (Essay on the History of Volyn land). Kyiv: Imperial University of Saint Vladimir.
- Merten, Ulrich (2015). Voices from the Gulag: Oppression of the German Minority in the Soviet Union. Lincoln, NE: American Historical Society of Germans from Russia. ISBN: 9780692603376
- Potocki, Jan (1805). Histoire anciènne du gouvernement de Volhynie: pour servir de suite à l'histoire primitive des peuples de la Russie. Saint Petersburg: Imperial Academy of Sciences.