1992 Landers earthquake facts for kids

Damage to the Yucca Lanes Bowling Center from the 1992 quake
|
|
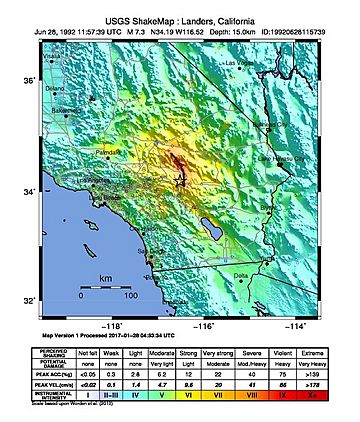
USGS ShakeMap made for the event
|
|
| UTC time | 1992-06-28 11:57:35 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 289086 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | June 28, 1992 |
| Local time | 4:57:35 am PDT |
| Magnitude | 7.3 Mw |
| Depth | 0.68 mi (1.09 km) |
| Epicenter | 34°13′01″N 116°25′59″W / 34.217°N 116.433°W |
| Type | Strike-slip |
| Areas affected | Southern California United States |
| Total damage | $92 million |
| Max. intensity | IX (Violent) |
| Foreshocks | 6.1 Mw April 23 at 4:51 |
| Casualties | 3 killed 400+ injured |
The 1992 Landers earthquake happened on Sunday, June 28, 1992. Its center was near the town of Landers, in San Bernardino County, California. This earthquake had a strength of 7.3 on the moment magnitude scale. It also reached a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX, which means it was very strong and caused serious damage.
Contents
What Happened During the Earthquake?
On June 28, 1992, at 4:57 a.m. local time, a magnitude 7.3 earthquake shook much of Southern California. The ground kept shaking for about two to three minutes. Many people thought this might be the "Big One" earthquake that scientists talk about.
Even though this earthquake was much stronger than the 1994 Northridge earthquake, it caused less damage and fewer deaths. This is because it happened in the Mojave Desert, an area with very few people living there.
The Landers earthquake was a "right-lateral strike-slip" event. This means that the ground on one side of the fault moved to the right compared to the other side. The earthquake caused several different cracks in the Earth's crust to break. These cracks stretched for about 75 to 85 kilometers (47 to 53 miles).
The ground broke open on the surface for about 70 kilometers (43 miles). In some places, the ground moved sideways by as much as 5.5 meters (18 feet). It also moved up or down by up to 1.8 meters (5.9 feet).
How Much Damage Did It Cause?
The area closest to where the earthquake started was hit very hard. Roads cracked and buckled. Buildings and chimneys fell down. There were also large cracks that opened up in the ground.
Further west, in the Los Angeles Basin, the damage was not as bad. Most of the damage in Los Angeles was from things falling off shelves. No freeway bridges collapsed, unlike the 1994 Northridge earthquake that happened later. This was because the Landers earthquake happened in a remote area.
Thousands of homes lost electricity, but power was usually back on within a few hours. Some homes also had damage from water splashing out of swimming pools.
Sadly, three people died because of this earthquake. Two people passed away from heart attacks. A 3-year-old boy from Massachusetts, who was visiting Yucca Valley, died when bricks from a chimney fell into the room where he was sleeping. More than 400 people were hurt because of the earthquake.
Other Earthquakes Connected to Landers
Before the Landers earthquake, a smaller earthquake happened on April 23, 1992. This was the 6.1 magnitude Joshua Tree earthquake, located south of where the Landers quake would strike.
About three hours after the main Landers earthquake, the 6.5 magnitude 1992 Big Bear earthquake hit. At first, people thought it was just an aftershock. However, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) later said it was a separate, but related, earthquake. These two earthquakes are now seen as part of a larger series of quakes in the region.
Another earthquake, the magnitude 5.7 Little Skull Mountain (LSM) earthquake, happened the next day, June 29, 1992. It was near Yucca Mountain, Nevada. Scientists think this quake might have been triggered by the energy waves from the Landers earthquake. Small earthquakes were happening more often at Little Skull Mountain after the Landers quake, right up until the main LSM earthquake hit.
What Do Scientists Think?
Scientists have a couple of ideas about why the Landers earthquake and other large quakes happened in the Mojave region.
One idea is that the San Andreas Fault might be changing. It could be that a new boundary between the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate is forming. This new boundary might run across the Mojave Desert and east of the Sierra Nevada Mountains.
Another idea is that these earthquakes are a sign of the Earth's crust pulling apart. This pulling apart might be spreading north from the Gulf of California. Scientists are still studying these ideas to learn more.
In Popular Culture
The Landers earthquake was shown in a television documentary series called Earth's Fury. This show, also known as Anatomy of Disaster in some countries, was about natural disasters. It aired on The Learning Channel and other TV channels around the world. The Landers earthquake was featured in an episode titled "Earthquake!"
Images for kids
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |


