Abraham Wald facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Abraham Wald
|
|
|---|---|

A young Wald
|
|
| Born | October 31, 1902 |
| Died | December 13, 1950 (aged 48) |
| Alma mater | King Ferdinand I University University of Vienna |
| Known for | Wald's equation Wald test Wald distribution Wald–Wolfowitz runs test Wald's martingale Wald's maximin model Mann–Wald theorem Decision theory Sequential analysis Sequential probability ratio test |
| Children | Robert Wald |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Mathematics Statistics Economics |
| Institutions | Columbia University Cowles Commission for Research in Economics |
| Doctoral advisor | Karl Menger |
| Doctoral students | Herman Chernoff Milton Sobel Charles Stein |
| Influences | Oskar Morgenstern John von Neumann Harold Hotelling Milton Friedman Jerzy Neyman |
| Influenced | Aryeh Dvoretzky Jacob Wolfowitz John Denis Sargan, Alok Bhargava |
Abraham Wald (born October 31, 1902 – died December 13, 1950) was a brilliant mathematician from Hungary. He made big contributions to areas like decision theory (how to make the best choices) and sequential analysis (a way to analyze data as it comes in). During World War II, he used his math skills to help protect bomber planes. He worked at Columbia University for most of his research career.
Contents
Early Life and Education
Abraham Wald was born on October 31, 1902. His hometown was Kolozsvár, which was then part of the Kingdom of Hungary. His family was Jewish and very religious. Because of his faith, he could not go to school on Saturdays. This was a rule in the Hungarian school system back then. So, his parents taught him at home until he was ready for college. They were very good teachers and knew a lot.
In 1928, Abraham finished his math degree at the King Ferdinand I University. Before that, in 1927, he started his advanced studies at the University of Vienna. He earned his Ph.D. in mathematics from there in 1931. His main teacher and guide during these studies was Karl Menger.
Moving to America
Even though Wald was very smart, he found it hard to get a job at a university in Austria. This was because of unfair treatment against Jewish people at the time. Luckily, a person named Oskar Morgenstern helped him. He created a job for Wald in the field of economics.
Things got worse for Jewish people in Austria in 1938. This was when Nazi Germany took control of Austria. Wald and his family faced serious problems because they were Jewish. Because of this, Wald moved to the United States. He was invited by the Cowles Commission for Research in Economics to work on economic research.
Helping During World War II
During World War II, Abraham Wald joined a special group. It was called the Statistical Research Group (SRG) at Columbia University. Here, he used his amazing math skills to solve problems related to the war. He worked on new ways to analyze data and check products.
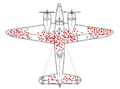
One important problem the SRG worked on was about bomber planes. They wanted to find out how to protect planes from enemy fire. They looked at planes that came back from missions. They studied where these planes had been hit. Wald figured out a clever way to estimate where all planes were hit, even those that didn't make it back. This helped them decide where to add more armor to the planes. His work was very important for a new field called operational research.
Later Life and Legacy
In 1950, Abraham Wald and his wife were on a trip to India. They were invited by the Indian government to give lectures. Sadly, the plane they were on crashed in the Nilgiri Mountains in southern India. Both Abraham and his wife died in the accident. Their two children were safe at home in the United States.
After his death, some people, like Sir Ronald A. Fisher, criticized Wald's work. Fisher said Wald was a mathematician who didn't have enough real-world science experience. However, another famous statistician, Jerzy Neyman, defended Wald's work. He explained how important Wald's ideas were, especially in designing experiments. Many people still recognize Wald's big impact on the field of statistics.
Abraham Wald was also the father of a well-known American physicist named Robert Wald.
Notable Publications
- — (1947). Sequential Analysis. New York: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-91806-7. "See Dover reprint: ISBN: 0-486-43912-7"
Images for kids
See Also
 In Spanish: Abraham Wald para niños
In Spanish: Abraham Wald para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |