Anaerobic digestion facts for kids
Anaerobic digestion is a natural process where tiny living things called microbes break down organic materials. This happens when there is no oxygen around. Think of it like a special kind of "eating" without air!
People use this process for many reasons. It helps manage waste from homes and industries. It also creates useful things like fuel. Many foods and drinks we enjoy, like yogurt or bread, are made using a similar process called fermentation.
This "airless eating" happens naturally in places like wet soils and at the bottom of lakes and oceans. That's where Alessandro Volta discovered "marsh gas" (which is methane) way back in 1776!
Anaerobic digestion is a key part of treating waste that can break down, like food scraps and sewage sludge. It helps stop harmful gases from escaping from landfills into our air. Farmers can also use special plants, like maize, to feed these digesters.
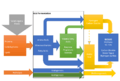
This process is a great way to make renewable energy. It creates a gas called biogas. Biogas is mostly methane and carbon dioxide. We can use this biogas directly as fuel, or turn it into a cleaner gas called biomethane. The leftover material, called digestate, is full of nutrients and makes excellent fertilizer for plants.
Using anaerobic digestion helps our planet in several ways:
- It helps us use less fossil fuels.
- It makes waste treatment plants use less energy.
- It stops methane from landfills from going into the air.
- It means we need fewer man-made chemical fertilizers.
- It can reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
- It helps reduce energy loss when power travels through the power lines.
Because it helps turn waste into resources and new technologies have made it cheaper, many countries are now paying more attention to anaerobic digestion. Countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, Denmark, and the United States are all looking into it.
Images for kids
-
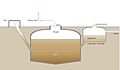
Schematic of an anaerobic digester as part of a sanitation system. It produces a digested slurry (digestate) that can be used as a fertilizer, and biogas that can be used for energy.
See also
 In Spanish: Digestión anaeróbica para niños
In Spanish: Digestión anaeróbica para niños