Betic midwife toad facts for kids
The Betic midwife toad (Alytes dickhilleni) is a special type of frog. It belongs to the Alytidae family. This toad is found only in the mountains of southeastern Spain. This means it is endemic to that area.
Its natural homes include cool forests, wet marshes, and ponds. It also lives in fields where animals graze. Sadly, this toad is in danger because it is losing its natural home.
Quick facts for kids Betic midwife toad |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
Contents
What Does the Betic Midwife Toad Look Like?
The Betic midwife toad is mostly grey. It has small dark and light spots all over its skin. It can grow to be about 3.5 centimeters long. That's about the size of a large paperclip!
This toad has big, bulging eyes. Its pupils are shaped like a thin, vertical line. There is a special grey area between its eyes. It also has small glands behind its eyes called parotoid glands. Unlike some other toads, it does not have bright orange spots.
Where Do Betic Midwife Toads Live?
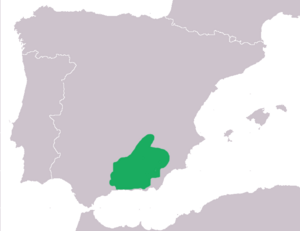
The Betic midwife toad lives in the Sierra Nevada Mountains in southeastern Spain. These mountains are very important for the toad. The toads live in different mountain areas, so their groups are spread out.
You can find many of them in the Alcaraz, Segura, and Cazorla mountains. They are less common in drier places like Filabres, Baza, and Gádor.
These toads usually live in oak and pine forests. They also like open, rocky areas, especially where there is limestone. They can be found at high places, from about 700 to 2,000 meters up. In dry areas, they often stay close to water springs.
How Do Betic Midwife Toads Live and Reproduce?
The Betic midwife toad is a nocturnal animal. This means it is active at night. During the day, it hides under rocks or in cracks to stay safe.
When it's time to have babies, the male and female toads mate on land. After mating, the male toad does something very special. He wraps the eggs around his back legs. He carries the eggs with him until the baby tadpoles are ready to hatch.
When the tadpoles are ready, the male toad takes them to water. He can put them in mountain streams, water troughs for animals, or even small reservoirs. The tadpoles grow slowly. They might even stay in the water through the winter. After a while, they change into young frogs. This change is called metamorphosis.
Why Is the Betic Midwife Toad in Danger?
The IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) says this toad is endangered. This means its numbers are going down.
The biggest problems for the Betic midwife toad are:
- Drought: Not enough rain means less water for them to live and lay eggs in.
- Water Use: People taking too much water from streams and ponds.
- Farming Changes: New ways of farming can destroy their homes.
- Disease: A fungal disease called chytridiomycosis is also making them sick.
On January 21, 2008, a group called EDGE (Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered) talked about the most unusual and endangered amphibians. They said that many unique amphibians, like the Betic midwife toad, are not getting enough help. The Betic midwife toad is one of the top 10 endangered species on their list.


