Windows NT facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Windows NT |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Developer | Microsoft, with Dave Cutler as the lead architect |
| Written in | C, Assembly language (core) C++ (user mode applications, kernel graphical subsystem) C# (user mode applications) |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | July 27, 1993 (as Windows NT 3.1) |
| Latest release | 23H2 (10.0.22631.3737) (June 11, 2024 ) [±] |
| Latest preview |
24H2 (10.0.26100.712) (May 22, 2024 )
23H2 (10.0.22635.3720) (June 7, 2024 )
24H2 (10.0.26120.770) (June 7, 2024 )
|
| Repository |
|
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services |
| Supported platforms | IA-32, x86-64, ARM and ARM64 (and historically Intel i860, DEC Alpha, Itanium, MIPS, and PowerPC) |
| Kernel type | Hybrid |
| Influenced by | RSX-11, VAXELN, OpenVMS, MICA, Mach (kernel) MS-DOS, OS/2, Windows 3.1 (userland) |
| Default user interface |
Graphical (Windows shell) |
| License | Depending on version, edition or customer choice: Trialware, commercial software, volume licensing, OEM-only, SaaS, S+S |
Windows NT is a special type of operating system made by Microsoft. It's a big part of the Windows family. The very first version, called Windows NT 3.1, came out on July 27, 1993.
Windows NT was first designed for powerful computers used in offices and for servers. But later, it became the base for Windows versions that people use at home, like Windows XP in 2001. The core technology of Windows NT is still used today in the newest Windows versions, including Windows Server 2025.
The "NT" in the name stood for "New Technology." It brought many big improvements to Windows. For example, it fixed old limits on how much computer memory Windows could use. Even though the "NT" name isn't used in most Windows names anymore, all modern Windows versions are built on this same powerful technology.
Windows NT offers many cool features. It can handle many tasks at once and let multiple users work on the same computer. It also uses a "pure" 32-bit or 64-bit system, which means it can handle more data. It supports different types of computer processors and has special services like Active Directory.
Contents
Windows NT: A Family of Operating Systems
Windows NT is like a family of different computer operating systems. It's a special group within the larger Windows family.
Early Windows NT Versions
The first Windows NT version, Windows NT 3.1, was made for powerful workstation and server computers. It was mostly for businesses. It worked alongside other Windows versions, like Windows 3.1x, which were for home users. In 1996, Windows NT 4.0 came out. It looked more like Windows 95, which was popular at the time.
NT Becomes the Core of Windows
Eventually, Microsoft decided to use the Windows NT technology for all Windows computers. They stopped making the older Windows 9x family. Starting with Windows 2000, the "NT" part was removed from the product name. However, the NT technology still runs deep inside the system.
How Windows NT Is Installed
Windows NT versions are installed using a program called Windows Setup. For newer versions, starting with Windows Vista, this setup uses a small, simple version of Windows NT itself. This small version is called the Windows Preinstallation Environment. It helps get the main operating system ready to install.
Since Windows Vista, the files needed to install Windows are stored in a special format. This format is called the Windows Imaging Format. You can even install Windows using text commands, skipping the usual graphical installer.
The Story Behind the Name "NT"
The name "NT" has an interesting history. Some people thought it was a secret code based on another operating system called VMS. However, the project was first meant to be a follow-up to OS/2. It was even called "NT OS/2" before it became "Windows NT."
Two of the original developers said the name came from the first computer chip it was designed for, the Intel i860, which was code-named N10. In 1991, Bill Gates said that "Windows NT stands for 'New Technology'." Years later, he said the letters no longer had a specific meaning. Even though "NT" was dropped from names like Windows 2000, Microsoft still said it was "Built on NT Technology."
Key Features of Windows NT
Windows NT was designed to be very flexible. It could work on different computer hardware and run different software.
Working on Different Computers
Many versions of Windows NT have been made for various computer processors. These include IA-32, MIPS, DEC Alpha, PowerPC, Itanium, x86-64, and ARM. The idea was to have one main code base that could adapt to each type of computer. However, support for some older processors was later stopped.
Software Compatibility
Windows NT could run many different types of software. It supported various ways for programs to talk to the computer, called APIs. These included the main Windows API, and older ones like POSIX and OS/2 APIs. It could even run some older MS-DOS and 16-bit Windows programs on certain computers.
Security and Networking
Windows NT has strong security features. It uses access control lists to decide who can access files and services. This helps keep your computer safe. It also supports computer networking, allowing computers to connect and share information.
Memory and Multitasking
Windows NT 3.1 was the first Windows version to use 32-bit memory addressing. This allowed it to use much more computer memory. It also had "preemptive multitasking." This means the operating system could manage programs running at the same time. It didn't have to wait for programs to give up control of the computer.
User Interface and File System
The first Windows NT looked a lot like Windows 3.1. But with Windows NT 4.0, the look changed to match Windows 95. This included the familiar taskbar and Start menu. A major feature of NT is NTFS, a secure file system that helps keep your data organized and safe.
Driver Model
Windows NT introduced its own way for hardware to communicate with the operating system, called the Windows NT driver model. This was later improved and became the Windows Driver Model, used in Windows 98 and later versions.
How Windows NT Was Developed
Microsoft decided to create a new, flexible operating system in 1988. It would be able to run on different computers and handle many tasks at once. Development started in 1989. At first, it was called OS/2 3.0.
Changing Focus to Windows
Microsoft also worked on a simpler Windows version for DOS, which became Windows 3.0. This version was very successful. Because of this, Microsoft decided to change the new OS/2 3.0 to be more like Windows. This caused problems with IBM, who was working with Microsoft on OS/2. They eventually stopped working together.
IBM continued with OS/2, and Microsoft focused on the newly named Windows NT. Windows NT eventually became much more successful.
The Team Behind NT
Microsoft hired a team of developers led by Dave Cutler from another company. Many ideas in Windows NT came from their earlier work. The team also included members from the OS/2 project.
Some engineers noticed that Windows NT was very similar to an operating system called VMS. Microsoft eventually paid the other company and agreed to help them.
Windows NT's core parts, like how it handles memory and tasks, are very similar to VMS. Windows NT also uses a "hybrid kernel." This means it combines different ways of managing the computer's core functions.
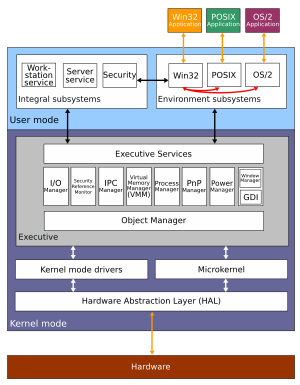
Windows NT Architecture
Windows NT has a special layered design. It has two main parts: user mode and kernel mode.
User Mode vs. Kernel Mode
Programs you use every day, like games or web browsers, run in user mode. They have limited access to the computer's resources. The kernel mode has full access to the computer's memory and hardware. This is where the core parts of Windows NT live. The Windows NT kernel is a hybrid kernel. It includes a simple kernel, a hardware abstraction layer (HAL), and other services. All these parts work in kernel mode.
Starting Up Windows NT
When you turn on a computer with Windows NT, a special program starts first. This program helps load the main parts of the operating system. It also loads important device drivers. After that, the system starts the login process, and then you see the familiar Windows desktop.
Programming Languages Used
Windows NT is mostly written in C and C++. A very small part is written in assembly language. Using C and C++ helps the operating system work on many different types of computers.
Windows NT Releases
Here are some of the different versions of Windows that use the Windows NT technology.
| Version | Marketing name | Editions | Release date | Build number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | Windows NT 3.1 | Workstation, Advanced Server | July 27, 1993 | 528 |
| 3.5 | Windows NT 3.5 | Workstation, Server | September 21, 1994 | 807 |
| 3.51 | Windows NT 3.51 | May 30, 1995 | 1057 | |
| 4.0 | Windows NT 4.0 | Workstation, Server, Enterprise Server, Terminal Server, Embedded | August 24, 1996 | 1381 |
| 5.0 | Windows 2000 | Professional, Server, Advanced Server | February 17, 2000 | 2195 |
| Datacenter Server | September 26, 2000 | |||
| 5.1 | Windows XP | Home, Professional, Media Center, Tablet PC, Starter, Embedded, Home N, Professional N | October 25, 2001 | 2600 |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | N/A | July 8, 2006 | ||
| 5.2 | Windows XP | 64-bit Edition (IA-64) | March 28, 2003 | 3790 |
| Windows Server 2003 | Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, Storage, Small Business Server, Compute Cluster | April 24, 2003 | ||
| Windows XP | Professional x64 Edition (x86-64) | April 25, 2005 | ||
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, Storage, Small Business Server, Compute Cluster | December 6, 2005 | ||
| Windows Home Server | N/A | November 4, 2007 | ||
| 6.0 | Windows Vista | Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, Ultimate | Business: November 30, 2006 Consumer: January 30, 2007 |
6000 (RTM) 6001 (SP1) 6002 (SP2) 6003 (SP2 Update) |
| Windows Server 2008 | Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web Server, HPC Server, Itanium-Based Systems | February 27, 2008 | 6001 (RTM) 6002 (SP2) 6003 (SP2 Update) |
|
| 6.1 | Windows 7 | Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Professional, Enterprise, Ultimate | October 22, 2009 | 7600 (RTM) 7601 (SP1) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Foundation, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web Server, HPC Server, Itanium-Based Systems | |||
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Home Server Premium | April 6, 2011 | 7601 (SP1) | |
| Windows Thin PC | N/A | June 6, 2011 | ||
| 6.2 | Windows 8 | Core, Pro, Enterprise, RT | October 26, 2012 | 9200 |
| Windows Server 2012 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | September 4, 2012 | ||
| 6.3 | Windows 8.1 | Core, Pro, Enterprise, RT, Embedded Industry Pro/Enterprise | October 17, 2013 | 9600 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter | |||
| 10.0 | Windows 10 | Home Single Language, Home China, Home, Pro, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise, Education, S, IoT Core, Mobile, Mobile Enterprise | July 29, 2015 | 10240 (RTM) 10586 (1511) 14393 (1607) 15063 (1703) 16299 (1709) 17763 (1809) 18362 (1903) 18363 (1909) 19041 (2004) 19042 (20H2) 19043 (21H1) 19044 (21H2) 19045 (22H2) |
| Windows Server 2016 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Multipoint Premium Server, Storage Server, Hyper-V Server | September 26, 2016 | 14393 | |
| Windows Server 2019 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Multipoint Premium Server, Hyper-V Server | October 2, 2018 | 17763 | |
| Windows Server 2022 | August 18, 2021 | 20348 | ||
| Windows 11 | Home Single Language, Home China, Home, Pro, Education, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise, IoT Enterprise, SE | October 5, 2021 | 22000 (RTM) 22621 (22H2) 22631 (23H2) 26100 (24H2) |
|
| Windows Server 2025 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Multipoint Premium Server, Hyper-V Server | November 1, 2024 | 26100 |
Changes in User Interface
Early Windows NT versions, like 3.1 to 3.51, used the Program Manager and File Manager. These were similar to Windows 3.1. But Windows NT 4.0 and later versions switched to Windows Explorer. This brought the taskbar and Start menu that first appeared in Windows 95.
Version Numbers
The first Windows NT was version 3.1. This matched the Windows 3.1 that was popular then. It also made the new system seem more reliable. The NT version number is not usually shown to users anymore. However, it is still used internally by Microsoft. This number helps show how much the core of the operating system has changed.
Supported Computer Platforms
Windows NT was designed to work on many different types of computer hardware.
32-bit Computers
To make sure Windows NT could run on various computers, it was first developed on non-x86 systems. Then, it was adapted for x86 computers. Windows NT 3.1 was released for Intel x86 PCs, and also for DEC Alpha and MIPS computers. Windows NT 3.51 later added support for PowerPC processors.
Windows NT 4.0 was the last major version to support Alpha, MIPS, or PowerPC. In 2011, Microsoft announced that future Windows NT versions would support ARM architecture. This led to Windows RT for tablets and Windows NT being used in Windows Phone 8.
The Xbox and Xbox 360 game consoles use a special version of Windows NT. The newer Xbox One and Xbox Series X/S also use a simplified Windows operating system. Windows 11 is the first Windows NT version for regular users that does not support 32-bit computers.
64-bit Computers
Microsoft also created 64-bit versions of Windows NT. These were first planned for Itanium and DEC Alpha processors. While Windows 2000 only supported 32-bit Intel, later versions like Windows XP and Server 2003 had special editions for Itanium.
Microsoft adopted x64 processors more widely. Every version of Windows since Windows XP has x64 editions. The first Windows NT version to support ARM64 devices was Windows 10, version 1709. This was a full version of Windows, not the simpler Windows RT.
Hardware Requirements
The computer requirements for Windows NT versions stayed pretty similar for a long time. However, with Windows Vista (version 6.0), the requirements jumped quite a bit. For example, it needed ten times more free disk space than the previous version. Windows 11 (version 10.0) also has higher requirements. It often needs newer computers made after 2018.
| Windows version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space |
|---|---|---|---|
| NT 3.1 | i386, 25 MHz | 12 MB | 90 MB |
| NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 16 MB | ||
| NT 3.5 Workstation | 12 MB | ||
| NT 3.5 Server | 16 MB | ||
| NT 3.51 Workstation | 12 MB | ||
| NT 3.51 Server | 16 MB | ||
| NT 4.0 Workstation | i486, 25 MHz | 12 MB | 124 MB |
| NT 4.0 Server | 16 MB | ||
| 2000 Professional | Pentium, 133 MHz | 32 MB | 650 MB |
| 2000 Server | 128 MB | ||
| XP | Pentium, 233 MHz | 64 MB | 1.5 GB |
| Server 2003 | 133 MHz | 128 MB | |
| Vista Home Basic | 800 MHz | 512 MB | 20 GB |
| Vista (other editions) | 1 GHz | 1 GB | 40 GB |
| 7 for IA-32 | 16 GB | ||
| 7 for x64 | 2 GB | 20 GB | |
| 8 for IA-32 | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE | 1 GB | 16 GB |
| 8 for x64 | 2 GB | 20 GB | |
| 8.1 for IA-32 | 1 GB | 16 GB | |
| 8.1 for x64 | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE, CMPXCHG16b, PrefetchW and LAHF/SAHF | 2 GB | 20 GB |
| 10 for IA-32 (RTM-v1809) | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE | 1 GB | 16 GB |
| 10 for x64 (RTM-v1809) | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE, CMPXCHG16b, PrefetchW and LAHF/SAHF | 2 GB | 20 GB |
| 10 for IA-32 (v1903-22H2) | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE | 1 GB | 32 GB |
| 10 for x64 (v1903-22H2) | 1 GHz with NX bit, SSE2, PAE, CMPXCHG16b, PrefetchW and LAHF/SAHF | 2 GB | |
| 11 for x64 | Intel 8th-Gen CPU or AMD Zen+-based CPU; Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 or equivalent crypto-processor A X86-64 v2 CPU is required starting from version 24H2, dropping unofficial support for X86-64 v1. |
4 GB | 64 GB |
| 11 for ARM64 | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850, 7c, 8c, 8cx; Microsoft SQ1, SQ2. An ARMv8.1 CPU is now required starting from version 24H2, dropping unofficial support for ARMv8.0. |
See also
 In Spanish: Windows NT para niños
In Spanish: Windows NT para niños
- Windows domain
- ReactOS (an open source project with the goal of providing binary- and device driver-level compatibility with Windows NT)
- Windows Preinstallation Environment
- Microsoft Servers