Windows 7 facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Windows 7 |
|
|---|---|
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
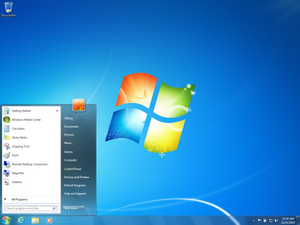
Screenshot of Windows 7, showing its Start Menu, desktop, taskbar, and the glass effect of Windows Aero
|
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
July 22, 2009 |
| General availability |
October 22, 2009 |
| Final release | Service Pack 1 with January 2023 monthly update rollup (6.1.7601.26321) / February 8, 2023 |
| Repository |
|
| Marketing target | Consumer and business |
| Update method | Windows Update |
| Supported platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 8 (2012) |
| Official website | (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015. Extended support ended on January 14, 2020. Paid Extended Security Updates (ESU), only for Professional & Enterprise volume licensed editions: Support ended on January 10, 2023. See § Extended Security Updates for details. Windows Thin PC had shorter support period and some embedded editions had exceptionally long support or until October 8, 2024. See § Support lifecycle for details. |
|
Windows 7 is a computer operating system made by Microsoft. It was first released on July 22, 2009, and became widely available on October 22, 2009. This system came after Windows Vista. Its server version, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released at the same time. Windows 7 sold over 630 million copies before Windows 8 took its place in October 2012.
Microsoft stopped providing full support for Windows 7 on January 14, 2020. This means it no longer receives regular updates. However, businesses could pay for extra security updates for up to three more years.
Windows 7 was designed to be a better version of Windows Vista. It aimed to fix problems Vista had, like its performance and how it worked with other programs. Windows 7 also made the Windows Aero look even better. It added a new taskbar where you could pin apps. New features included libraries for files, a HomeGroup for sharing, and multitouch support. A new "Action Center" helped users check their computer's security.
People really liked Windows 7, much more than Vista. Critics said it ran faster and was easier to use. It also had fewer annoying pop-up messages. Windows 7 was a huge success for Microsoft. It broke sales records even before it was officially released. By January 2018, Windows 10 became more popular worldwide. As of 2025, only about 2% of computers still use Windows 7.
Contents
What's New in Windows 7?
Windows 7 brought many new features and improvements. These changes made the system faster and easier to use. It also added new ways to interact with your computer.
Touch and Performance
Windows 7 improved how it recognized touch and handwriting. It also worked better with multi-core processors, which are like having multiple brains in your computer. The system started up faster too. It added support for virtual hard disks, which are like fake hard drives.
Updated Tools and Features
Many tools in Windows 7 were updated. The Calculator got new modes for programmers and statisticians. It could also convert units like length and weight. The Control Panel gained new options for display settings and security. The Windows Security Center was renamed "Action Center." This new center helped you keep track of your computer's safety and maintenance.
Taskbar Changes
The taskbar, at the bottom of your screen, changed a lot. The old Quick Launch bar was replaced. Now, you could "pin" your favorite programs directly to the taskbar. These pinned apps also had "Jump Lists. Jump Lists let you quickly open recent files or do common tasks for that app. You could also rearrange the buttons on the taskbar.
On the far right of the taskbar, there's a small button. If you hover over it, all open windows become transparent. This lets you quickly see your desktop. Clicking it minimizes all windows, and clicking it again brings them back.
Window Management
Windows 7 made managing windows easier with "Aero Snap" and "Aero Shake."
- Aero Snap: If you drag a window to the top of the screen, it maximizes. Dragging it to the left or right side makes it fill exactly half the screen. This is great for working with two windows side-by-side.
- Aero Shake: If you click and shake a window's title bar quickly, all other open windows will minimize. Shake it again, and they all come back.
Security and Sharing
Windows 7 included Windows Defender for basic protection. You could also download Microsoft Security Essentials for free antivirus. The system also had "Shadow Copy," which automatically saved older versions of your files. This helped you recover files if they were accidentally changed or deleted.
A new feature called "Libraries" helped organize your files. You could gather files from different folders into one "Library." For example, your "Documents" library could show files from your personal documents folder and a public documents folder. This system also worked with "HomeGroup," a new way to share files and printers with other computers in your home network.
User Account Control (UAC)
The User Account Control (UAC) system was improved. It showed fewer pop-up warnings than in Vista. You could also adjust how often UAC asked for permission using a simple slider. This made it less annoying while still keeping your computer safe.
What Was Removed?
Some features and programs from Windows Vista were removed or changed in Windows 7. For example, the old "Classic" Start Menu look was gone. Also, programs like Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Movie Maker, Windows Calendar, and Windows Mail were not included. Instead, Microsoft offered newer versions of these as part of the Windows Live Essentials suite, which you could download separately.
Different Versions of Windows 7
Windows 7 came in six different versions, also called "editions." The most common ones were Home Premium, Professional, and Ultimate. These were sold in stores and came pre-installed on most new computers.
- Home Premium was for home users.
- Professional was for small businesses and added features like joining a computer network domain.
- Ultimate had all the features of Home Premium and Professional, plus advanced tools like BitLocker for encrypting your hard drive.
Each version included all the features of the one below it, plus more. For example, Professional had everything Home Premium had, plus extra business features.
Other versions included:
- Starter: A simpler version for low-cost computers like netbooks. It had fewer features and couldn't change the desktop background.
- Home Basic: Sold only in certain countries, it was between Starter and Home Premium.
- Enterprise: Similar to Ultimate, but sold only to large businesses through special licenses.
Most versions of Windows 7 supported both 32-bit and 64-bit computer systems. The Starter edition only supported 32-bit systems. If you bought a retail copy, it usually came with two DVDs: one for 32-bit and one for 64-bit. The installation disc was the same for many versions; your product key determined which version was installed. You could also upgrade to a higher version later using the Windows Anytime Upgrade service.
How Long Was Windows 7 Supported?
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | January 13, 2015 |
| Extended support | January 14, 2020 |
| Applicable Windows 7 editions: | |
| Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Professional, Enterprise, and Ultimate, as well as Professional for Embedded Systems and Ultimate for Embedded Systems | |
| Exceptions | |
| Professional and Enterprise volume licensed editions, as well as Professional for Embedded Systems | Extended Security Updates (ESU) support ended on January 10, 2023 |
| Windows Thin PC | Mainstream support ended on October 11, 2016 Extended support ended on October 12, 2021 |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | Mainstream support ended on October 13, 2015 Extended support ended on October 13, 2020 Extended Security Updates (ESU) support ended on October 10, 2023 |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 7 | Mainstream support ended on October 11, 2016 Extended support ended on October 12, 2021 Extended Security Updates (ESU) support ended on October 8, 2024 |
Microsoft provides support for its operating systems for a certain period. This includes updates and technical help.
End of Regular Support
Support for the first version of Windows 7 (without Service Pack 1) ended on April 9, 2013. Users needed to update to Service Pack 1 to keep getting updates. Microsoft stopped selling new retail copies of Windows 7 in October 2014. They also stopped selling new licenses for most versions to computer makers by October 31, 2014.
Mainstream support for Windows 7 ended on January 13, 2015. Extended support, which included security updates, ended on January 14, 2020. After this date, most Windows 7 users no longer received free updates.
Extended Security Updates (ESU)
For businesses, Microsoft offered a paid "Extended Security Updates" (ESU) service. This service provided security updates for Windows 7 Professional and Enterprise for up to three years after the official end of support. This program ended on January 10, 2023.
Some special versions of Windows 7, used in embedded systems (like in ATMs or point-of-sale machines), had longer support. For example, support for Windows Embedded POSReady 7 ended on October 8, 2024. This was the very last date for updates for any Windows 7-based system.
Third-Party Support
Even after Microsoft stopped supporting Windows 7, some other companies continued to offer limited support for their software. For example, web browsers like Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome stopped supporting Windows 7 after version 109 in January 2023. However, Mozilla Firefox Extended Support Release (ESR) still supports Windows 7 until at least August 2025. The gaming platform Steam also ended support for Windows 7 on January 1, 2024.
System Requirements
To run Windows 7, your computer needed to meet certain minimum requirements. These varied slightly depending on whether you used a 32-bit or 64-bit version.
| Component | Operating system architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit | 64-bit | |
| Processor | 1 GHz IA-32 processor Support for SSE2 required after March 2018 cumulative update |
1 GHz x86-64 processor |
| Memory (RAM) | 1 GB | 2 GB |
| Graphics card | DirectX 9 graphics processor with WDDM driver model 1.0 | |
| Storage space | 16 GB | 20 GB |
| Installation media | DVD drive or USB drive | |
Memory Limits
The amount of RAM Windows 7 could use depended on the version and whether it was 32-bit or 64-bit.
| Edition | Processor architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| IA-32 (32-bit) | x64 (64-bit) | |
| Ultimate | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Enterprise | ||
| Professional | ||
| Home Premium | 16 GB | |
| Home Basic | 8 GB | |
| Starter | 2 GB | N/A |
Processor Limits
Windows 7 Professional and higher versions could use up to 2 physical processors. The Starter, Home Basic, and Home Premium versions could only use 1. However, modern processors often have multiple "cores" or "threads," which act like extra mini-processors. 32-bit Windows 7 could use up to 32 of these logical processors, while 64-bit versions could use up to 256.
Updates and Service Packs
Microsoft released updates and service packs to improve Windows 7. These updates fixed bugs and added new features.
Service Pack 1
Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on February 22, 2011. It was a smaller update compared to service packs for older Windows versions. SP1 added support for new processor features and improved some network connections. It also fixed a few bugs related to HDMI audio and printing.
Convenience Rollup
In May 2016, Microsoft released a "Convenience rollup update." This package included all updates released between SP1 and April 2016. It made it easier to update a fresh Windows 7 installation. After October 2016, all security updates for Windows 7 became "cumulative." This meant you downloaded one large package each month instead of many small ones.
Monthly Updates
From September 2018 until its end of life, Windows 7 received monthly updates. These updates came in two packages: one with security and quality updates, and a smaller one with only security updates. Users could choose which one to install. The last free security updates were released on January 14, 2020.
After Support Ended
Even after January 14, 2020, a few special updates were released. In February 2020, an update fixed a problem where some users' desktop backgrounds turned black. In June 2020, an update rolled out the new Chromium-based Microsoft Edge browser to many Windows 7 computers.
Microsoft also started showing full-screen warnings on Windows 7 PCs after January 15, 2020. These warnings told users that support had ended and encouraged them to upgrade to Windows 10.
See also
 In Spanish: Windows 7 para niños
In Spanish: Windows 7 para niños