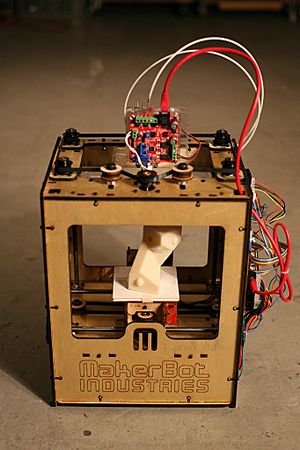
3D printing facts for kids
3D printing is a cool way to make real, solid objects. Imagine building something by adding very thin layers, one on top of the other. That's how a 3D printer works! Most 3D printers use plastic because it is easy to use and not too expensive. Some special printers can even use metals or ceramics, but these are usually very costly.
3D printers are super helpful because they can create new things quickly and with amazing detail. This means an engineer can try out many new designs without waiting a long time for them to be made. They are also great for fixing plastic parts, making toys, figures, and models. Many people even print 3D objects right at home! Since 2003, more and more 3D printers have been sold, and their prices have become much lower.
Contents
History of 3D Printing
- 1974: David E. H. Jones first wrote about the idea of 3D printing in a science magazine.
- 1984: Alain Le Méhauté and others applied for a patent for stereolithography. This was a laser-based 3D printer.
- 1989: S. Scott Crump created FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling). This is the technology used by most 3D printers today.
- 1992: The first FDM machine was sold by S. Scott Crump's company, Stratasys.
- 2005: RepRap became the first open source printer project. This meant its designs were free for everyone to use and improve.
- 2008: Shapeways became the first service that would 3D print an object and send it to customers.
- 2017: The first 3D printed house that people could live in was built in Russia.
How 3D Printers Work
To make something with a 3D printer, there are a few main steps.
Designing Your Model
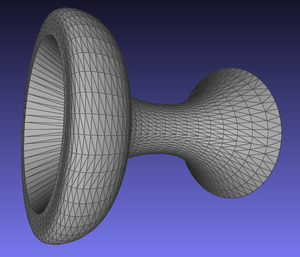
The first step is to create your object on a computer. People use special software called CAD (Computer Aided Design). They can also use a 3D scanner. With CAD, you start with simple shapes and build your design from there. 3D scanners are machines that measure an object and automatically create a computer model of it. Scanners are fast but can be expensive. CAD models are often saved as STL files. These files store the object as many tiny triangles to save space.
The Printing Process
There are many different ways 3D printers work and many materials they can use. Each method has its good and bad points. When choosing a printer, people usually think about how fast it prints, how much it costs, and what colors it can use. Printers that work directly with metals are generally very expensive. However, less costly printers can make a mold, which is then used to create metal parts.
Typical layers are about 100 micrometers thick. That's about one-tenth the thickness of a human hair! Printing can take anywhere from less than an hour to many days. It depends on how big and detailed the object is.
Finishing Your Print
After the printer finishes, people sometimes "finish" the model. This means making small changes to make it look even better. Finishing often includes removing extra material that the printer added to support the model while it was being built. This can sometimes take a lot of time. While there are ways to speed it up, removing plastic by hand is often the easiest method.
Uses for 3D Printing
3D printing is used in many exciting ways!
Printing at Home
Many people are working to create affordable 3D printers for home use. Libraries have also started buying smaller 3D printers. This lets people learn about them without having to buy one themselves. Groups like DIY (Do It Yourself) communities, schools, and hacker communities have done a lot of work with 3D printing. By 2017, more people were using 3D printers at home for small items like gears and decorations.
Medical Uses
3D printing helps make medical supplies more cheaply. Experts believe two of the biggest uses will be for making hearing aids and false teeth. In March 2014, doctors in Swansea used 3D printed parts to rebuild the face of a motorcyclist who had a serious accident.
Making Things for Industry
In 2014, a Swedish company made a supercar using many 3D printed parts. The Urbee was the first car in the world to have its body and windows 3D printed. In 2015, a Royal Air Force Eurofighter Typhoon fighter jet flew with 3D printed parts. The United States Air Force and the Israeli Air Force have also started using 3D printers to make spare parts for their planes.
Food Printing
Yes, food can be 3D printed! Many different foods can be printed, like chocolate, candy, crackers, pasta, and even pizza. NASA is printing food to create less waste and to make sure astronauts get all the right nutrients. In 2018, Giuseppe Scionti printed a food that was similar to meat.
Historical Preservation
In recent years, 3D printing has been used to help protect important historical items. Many museums have bought 3D printers to make pieces to fix their old relics. The Metropolitan Museum of Art and the British Museum now use their 3D printers to make copies of items to sell in their gift shops. Some museums even sell digital versions of their items online, so anyone can 3D print them at home!
See also
 In Spanish: Impresión 3D para niños
In Spanish: Impresión 3D para niños
Images for kids
-
CAD model used for 3D printing
-
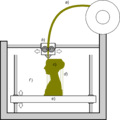
Schematic representation of the 3D printing technique known as fused filament fabrication; a filament a) of plastic material is fed through a heated moving head b) that melts and extrudes it depositing it, layer after layer, in the desired shape c). A moving platform e) lowers after each layer is deposited. For this kind of technology additional vertical support structures d) are needed to sustain overhanging parts