Windows Server 2016 facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Windows Server 2016 |
|
|---|---|
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
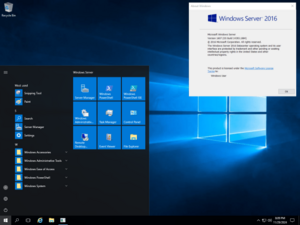
Screenshot of Windows Server 2016 with Desktop Experience
|
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
| Written in |
|
| OS family | Windows Server |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
September 26, 2016 |
| General availability |
October 12, 2016 |
| Latest release | 1607 (10.0.14393.8246) (July 8, 2025 ) [±] |
| Repository |
|
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Supported platforms | x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) Windows PowerShell (Command line) |
| License | Trialware, Volume licensing, Microsoft Software Assurance, MSDN subscription, Microsoft Imagine |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2019 (2018) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2016 (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
|
|
Windows Server 2016 is a special computer operating system made by Microsoft. Think of it like the brain for powerful computers that run networks, websites, and online services for businesses. It's part of the Windows NT family, just like the Windows you might use at home, but it's designed for bigger jobs.
This version was created alongside Windows 10. It came after Windows Server 2012 R2. Microsoft officially released Windows Server 2016 on September 26, 2016. It became widely available to everyone on October 12, 2016. The next version, Windows Server 2019, came out later. Microsoft stopped providing regular support for Windows Server 2016 on January 11, 2022. Extended support, which includes security updates, will continue until January 12, 2027.
Contents
What's New in Windows Server 2016?
Windows Server 2016 brought many new features to help businesses manage their computer systems better. Here are some of the important ones:
- Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS): This helps businesses let users log in to different services using one account. It can even work with accounts not stored in Microsoft's main directory system.
- Windows Defender: This is Microsoft's built-in antivirus software. It comes installed and turned on by default to help protect the server from harmful programs.
- Remote Desktop Services: This allows people to connect to the server from another computer. It got better at handling graphics and became more stable.
- Storage Features: New tools help manage how data is stored. For example, "Storage Replicas" can copy data between servers. This helps protect important information in case of a disaster.
- Failover Clustering: This feature helps keep services running even if one server breaks down. It allows for easier upgrades of server clusters.
- Web Application Proxy: This helps secure web applications. It can redirect web traffic from HTTP to HTTPS for better security.
- IIS 10: This is the web server software. It supports a newer, faster way of sending web pages called HTTP/2.
- Windows PowerShell 5.1: This is a powerful tool that uses commands to manage the server.
- Windows Server Containers: These are like small, isolated packages that can run applications. They make it easier to develop and deploy software.
How Networking Works
Networking features in Windows Server 2016 help computers talk to each other and the internet.
- DHCP: This system automatically gives IP addresses to devices on a network. In this version, it no longer supports an older security feature called Network Access Protection.
- DNS (Domain Name System): This is like the internet's phone book, translating website names into IP addresses.
- DNS Client: Better support for computers with multiple network connections.
- DNS Server: New ways to set up rules for how DNS works and new types of records.
- Windows Server Gateway: This helps connect different networks securely. It now supports a type of tunnel called GRE.
- IP Address Management (IPAM): This tool helps manage all the IP addresses on a network. It got better at finding and managing DNS and DHCP servers.
- Network Controller: This is a new tool that helps manage and fix virtual and physical network devices in a data center.
- Hyper-V Network Virtualization: This allows for creating virtual networks. It includes new ways to manage virtual switches and better support for network standards.
Hyper-V: Running Virtual Machines
Hyper-V is a technology that lets you run multiple "virtual computers" (called virtual machines or VMs) on one physical server. This saves money and makes managing servers easier.
- Rolling Cluster Updates: You can update a group of Hyper-V servers without stopping all of them at once. This means services can keep running while updates happen.
- Storage Quality of Service (QoS): This helps make sure virtual machines get the storage performance they need.
- New Virtual Machine Files: Virtual machine settings and data are now stored in new, more efficient file formats.
- Production Checkpoints: You can take "snapshots" of running virtual machines. This is useful for testing or going back to an earlier state.
- Hyper-V Manager: The tool for managing Hyper-V got updates, making it easier to use.
- Integration Services: Tools that help Windows guest operating systems work better inside Hyper-V are now updated through Windows Update.
- Hot Add/Remove: You can add or remove network adapters and memory to virtual machines while they are running.
- Linux Secure Boot: Better security for Linux virtual machines.
- Storage Resiliency: If a virtual machine temporarily loses connection to its storage, it will pause instead of crashing. This helps prevent data loss.
Nano Server: A Tiny Server Option
Microsoft introduced a new way to install Windows Server called Nano Server. It's a very small version of the operating system.
- Minimal Size: Nano Server is much smaller than a regular Windows Server installation. This means it uses less disk space and needs fewer security updates.
- No Graphical Interface: It doesn't have a desktop or a graphical user interface (GUI). You manage it remotely using command-line tools like Windows PowerShell.
- Faster Reboots: Because it's so small, Nano Server restarts much faster.
- Limited Availability: Nano Server is mainly for businesses with special agreements with Microsoft or for use on cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure.
- Container Host: Since late 2017, Nano Server is mostly used as a host for containers.
How Windows Server 2016 Was Developed
Microsoft changed how its teams worked together to create Windows Server 2016. The server team worked closely with the Azure cloud team.
Microsoft also showed a version of Server 2016 running on ARM processors. This was a big step, as most servers use Intel processors. However, this ARM version was mainly for Microsoft's own use in its Azure cloud services.
Early Versions (Previews)
Before the final release, Microsoft let people try out early versions of Windows Server 2016. These were called "Technical Previews."
- Technical Preview 1: Released on October 1, 2014.
- Technical Preview 2: Released on May 4, 2015. This version introduced the Nano Server option and improvements to Hyper-V.
- Technical Preview 3: Released on August 19, 2015. This version added Windows Server Containers and changed how the desktop experience was installed.
- Technical Preview 4: Released on November 19, 2015. Nano Server gained more features, and Hyper-V Containers were introduced.
- Technical Preview 5: Released on April 27, 2016. This was the last preview, focusing on refinements and improvements to containers and Nano Server.
Official Release
Windows Server 2016 was officially released on September 26, 2016. A big change with this version was how it was licensed. Instead of paying per processor, businesses now paid based on the number of CPU cores in their servers. This meant that larger servers with many cores might need more licenses.
Different Versions and Updates
After the main release, Microsoft also offered "Semi-Annual Channel" releases. These were smaller, more frequent updates with new features.
Version 1709
Released on October 17, 2017, this version was simply called "Windows Server." It was the first to follow the "Semi-Annual Channel" update plan. This version only offered the Server Core and Nano Server modes, meaning no graphical desktop. Nano Server in this version was only available as a container.
Version 1803
This was the second Semi-Annual Channel release. It was the last version based on the Windows Server 2016 code. Later versions, like Windows Server 2019, started from a newer code base.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Windows Server 2016 para niños
In Spanish: Windows Server 2016 para niños
- Microsoft Servers
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of operating systems
- List of operating systems