Aetolia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Aetolia
Αἰτωλία
|
|
|---|---|
|
Region of Ancient Greece
|
|

Ancient and modern Thermon, Aetolia
|
|
Map of ancient Aetolia
|
|
| Country | Greece |
| Location | Western Greece |
| Major cities | Thermon |
| Dialects | Doric |
| Key periods | Aetolian League (290–189 BC) |
Aetolia (Greek: Αἰτωλία, romanized: Aitōlía) is a mountainous region in Greece. It is located on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth. Today, it forms the eastern part of a modern area called Aetolia-Acarnania.
Contents
Geography of Aetolia
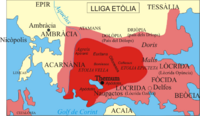
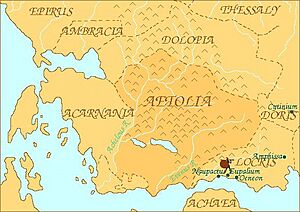
Aetolia had clear natural borders. The Achelous River separated it from Acarnania to the west. To the north, it bordered Epirus and Thessaly. The Ozolian Locrians were to its east. The entrance to the Corinthian Gulf marked its southern edge.
In ancient times, Aetolia was divided into two main parts. "Old Aetolia" was in the west. It stretched from the Achelous River to the Evenus River and the city of Calydon. "New Aetolia," also called "Acquired Aetolia," was in the east. This part extended from the Evenus River and Calydon to the Ozolian Locrians.
The land near the coast was flat and fertile, meaning it was good for farming. However, the inner parts of Aetolia were mountainous and not very productive. These mountains were known for their wild animals. They became famous in Greek mythology as the place where the legendary Calydonian Boar hunt took place.
History of Aetolia
Early History of Aetolia
The region of Aetolia was first home to tribes like the Curetes and Leleges. Later, Greeks from Elis arrived and started new settlements. These new settlers were led by a mythical hero named Aetolus. The Aetolians also took part in the famous Trojan War, led by their king Thoas.
The mountain tribes of Aetolia included groups like the Ophioneis and the Eurytanians. Ancient historians often described these tribes as living a simple, rough lifestyle. Some even said they spoke a difficult language and ate raw food. They were known for being warlike and often raided other areas.
The Aetolians worshipped several gods. They honored Apollo as a god of calm nature and Artemis as a goddess of the wild. They also worshipped Athena, but focused on her role as a war goddess. They called Apollo and Artemis "Laphrios gods," meaning they were patrons of war spoils. There was an important shrine to Apollo at Thermos, which became a major religious center.
Aetolian League and Conflicts
The Aetolians did not join the Persian Wars. In 426 BC, they defeated the Athenians and their allies in a battle. Later, in 338 BC, they took back the city of Naupaktos with help from Philip II. During the Lamian War, the Aetolians helped the Athenian general Leosthenes defeat Antipater. This led to conflicts with Macedonian generals, but the Aetolians managed to survive.
The Aetolians formed a strong group called the Aetolian League. This league grew into a powerful alliance by about 340 BC. It was created to help Aetolian cities protect each other. The Aetolian League became a major rival to the Macedonian kings and the Achaean League.
The Aetolians became very famous for their bravery. They fought bravely against the Macedonians. They also played a key role in stopping a Gallic invasion led by Brennus. They even saved the important sanctuary of Delphi. After this victory, they started the Sotiria Games to honor Zeus the Saviour.
In 232 BC, the Illyrians attacked the Aetolians and took many prisoners and valuable items. In 229 BC, the Aetolians fought in a naval battle near the island of Paxos. They were allied with Korkyra and the Achaean League, but they lost to the Illyrians and Acarnanians.
The Aetolians' power continued to grow as they took control of more lands. They united areas like Ozoloi, Locrians, and Phocians under their League. Between 220 and 217 BC, a major conflict called the Social War broke out. This war was between the Achaean and Aetolian Leagues. The Aetolians started it with help from the Spartans and Eleans. The Achaeans had allies like the Macedonians and Boeotians.
Aetolia and Rome
The Aetolians decided to ally with the Romans. Meanwhile, Philip V destroyed the temple of Apollo Thermios and allied with the Carthaginians. The Aetolians continued to fight alongside the Romans, even in the Battle of Cynoscephalae in 196 BC.
However, the Aetolians later sided with Antiochus III against the Roman Republic. When Antiochus III was defeated in 189 BC, the Aetolians became subjects of Rome. After the Romans conquered the Achaeans in 146 BC, Aetolia became part of the Roman province of Achaea.
When Roman soldiers left due to civil wars in Rome, the Aetolians began fighting among themselves. After Octavius won the Battle of Actium, the Aetolians who had supported Antony completely broke apart. Octavius gave the city of Calydon to the Achaeans. They destroyed it and moved the statue of Artemis Laphria to Patras. Centuries later, at the end of the Roman Empire, Aetolia faced invasions from groups like the Goths and Huns.
Some ancient writers, like Polybius, wrote negatively about Aetolia. This is partly because Polybius relied on information from Aetolia's rival, Aratus of Achaea. Also, Polybius was from Megalopolis, a main city of the rival Achaean League.
Aetolia in the Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, Aetolia was part of the Byzantine Empire. Later, it came under the control of the Turks.
List of Famous Aetolians

Here are some notable people from Aetolia:
- Agetas, a general
- Aitolos, a mythological hero
- Leda, Queen of Sparta and mother of famous figures like Helen
- Andraemon, father of Thoas
- Thoas, a hero of the Trojan War
- Titormus, a famous wrestler
- Alexander Aetolus, a poet
- Damocritus, a general
- Dorimachus, a general
- Nicolaus of Aetolia, a general
- Theodotus of Aetolia, a general
- Pyrrhias, an Olympic racer in 200 BC
- Pyrrhias of Aetolia, a general
- Agelaus of Naupactus, a leading figure in the Aetolian League
- Cosmas of Aetolia, (1714–1779) a monk
- Dimitrios Makris, a fighter in the Greek War of Independence (1821)
See also
- Aetolian League
- List of traditional Greek place names
- Aetolia Game