Windows 2000 facts for kids
 |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model | Shared source |
| Released to manufacturing |
December 15, 1999 |
| Latest release | 5.0 SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (5.0.3700.6690) / February 17, 2000 |
| Repository |
|
| Kernel type | Hybrid kernel |
| License | Microsoft EULA |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported as of July 13, 2010 | |
Windows 2000 (also called Win2K or W2K) was a computer operating system made by Microsoft. It was designed to work on computers with one or many processors. This system was part of the Microsoft Windows NT family. It was officially released on February 17, 2000.
Windows 2000 came in four main versions. These were Professional, Server, Advanced Server, and Datacenter Server. There were also special versions for powerful 64-bit computers. While it was made for businesses, many people used it at home too.
Contents
How Windows 2000 Works
Windows 2000 used two special ways for programs to run. These were called 'User Mode' and 'Kernel Mode'.
User Mode and Kernel Mode
The Kernel Mode was like the computer's brain. It helped hardware parts, like your printer or mouse, talk to the computer. This mode let drivers (software that tells the computer how to use hardware) communicate directly.
The User Mode was where your regular computer programs ran. This mode kept them separate. This way, if a program had a problem, it wouldn't crash the whole computer.
Common Features for All Versions
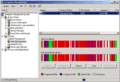
All versions of Windows 2000 shared many useful tools. These included the Microsoft Management Console (MMC). This tool helped people manage different parts of the computer. It also had a disk defragmentation tool. This tool helped organize files on your hard drive.
Windows 2000 also supported many different languages. It had features to help people with disabilities use the computer more easily. It used a special way to store files called NTFS 5. It also had the Encrypted File System (EFS) to keep your files safe.
Server Features
The Windows 2000 Server versions had even more features. They could provide Active Directory services. This was a way to organize computer resources like printers and user accounts. They also had a distributed file system. This allowed files to be shared easily across many computers.
History of Windows 2000
Windows 2000 was developed from earlier Microsoft Windows NT operating systems. It was first called Windows NT 5.0. Microsoft changed its name to Windows 2000 in October 1998. It was the first Windows version released without a secret code name.
Development and Release
The first test version, called a beta version, came out in September 1997. More test versions were released until Beta 3 in April 1999. Microsoft released the final version to its partners in December 1999. The public could buy Windows 2000 starting February 17, 2000. Many people said it was the most stable Windows system yet.
Updates and Replacements
Microsoft released several updates called Service Packs. Service Pack 1 came out in August 2000. Service Pack 4, the last one, was released in June 2003. After that, Microsoft offered an "Update Rollup" instead of a Service Pack 5.
Later, Microsoft replaced Windows 2000 Professional with Windows XP Professional. The server versions were replaced by Windows Server 2003. There was a plan for a home version of Windows 2000, called Neptune. However, that project was stopped. Its ideas were used to help create Windows XP instead.
Security Challenges
Windows 2000 faced some security problems. Famous computer worms like Code Red and Blaster caused issues. These worms attacked computers using Windows 2000. They caused many problems for computer users and businesses. This made Microsoft focus more on improving its security.
Windows 2000 was the last version of Windows that could run on older 486 computers.
Images for kids
-
Windows 2000's Computer Management console can perform many system tasks. This image shows a disk defragmentation in progress.
See also
 In Spanish: Windows 2000 para niños
In Spanish: Windows 2000 para niños
| Preceded by Windows 98 |
Windows Versions 2000-2001 |
Succeeded by Windows ME |