Zamboanga Peninsula facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Zamboanga Peninsula
Peninsula de Zamboanga
Lawis sa Zamboanga |
|
|---|---|

Vintas of Zamboanga
|
|
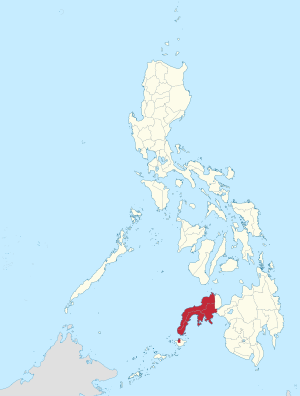
Location in the Philippines
|
|
|
OpenStreetMap
|
|
| Country | Philippines |
| Island group | Mindanao |
| Regional center | Pagadian |
| Largest city | Zamboanga City |
| Area | |
| • Total | 17,056.73 km2 (6,585.64 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation
(Mount Pinukis)
|
1,532 m (5,026 ft) |
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|
| • Total | 3,875,576 |
| • Density | 227.21682/km2 (588.48887/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Zamboangueño, Samboanganon |
| GDP (Nominal, 2024) | |
| • Total | US$10.2 billion |
| • Per capita | US$2,525 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-09 |
| Provinces |
4
|
| Independent cities | |
| Component cities |
4
Dapitan
Dipolog Isabela City Pagadian |
| Municipalities | 87 |
| Barangays | 2,314 |
| Cong. districts | 10 |
| Languages | |
| HDI | |
| HDI rank | 16th in the Philippines (2019) |
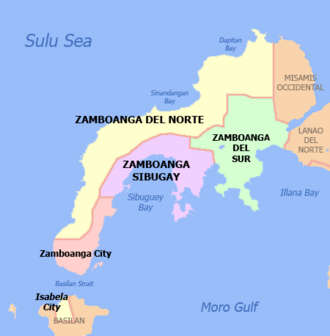
The Zamboanga Peninsula is a region in Mindanao, Philippines. It is also known as Region IX. This area includes the provinces of Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga Sibugay, and Zamboanga del Sur. It also has the cities of Isabela and Zamboanga City.
This region was once called Western Mindanao. The city of Pagadian is the main center for the region's government. Zamboanga City is the biggest city and the main place for business and industry.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Zamboanga comes from the Sinama word samboangan. This word means "mooring place" or a place where boats can tie up. It was the first name for Zamboanga City, and the whole peninsula got its name from there.
Some people mistakenly think the name comes from an Indonesian word meaning "place of flowers." However, historical records show that samboangan has been used for centuries.
A Look Back: History of Zamboanga Peninsula
Early Times
Long ago, the Zamboanga Peninsula was a large area. Many different groups of people lived here, with the Subanen people being the largest. Later, some southern parts of the region were influenced by the Javanese Majapahit Empire. However, this empire never fully took over the area.
The Sultanates
In the 1300s, the Sultanate of Sulu ruled the southwestern parts of the peninsula. Later, in the 1400s and 1500s, missionaries from Malaysia helped spread Islam in the southern Philippines. Sharif Kabungsuwan started the Sultanate of Maguindanao. This sultanate became very powerful and covered most of Mindanao, including the Zamboanga Peninsula.
The sultans of Maguindanao, especially Muhammad Kudarat, bravely fought against the Spanish. The Spanish called the Muslim people of the region "Moros." This name came from the "Moors" in Spain, even though the two groups were very different. Many battles between the Spanish and the Moros happened in the Zamboanga Peninsula.
Spanish Control
In 1569, the Spanish built a settlement and fort in Zamboanga. This place became important for their efforts to control the southern island. It also helped protect the area from invaders and pirates. The province of Zamboanga was partly founded by soldiers from Peru.
The Zamboanga Peninsula was a key battleground during the Spanish-Moro conflict. There were many fights between Spanish soldiers and Moro raiders. Even though the Spanish built churches, they faced many attacks and sometimes had to leave the region.
Becoming a Province
After the United States took over the Philippines in 1898, Zamboanga had a short period as an independent state called the Republic of Zamboanga. It then became part of the Moro Province. In 1916, Zamboanga became its own separate province.
During World War II, the Japanese army occupied the Zamboanga Peninsula in 1942. American and Filipino forces freed the peninsula in 1945.
On June 6, 1952, the province was divided into Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur. Zamboanga City became part of Zamboanga del Sur.
The Region Today
In 1972, the provinces that were once part of Zamboanga Province, along with the Sulu Archipelago, were organized into Region IX. This region was first called Western Mindanao.
In 2001, Zamboanga Sibugay was created as a new province from parts of Zamboanga del Sur. Also in 2001, the people of Basilan voted to join the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM). However, the capital city of Isabela chose to stay part of the Zamboanga Peninsula region. Isabela City also chose not to join the Bangsamoro region in 2019.
Recently, in 2024, a court ruling meant that Sulu might rejoin the Zamboanga Peninsula region. Sulu was part of this region before it joined the ARMM in 1989.
Where is the Regional Center?
There has been some discussion about where the main government center for Region IX should be.
- In 1978, the regional center was moved from Jolo to Zamboanga City.
- In 1990, President Corazon Aquino said that Pagadian would be the new regional center.
- In 1996, President Fidel Ramos's order stated that Zamboanga City was the regional center.
- In 2001, President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo renamed the region to Zamboanga Peninsula. Her order did not clearly state where the regional center was.
- In 2004, an order directed regional offices to move to Pagadian. However, some offices, like Trade and Industry, Tourism, and Labor, were allowed to stay in Zamboanga City.
- In 2010, a temporary stop was put on moving offices to Pagadian because it was costly for employees.
- In 2020, the temporary stop was lifted, confirming Pagadian as the government center. Zamboanga City remained the business and industrial center.
- On April 19, 2023, another temporary stop was put in place to study the effects of moving the offices. Offices already in Pagadian continue to operate there.
Geography and Location
The Zamboanga Peninsula is located on the western side of Mindanao. It lies between the Moro Gulf (part of the Celebes Sea) and the Sulu Sea. The peninsula has many bays and islands along its coast. It is connected to the rest of Mindanao by a narrow strip of land between Panguil Bay and Pagadian Bay.
The province of Misamis Occidental is located on the northeastern part of the geographic peninsula. However, it is part of a different region called Northern Mindanao.
Provinces and Cities
The Zamboanga Peninsula has three provinces, one highly urbanized city, four component cities, 67 municipalities, and 1,904 barangays.
| Province or City | Capital | Population (2020) | Area | Density | Cities | Muni. | Barangay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||||||
| Zamboanga del Norte | Dipolog City | 27.0% | 1,047,455 | 7,300.11 | 2,818.59 | 140 | 360 | 2 | 25 | 691 | ||
| Zamboanga del Sur | Pagadian City | 27.1% | 1,050,668 | 4,484.21 | 1,731.36 | 230 | 600 | 1 | 26 | 681 | ||
| Zamboanga Sibugay | Ipil | 17.3% | 669,840 | 3,481.28 | 1,344.13 | 180 | 470 | 0 | 16 | 389 | ||
| Zamboanga City | † | — | 25.2% | 977,234 | 1,414.70 | 546.22 | 690 | 1,800 | 1 | — | 98 | |
| Isabela City | ‡ | — | 3.4% | 130,379 | 233.73 | 90.24 | 560 | 1,500 | 1 | — | 45 | |
| Total | 3,875,576 | 16,904.03 | 6,526.68 | 230 | 600 | 5 | 67 | 1,904 | ||||
|
||||||||||||
Governors and Vice Governors
Cities of the Region
- Dapitan is one of the two cities in Zamboanga del Norte. It is known as the "Shrine City" because José Rizal, a national hero, was exiled here. You can also find the old St. James Parish and Dakak beach resort here.
- Dipolog is the capital of Zamboanga del Norte. It is called the "Orchid City of the South" because of its many orchids. It has natural and historical sites like Dipolog Cathedral and the 3,003 steps to Linabo Peak.
- Isabela is a city in Basilan province. It was the capital of Basilan until 2017. Even though Basilan is now part of the BARMM region, Isabela City remains part of the Zamboanga Peninsula. It was named after Queen Isabella II.
- Pagadian is the capital of Zamboanga del Sur and the region's administrative center. It is known as the "Little Hong Kong of the South" because of its hilly landscape. It also has a large Chinese community.
- Zamboanga City is the only highly urbanized city in the region. It is located at the southwestern tip of the peninsula. Zamboanga City is the region's main economic and industrial hub. It has the largest airport and seaport in the region.
- † Regional center
| City | Population (2020) | Area | Density | City class | Province | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dapitan | 85,202 | 390.53 | 150.78 | 220 | 570 | Component | Zamboanga del Norte |
| Dipolog | 138,141 | 241.13 | 93.10 | 570 | 1,500 | Component | Zamboanga del Norte |
| Isabela | 130,379 | 140.7 | 54.3 | 930 | 2,400 | Component | Basilan |
| † Pagadian | 210,452 | 378.80 | 146.26 | 560 | 1,500 | Component | Zamboanga del Sur |
| Zamboanga City | 977,234 | 1,414.7 | 546.2 | 690 | 1,800 | Highly urbanized | Zamboanga del Sur |
People of Zamboanga Peninsula
The Zamboanga Peninsula is home to many different groups of people. The total population of the region was 3,875,576 in 2020.
Economy and Resources
|
||||
The Zamboanga Peninsula has a growing economy. In 2022, Zamboanga City made up 32.6% of the region's total economy. Zamboanga del Norte followed with 26.8%, then Zamboanga del Sur with 23.7%. Zamboanga Sibugay grew the fastest in 2022, with an 8.6% increase.
The region has the first export-processing zone in Mindanao. Farming and fishing are the main ways people earn a living here. Other industries include processing rice, corn, oil, and rubber. Local crafts include rattan furniture, baskets, weaving, and brass work.
Dipolog is known for its bottled sardine companies, which export products worldwide. Dapitan has many tourist spots like Dakak Park and Beach Resort and Rizal Shrine. Glorious Fantasyland is also one of the few amusement parks in Mindanao.
Even though Pagadian is the government center, Zamboanga City remains the strongest and fastest-growing economy in the region. It is still the main business and industrial center.
Natural Resources
The region has large forest areas. In the past, it exported logs, lumber, and plywood. It also has many minerals like gold, chromite, coal, iron, lead, and manganese. Non-metal resources include coal, silica, salt, and marble. The fishing grounds are used for both commercial and local fishing. There are also fish farms for different types of fish.
Shopping Malls
The Zamboanga Peninsula has several shopping malls, with more being built. These malls provide places for shopping, dining, and entertainment for the people in the region.
Major Malls in Zamboanga Peninsula
| Name | Location | Gross floor area | Opened | Status | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaisano Capital Pagadian | Rizal Avenue, Pagadian, Zamboanga del Sur | 46,307 m2 | 2008 | Operating | First Gaisano Capital in the region. |
| CityMall Tetuan | Don Alfaro Street, Tetuan, Zamboanga City | 15,344 m2 | 2015 | Operating | First CityMall in the region and in Zamboanga City. |
| KCC Mall de Zamboanga | Camins Avenue, Zamboanga City | 162,000 m2 | 2015 | Operating | First KCC Mall and the largest mall in the region. |
| CityMall Dipolog | Sto. Filomena, Dipolog, Zamboanga del Norte | 12,862 m2 | 2018 | Operating | First CityMall in Zamboanga del Norte. |
| SM City Mindpro | La Purisima Street, Zamboanga City | 59,383 m2 | 2020 | Operating | First SM mall in the region. Originally Mindpro Citimall, it was acquired by SM Prime Holdings in 2016. |
| Gaisano Grand Ipil | Ipil, Zamboanga Sibugay | 53,985 m2 | 2023 | Operating | First Gaisano Grand mall in the region, and first national-scale mall in Zamboanga Sibugay. |
| Gaisano Capital Molave | Molave, Zamboanga del Sur | 13,206 m2 | Permanently Closed | For Sale | The second Gaisano Capital in Zamboanga del Sur and in the region. |
| Robinsons Pagadian | Pagadian, Zamboanga del Sur | 57,221 m2 | 2024 | Under-construction | Set to become the first Robinsons mall in the region. |
| Grand CityMall Guiwan | Guiwan, Zamboanga City | 33,814 m2 | 2024 | Under-construction | The second CityMall in Zamboanga City, and the third in the region. Set to become the largest CityMall in the country. |
| SM City Zamboanga | Vitaliano Agan Avenue, Zamboanga City | 110,055 m2 | 2024 | Under-construction | The second SM Supermall in Zamboanga City and in the region. |
| Gaisano Grand Dipolog | Sto. Filomena, Dipolog, Zamboanga del Norte | TBA | TBD | Under-construction | Set to become the first Gaisano Grand mall in Zamboanga del Norte. |
Transportation and Roads
Airports
- Dipolog Airport is the main airport for Dipolog City in Zamboanga del Norte. It is a major domestic airport.
- Pagadian Airport serves Pagadian City and the provinces of Zamboanga del Sur and Zamboanga Sibugay. It is also a major domestic airport.
- Zamboanga International Airport is the main airport for Zamboanga City. It is Mindanao's third-busiest airport. There are plans to move this airport to Mercedes by 2030.
Seaports
- Port of Dapitan is managed by the Philippine Ports Authority.
- Port of Pagadian has recently started its operations again.
- Ipil Port is another important port in the region.
- Port of Zamboanga is a major hub for sardine exports to other countries. Many shipping lines operate here.
Roads and Bridges
- Zamboanga City By-Pass Road is a 36.77 km road. It helps traffic move around Zamboanga City. This project was finished in 2018.
- Pan-Philippine Highway (AH26) is a major highway that passes through Zamboanga del Sur and Zamboanga Sibugay. Zamboanga City is where this highway ends.
Famous People
Many notable people come from the Zamboanga Peninsula. They have made contributions in various fields like politics, arts, and sports.
See also
 In Spanish: Península de Zamboanga para niños
In Spanish: Península de Zamboanga para niños