Diatom facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Diatoms |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Marine diatoms | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: |
Bacillariophyceae
|
Diatoms are tiny, single-celled living things. They are a big group of algae, which are like simple plants. The name "diatom" means "cut through" because their cell walls have a split.
Diatoms are super common in the ocean and fresh water. They are a main type of plankton, which are tiny organisms that float in water. Most diatoms live alone, but some join together to form chains or simple groups.
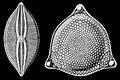
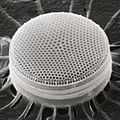
Each diatom cell has a special outer shell called a frustule. This shell is made of silica, which is a type of glass. Frustules come in many amazing and beautiful shapes. They often look like two uneven halves that fit together, like a small box with a lid.
How Diatoms Work
Diatoms have chloroplasts, which are like tiny factories inside their cells. These factories help them make their own food using sunlight, just like plants do. Scientists think diatoms got their chloroplasts from red algae a long, long time ago.
Diatoms Through Time
We know diatoms have been around for a very long time. The oldest diatom fossils we've found are from the Lower Jurassic period. This was about 185 million years ago!
However, some scientific clues suggest diatoms might be even older. Scientists have also studied the complete genetic code (genome) of two diatom types. They found that many genes in diatoms actually came from bacteria. This shows how different life forms can share genetic material over time.
Why Diatoms Matter
Diatoms are important for many reasons. They are often used to check how healthy our environment is. Because diatoms are sensitive to changes, scientists can study them to learn about water quality, both now and in the past.
Diatoms are also interesting to people working in nanotechnology. This field deals with extremely tiny things. The unique and intricate shapes of diatom frustules could inspire new designs for very small devices.
Images for kids
-
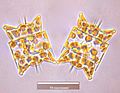
Selections from Ernst Haeckel's 1904 Kunstformen der Natur (Art Forms of Nature), showing pennate (left) and centric (right) frustules.
-
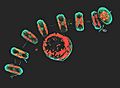
Some Thalassiosira diatoms form chain-like colonies, like these collected near the Antarctic peninsula coast by the schooner of the Tara Oceans Expedition for plankton research. This projection of a stack of confocal images shows the diatoms' cell wall (cyan), chloroplasts (red), DNA (blue), membranes and organelles (green).
-
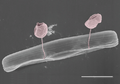
Pennate diatom from an Arctic meltpond, infected with two chytrid-like [zoo-]sporangium fungal pathogens (in false-colour red). Scale bar = 10 μm.
-
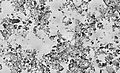
Intricate silicate (glass) shell, 32-40 million years old, of a diatom microfossil -
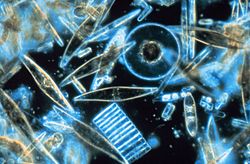
Diatomaceous earth as viewed under bright field illumination on a light microscope. This image consists of a mixture of centric (radially symmetric) and pennate (bilaterally symmetric) diatoms suspended in water. The scale is 6.236 pixels/μm, the image is 1.13 by 0.69 mm.
See also
 In Spanish: Diatomea para niños
In Spanish: Diatomea para niños